Title
题目
Assessment of Right Atrial Function Measured with Cardiac MRI Feature Tracking for Predicting Outcomes in Patients with Dilated Cardiomyopathy
使用心脏MRI特征追踪评估右心房功能以预测扩张型心肌病患者预后的研究
Background
背景
Right atrial (RA) function strain is increasingly acknowledged as an important predictor of adverse events in patients with diverse cardiovascular conditions. However, the prognostic value of RA strain in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) remains uncertain.
右心房(RA)功能应变正日益被认可为多种心血管疾病患者不良事件的重要预测指标。然而,RA应变在扩张型心肌病(DCM)患者中的预后价值仍不确定。
Method
方法
This multicenter, retrospective study included consecutive adult patients with DCM who underwent CMR between June 2010 and May 2022. RA strain parameters were obtained using CMR FT. The primary end points were sudden or cardiac death or heart transplant. Cox regression analysis was used to determine the association of variables with outcomes. Incremental prognostic value was evaluated using C indexes and likelihood ratio tests.
这项多中心、回顾性研究包括了2010年6月至2022年5月期间接受心脏MRI(CMR)的连续成年扩张型心肌病(DCM)患者。通过CMR特征追踪(FT)获取右心房(RA)应变参数。主要终点为突发性或心脏性死亡或心脏移植。使用Cox回归分析来确定变量与结局之间的关联。通过C指数和似然比检验评估增量预后价值。
Conclusion
结论
CMR FT-derived RA conduit strain was an independent predictor of adverse outcomes among patients with DCM, providing incremental prognostic value when combined in a model with clinical and conventional CMR risk factors.Published under a CC BY 4.0 license
通过心脏MRI特征追踪(CMR FT)获得的右心房传导应变是扩张型心肌病(DCM)患者不良结局的独立预测因子,当与临床和传统CMR风险因素结合在模型中时,提供了增量的预后价值。
Results
结果
A total of 526 patients with DCM (mean age, 51 years ± 15 [SD]; 381 male) were included. During a median followup of 41 months, 79 patients with DCM reached the primary end points. At univariable analysis, RA conduit strain was associated with the primary end points (hazard ratio [HR], 0.82 [95% CI: 0.76, 0.87]; P < .001). In multivariable Cox analysis, RA conduit strain was an independent predictor for the primary end points (HR, 0.83 [95% CI: 0.77, 0.90]; P < .001). A model combining RA conduit strain with other clinical and conventional imaging risk factors (C statistic, 0.80; likelihood ratio, 92.54) showed improved discrimination and calibration for the primary end points compared with models with clinical variables (C statistic, 0.71; likelihood ratio, 37.12; both P < .001) or clinical and imaging variables (C statistic, 0.75; likelihood ratio, 64.69; both P < .001).
共纳入了526名扩张型心肌病(DCM)患者(平均年龄51岁,标准差±15;其中381名男性)。在中位随访41个月期间,79名DCM患者达到了主要终点。在单变量分析中,右心房传导应变与主要终点相关(风险比 [HR],0.82 [95% CI: 0.76, 0.87];P < .001)。在多变量Cox分析中,右心房传导应变是主要终点的独立预测因子(HR,0.83 [95% CI: 0.77, 0.90];P < .001)。将右心房传导应变与其他临床和传统影像学风险因素结合的模型(C统计量,0.80;似然比,92.54)在主要终点的区分和校准方面优于仅包含临床变量的模型(C统计量,0.71;似然比,37.12;均P < .001)或包含临床和影像学变量的模型(C统计量,0.75;似然比,64.69;均P < .001)。
Figure
图

Figure 1: Flowchart of patient inclusion. The primary end points were defined as the combination of sudden or cardiac death or heart transplant. The secondary end points were defined as the combination of the primary end points, heart failure hospitalization, and life-threatening arrhythmias. DCM = dilated cardiomyopathy
图1:患者纳入流程图。主要终点定义为突发性或心脏性死亡或心脏移植的组合。次要终点定义为主要终点、心力衰竭住院和致命性心律失常的组合。DCM = 扩张型心肌病。

Figure 2: Examples of right atrial (RA) strain measurements in two patients with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM). (A, B) Four-chamber cardiac MRI (CMR) scan (A) and RA strain curve (B) in a 35-year-old male patient with RA conduit strain of greater than 7.77% who did not experience the primary end points (sudden or cardiac death or heart transplant). (C, D) Four-chamber CMR scan © and RA strain curve (D) in a 67-year-old male patient with RA conduit strain of less than 7.77% who experienced cardiac death 25 months after CMR. RA CMR feature tracking analysis was applied in the four-chamber views (A, C). RA strain values were obtained according to the RA strain curves (B, D). RA reservoir strain (εs), conduit strain (εe), and booster strain (εa) correspond to RA reservoir, conduit, and pump booster function, respectively
图2:两名扩张型心肌病(DCM)患者的右心房(RA)应变测量示例。(A, B) 35岁男性患者的四腔心脏MRI(CMR)扫描(A)和RA应变曲线(B),其RA传导应变大于7.77%,未经历主要终点(突发性或心脏性死亡或心脏移植)。(C, D) 67岁男性患者的四腔心脏MRI扫描©和RA应变曲线(D),其RA传导应变小于7.77%,在CMR后25个月经历了心脏性死亡。在四腔视图中应用了RA CMR特征追踪分析(A, C)。RA应变值根据RA应变曲线(B, D)获得。RA储备应变(εs)、传导应变(εe)和助推应变(εa)分别对应RA的储备、传导和泵助推功能。

Figure 3: Kaplan-Meier curves for the (A) primary (sudden or cardiac death or heart transplant) and (B) secondary (primary end points, heart failure hospitalization, and life-threatening arrhythmias) end points stratified by right atrial (RA) conduit strain cutoffs in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Patients with RA conduit strain of less than 7.77% or less than 8.35% have a higher rate of reaching the primary end points or the secondary end points, respectively, compared with patients with RA conduit strain greater than 7.77% and greater than 8.35%, respectively
图3:Kaplan-Meier曲线显示了扩张型心肌病患者根据右心房(RA)传导应变截断值分层的(A)主要终点(突发性或心脏性死亡或心脏移植)和(B)次要终点(主要终点、心力衰竭住院和致命性心律失常)。RA传导应变小于7.77%或小于8.35%的患者分别比RA传导应变大于7.77%和大于8.35%的患者更有可能达到主要终点或次要终点。
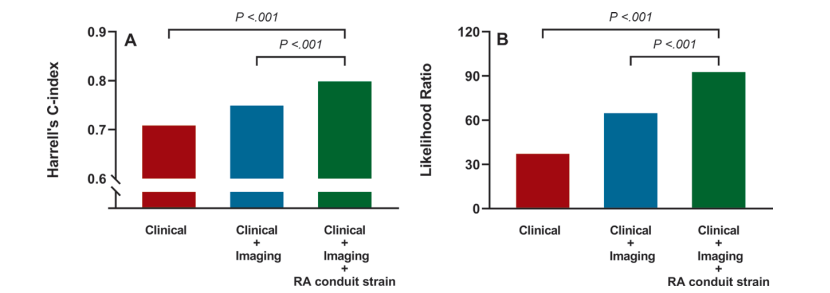
Figure 4: Evaluation of model (A) discrimination and (B) calibration for the primary end points (sudden or cardiac death or heart transplant). A model combining clinical variables (body mass index [calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared], fasting blood glucose, and New York Heart Association class), conventional imaging variables (left ventricular ejection fraction, right ventricular ejection fraction, left atrial emptying fraction passive, and late gadolinium enhancement), and right atrial (RA) conduit strain showed improved discrimination (C statistic, 0.80) and calibration (likelihood ratio, 92.54) compared with models that included only clinical variables (C statistic, 0.71; P < .001; likelihood ratio, 37.12; P < .001) or a model combining clinical and conventional imaging variables (C statistic, 0.75; P < .001; likelihood ratio, 64.69; P < .001). P values were obtained from Harrell C indexes and likelihood ratio test.
图4:对主要终点(突发性或心脏性死亡或心脏移植)模型的(A)区分能力和(B)校准能力的评估。结合了临床变量(体重指数[计算方法为体重(千克)除以身高(米)的平方]、空腹血糖和纽约心脏病协会分级)、传统影像学变量(左心室射血分数、右心室射血分数、左心房排空分数和晚期钆增强)以及右心房(RA)传导应变的模型相比,仅包含临床变量的模型(C统计量为0.71;P < .001;似然比为37.12;P < .001)或结合临床和传统影像学变量的模型(C统计量为0.75;P < .001;似然比为64.69;P < .001),显示了更好的区分能力(C统计量为0.80)和校准能力(似然比为92.54)。P值来自Harrell C指数和似然比检验。

Figure 5: Kaplan-Meier curves for the primary end points (sudden or cardiac death or heart transplant) stratified by right atrial (RA) conduit strain cutoffs and presence or absence of late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. In both (A) LGE-negative and (B) LGE-positive subgroups, patients with RA conduit strain of less than 7.77% had significantly poorer outcomes compared with patients with RA conduit strain greater than 7.77% (both log-rank P < .001).
图5:扩张型心肌病患者根据右心房(RA)传导应变截断值以及是否存在晚期钆增强(LGE)分层的主要终点(突发性或心脏性死亡或心脏移植)Kaplan-Meier曲线。在(A) LGE阴性和(B) LGE阳性亚组中,RA传导应变小于7.77%的患者与RA传导应变大于7.77%的患者相比,预后显著较差(均为log-rank P < .001)。
Table
表

Table 1: Baseline Characteristics of Patients with Dilated Cardiomyopathy
表1:扩张型心肌病患者的基线特征

Table 2: Comparison of Cardiac MRI Parameters Between Patients Who Did and Who Did Not Reach the Primary End Points
表2:达到和未达到主要终点的患者之间的心脏MRI参数比较

Table 3: Univariable and Multivariable Cox Proportional Hazards Analyses for the Association of Variables with Primary End Points
表3:单变量和多变量Cox比例风险分析,用于评估变量与主要终点的关联性

Table 4: Univariable and Multivariable Cox Proportional Hazards Analyses for the Association of Variables with Secondary End Points
表4:单变量和多变量Cox比例风险分析,用于评估变量与次要终点的关联性