Title
题目
A causal counterfactual graph neural network for arising-from-chair abnormality detection in parkinsonians
一种用于检测帕金森病患者起立异常的因果反事实图神经网络
Aastract
摘要
The arising-from-chair task assessment is a key aspect of the evaluation of movement disorders in Parkinson’s disease (PD). However, common scale-based clinical assessment methods are highly subjective and dependent on the neurologist’s expertise. Alternate automated methods for arising-from-chair assessment can be established based on quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) images with multiple-instance learning. However, performance stability for such methods can be typically undermined by the presence of irrelevant or spuriouslyrelevant features that mask the intrinsic causal features. Therefore, we propose a QSM-based arising-fromchair assessment method using a causal graph-neural-network framework, where counterfactual and debiasing strategies are developed and integrated into this framework for capturing causal features. Specifically, the counterfactual strategy is proposed to suppress irrelevant features caused by background noise, by producing incorrect predictions when dropping causal parts. The debiasing strategy is proposed to suppress spuriously relevant features caused by the sampling bias and it comprises a resampling guidance scheme for selecting stable instances and a causal invariance constraint for improving stability under various interferences. The results of extensive experiments demonstrated the superiority of the proposed method in detecting arising-from-chair abnormalities. Its clinical feasibility was further confirmed by the coincidence between the selected causal features and those reported in earlier medical studies. Additionally, the proposed method was extensible for another motion task of leg agility. Overall, this study provides a potential tool for automated arising-from-chair assessment in PD patients, and also introduces causal counterfactual thinking in medical image analysis.
起立任务评估是帕金森病(PD)运动障碍评估的关键方面。然而,常见的基于评分的临床评估方法高度主观,依赖于神经科医生的专业知识。基于定量敏感性映射(QSM)图像的起立评估可以通过多实例学习建立自动化方法。然而,这类方法的性能稳定性通常会被无关或虚假相关特征所削弱,这些特征掩盖了内在的因果特征。因此,我们提出了一种基于QSM的起立评估方法,使用因果图神经网络框架,并在该框架中开发并整合了反事实和去偏策略,以捕捉因果特征。具体而言,反事实策略旨在通过在去除因果部分时产生错误预测来抑制由背景噪声引起的无关特征。去偏策略旨在抑制由采样偏差引起的虚假相关特征,包括一个重采样指导方案,用于选择稳定实例,以及一个因果不变性约束,以提高在各种干扰下的稳定性。广泛实验的结果表明,所提出的方法在检测起立异常方面具有优越性。其临床可行性进一步得到了确认,因为所选择的因果特征与早期医学研究中报道的特征一致。此外,所提出的方法还可以扩展到另一项腿部灵活性运动任务。总体而言,本研究为PD患者的自动化起立评估提供了一种潜在工具,并在医学图像分析中引入了因果反事实思维。
Method
方法
In this work, we propose a causal classification framework based on a GNN backbone with multiple-instance learning, as shown in Fig. 3 (Section 3.1). Fig. 4 depicts the pipeline of this framework, involving mainly two strategies: 1) a counterfactual strategy to reduce irrelevant features (Section 3.2.1); and 2) a debiasing strategy to reduce spuriously relevant features, including a resampling guidance module (Section 3.2.2) and a causal invariance constraint (Section 3.2.3). Finally, Section 3.3 summarizes the overall model.
在本研究中,我们提出了一种基于GNN骨干网络的因果分类框架,并结合了多实例学习,如图3(第3.1节)所示。图4展示了该框架的流程,主要包括两种策略:1) 反事实策略,用于减少无关特征(第3.2.1节);2) 去偏策略,用于减少虚假相关特征,包括重采样指导模块(第3.2.2节)和因果不变性约束(第3.2.3节)。最后,第3.3节总结了整体模型。
Conclusion
结论
To identify PD patients with arising-from-chair abnormalities based on QSM images, we propose a causal counterfactual GNN under a multiple-instance-learning framework. A counterfactual strategy and a debiasing strategy are developed to address the challenge of performance instability. We conducted comprehensive experiments on a clinical dataset to validate the effectiveness of the proposed method in arising-from-chair abnormality detection. Furthermore, the selected causal features are consistent with brain characteristics reported in previous clinical medical studies. This observation confirms the clinical reliability of this method. Moreover, additional experiments on leg agility assessment further verify the technical extensibility of this method. At last, our counterfactual strategy enlightens the modern GNN-based medical image analysis to some degree.
为了基于QSM图像识别具有起立异常的帕金森病(PD)患者,我们提出了一种在多实例学习框架下的因果反事实图神经网络(GNN)。该方法开发了反事实策略和去偏策略,以应对性能不稳定的挑战。我们在一个临床数据集上进行了全面的实验,以验证所提出方法在检测起立异常方面的有效性。此外,所选的因果特征与先前临床医学研究中报道的大脑特征一致,这一发现进一步证实了该方法的临床可靠性。此外,在腿部灵活性评估任务上的额外实验进一步验证了该方法的技术扩展性。最后,我们的反事实策略在一定程度上启发了基于GNN的现代医学图像分析。
Figure
图
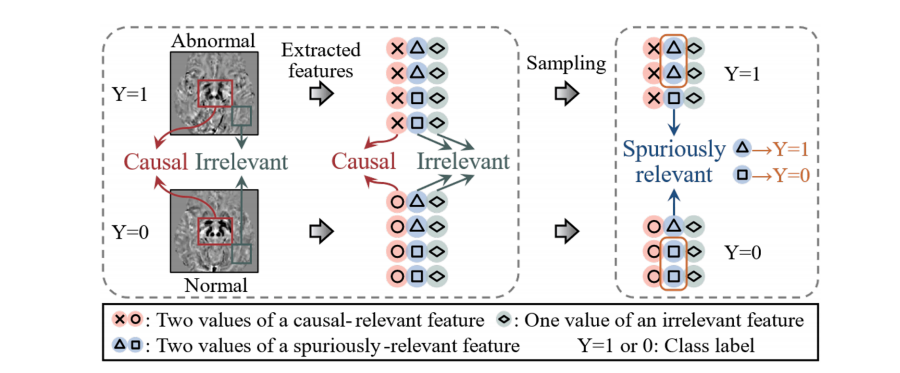
Fig. 1. Sources of irrelevant and spuriously relevant features in the identification of PD arising-from-chair abnormalities. Due to sampling bias, part of irrelevant features become spuriously relevant to the class label.
图1. 在识别帕金森病患者起立异常时无关特征和虚假相关特征的来源。由于采样偏差,部分无关特征变得与类别标签虚假相关。
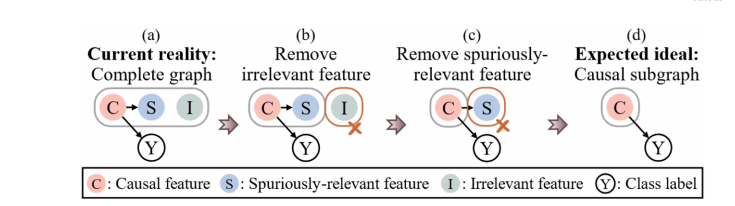
Fig. 2. Schematic diagrams of the proposed methodology from a causality perspective. In the current complete graph (a), the irrelevant and spuriously relevant are entangled with causal features. After removing irrelevant (b) and spuriously relevant © features, the remaining causal subgraph (d) allows for an ideal stable prediction.
图2. 从因果关系角度展示所提方法的示意图。在当前的完整图中(a),无关特征和虚假相关特征与因果特征交织在一起。在移除无关特征(b)和虚假相关特征©之后,剩余的因果子图(d) 使得理想的稳定预测成为可能。
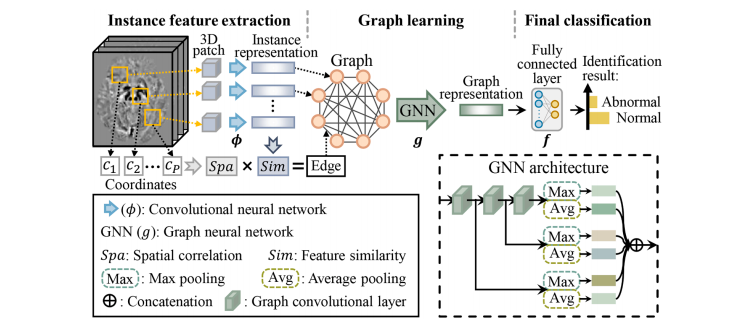
Fig. 3. The multiple-instance-learning-based GNN backbone without any causal strategies, including the feature extractor ϕ, the graph encoder g, and the classifier f. This is the basic architecture for the proposed method.
图3. 基于多实例学习的GNN骨干网络,不包含任何因果策略,包括特征提取器 ϕ、图编码器 g 和分类器 f。这是所提出方法的基本架构。
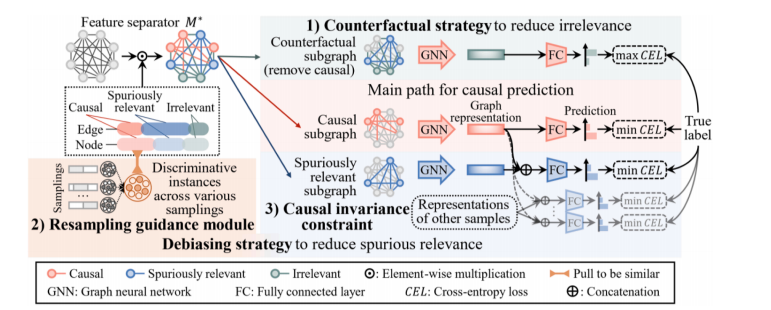
Fig. 4. The pipeline of the proposed causal GNN framework with three components, including 1) the counterfactual strategy designed to reduce irrelevant features;
图 4. 所提出的因果图神经网络框架的流程,包括三个组成部分,其中包括:1)旨在减少无关特征的反事实策略;
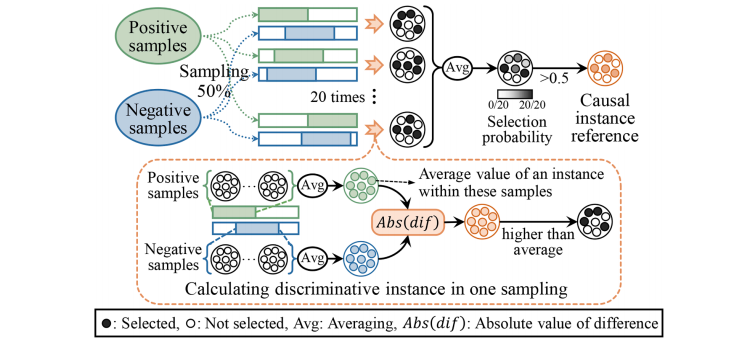
Fig. 5. Construction of the causal instance reference in the resampling guidance module.
图5. 重采样指导模块中因果实例参考的构建。
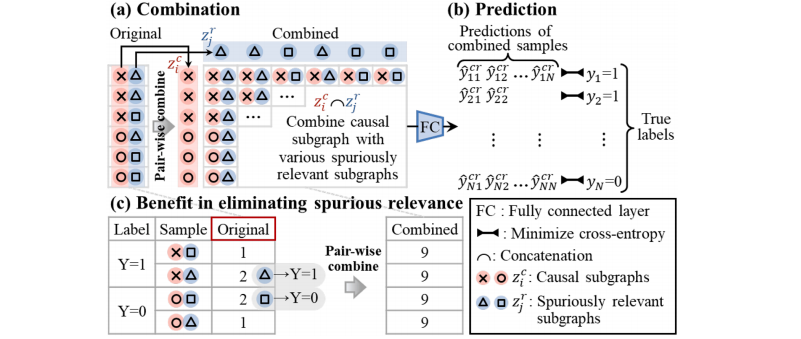
Fig. 6. An example to show how the causal invariance constraint (a) combines various causal and non-causal subgraphs and then (b) makes the prediction correct to © eliminate spurious relevance. (a, c) Originally, samples labeled Y = 1 with “×Δ” outnumbered those with “×□” (2 > 1), leading to unexpected spurious relevance between “Δ” and Y = 1. After the pair-wise combination, “Δ” and “□” are evenly distributed into two categories (9 = 9). (b) Keeping the combined predictions remain correct eliminates the sampling bias to capture stable causal features.
图6. 一个示例展示了因果不变性约束如何:(a) 结合各种因果和非因果子图,然后 (b) 使预测正确,从而 © 消除虚假相关性。(a, c) 最初,标记为 Y = 1 的样本中,“×Δ”的数量多于“×□”(2 > 1),这导致“Δ”与 Y = 1 之间出现意外的虚假相关性。经过成对组合后,“Δ”和“□”在两个类别中均匀分布(9 = 9)。(b) 保持组合后的预测正确性消除了采样偏差,从而捕捉到稳定的因果特征。
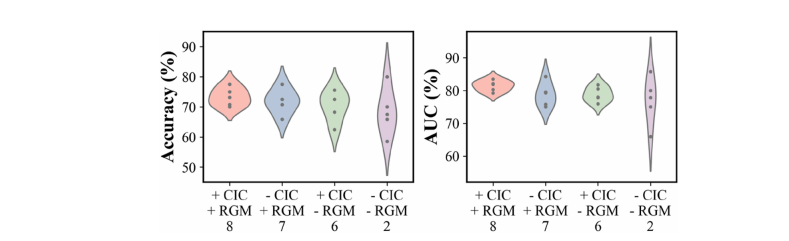
Fig. 7. Distributions of the accuracy and AUC metrics for 5-fold CV with and without the resampling guidance module (RGM) and the causal invariance constraint (CIC). The “+” and “-” symbols denote with and without a component, respectively. The numbers in the last row correspond to the serial model numbers in Table 3.
图7. 带有和不带有重采样指导模块(RGM)以及因果不变性约束(CIC)的5折交叉验证(CV)中准确性和AUC指标的分布。“+”和“-”符号分别表示包含和不包含该组件。最后一行的数字对应表3中的模型序号。
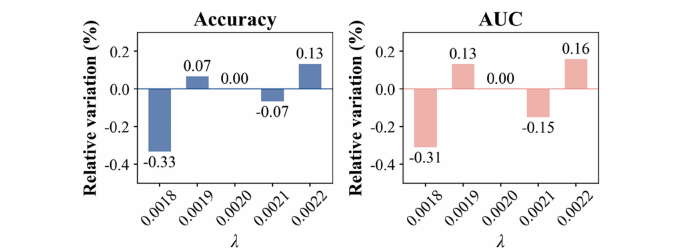
Fig. 8. Results of the hyperparameter sensitivity analysis: The relative variation of the accuracy and AUC when λ fluctuates by ±10% around its nominal value.
图8. 超参数敏感性分析结果:当 λ 围绕其标称值波动±10%时,准确性和AUC的相对变化。
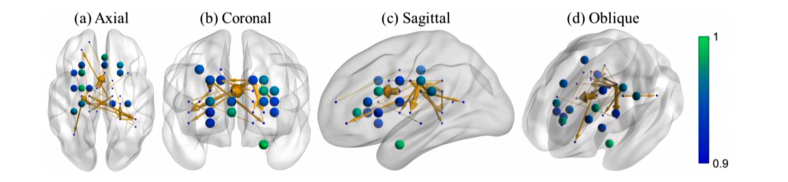
Fig. 9. Visualization of high-causality-score nodes and edges in the AAL3 brain template (Rolls et al., 2020). The node colors and the edge thicknesses reflect the causality scores. The nodes connected to those causal edges with causality scores below 0.9 are indicated by small dots.
图9. 在AAL3脑模板(Rolls等,2020)中高因果性评分的节点和边的可视化。节点的颜色和边的厚度反映了因果性评分。与因果性评分低于0.9的因果边相连的节点以小点表示。
Table
表
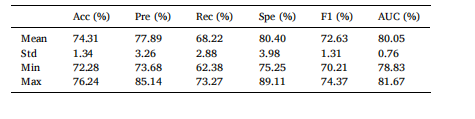
Table 1 Classification performance of the proposed method for 10 repetitions of 5-fold CV.
表1 所提出方法在10次重复5折交叉验证(CV)中的分类性能。
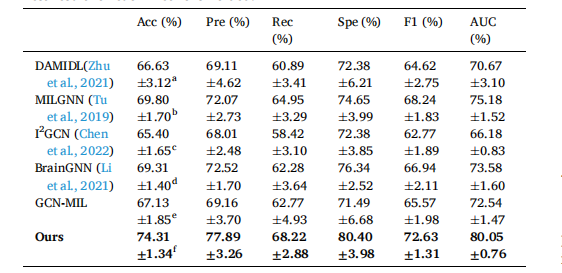
Table 2 Classification performance comparison with state-of-the-art methods on the arising-from-chair task. The result of each metric is shown as mean ± std. The best result for each metric is bolded.
表2 起立任务中与最先进方法的分类性能比较。每个指标的结果以平均值 ± 标准差表示。每个指标的最佳结果用粗体显示。
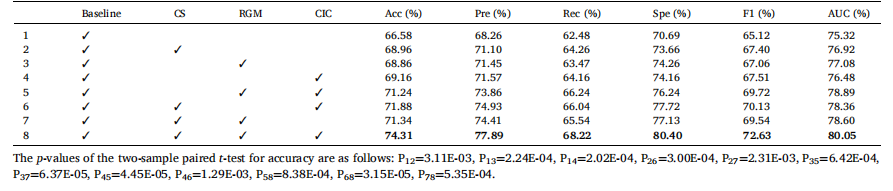
Table 3 Results of the ablation study for three key components, namely the counterfactual strategy (CS), the resampling guidance module (RGM), and the causal invariance constraint (CIC).
表3 三个关键组件的消融研究结果,分别为反事实策略(CS)、重采样指导模块(RGM)和因果不变性约束(CIC)。
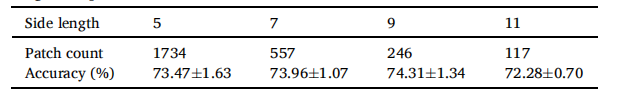
Table 4 Patch count and accuracy (shown as mean ± std) corresponding to varying side lengths of patches.
表4 不同边长的图像块对应的图像块数量和准确性(以平均值 ± 标准差表示)。
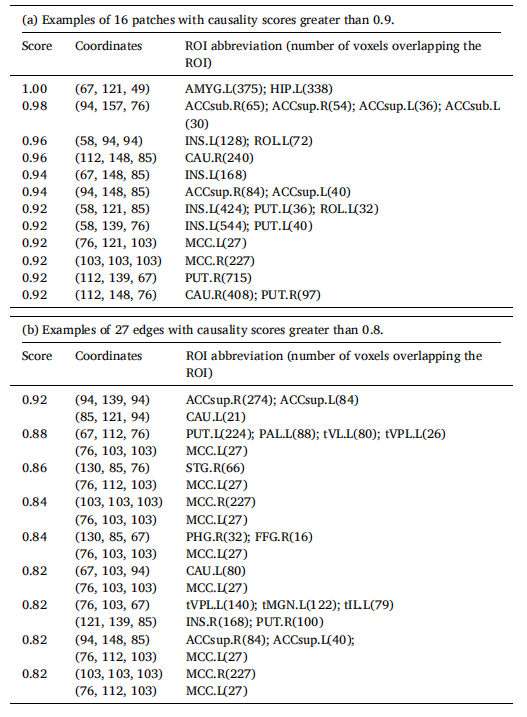
Table 5 Information of some causal nodes and edges, including causality scores, coordinates, and ROI abbreviations.
表5 一些因果节点和边的信息,包括因果性评分、坐标和感兴趣区(ROI)缩写。
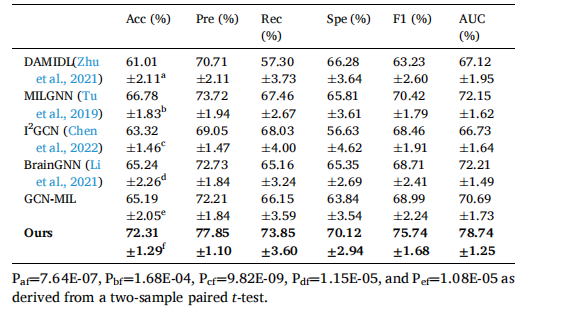
Table 6 Classification performance comparison with state-of-the-art methods on the right-leg agility assessment task. The result of each metric is shown as mean ±std. The best result for each metric is bolded.
表6 右腿灵活性评估任务中与最先进方法的分类性能比较。每个指标的结果以平均值 ± 标准差表示。每个指标的最佳结果用粗体显示。