Title
题目
Counterfactual Causal-Effect Intervention for Interpretable Medical Visual Question Answering
可解释医学视觉问答的反事实因果干预
01
文献速递介绍
深度学习的进步在计算机视觉、自然语言处理和信息检索领域成功地取得了最先进的(SOTA)成果。在医疗行业,深度学习技术促成了许多重要的应用。例如,在自然语言处理方面,利用患者临床记录进行预测分析的几项引人注目的研究已经出现。视觉问答(VQA)是一项计算机视觉和自然语言处理中的复杂任务,旨在回答与给定图像相关的自然语言问题。在通用领域,深度学习在VQA方面取得了巨大成功。将通用VQA迁移到医疗领域催生了一项新的下游任务:医学视觉问答(VQA-Med)。在VQA-Med任务中,使用患者的放射扫描(X射线、磁共振成像(MRI)和CT)代替通用领域的标准图像,并配有临床相关的问答(QA)对。VQA-Med技术可以帮助医生提高诊断效率,并帮助患者理解他们的病情。然而,VQA-Med具有挑战性,因为它需要对专业医学图像和文本QA对进行深入理解和高水平交互,以生成合理且可信的答案。
Abstract
摘要
医学视觉问答(VQA-Med)是一项具有挑战性的任务,涉及回答与医学图像相关的临床问题。然而,大多数当前的VQA-Med方法忽略了特定病变或异常特征与答案之间的因果关系,同时也未能为其决策提供准确的解释。为了探索VQA-Med的可解释性,本文提出了一种基于反事实因果干预策略的新型CCIS-MVQA模型。该模型由用于图像特征提取的改进ResNet、用于问题特征提取的GloVe解码器、用于视觉和语言特征融合的双线性注意网络以及用于生成可解释性和预测结果的可解释性生成器组成。所提出的CCIS-MVQA引入了一种层级相关传播方法,以自动生成反事实样本。此外,CCIS-MVQA在整个训练阶段应用反事实因果推理,以增强可解释性和泛化能力。在三个基准数据集上的大量实验表明,所提出的CCIS-MVQA模型优于最先进的方法。生成了足够的可视化结果来分析CCIS-MVQA的可解释性和性能。
Method
方法
The VQA-Med task is a multi-class classification problem, and we consider an image-question pair ( ) , V Q , where Qrepresents a medical-related question, and V is a medical image. A dataset { } , ,Nii i i D v q a = consists of triplets of images i v V ∈ , questions i q Q∈ , and candidate answers i a A ∈ . VQA-Med can be expressed as a question-and-answer model to find the answer with the highest probability from candidate answers as: ( ) ˆ argmax | ,ii i iaa P a v q θ∈=A, (1) where θ is the parameter in question answering model. As shown in Fig. 1, the proposed CCIS-MVQA consists of four main components.
VQA-Med任务是一个多类分类问题,我们考虑一个图像-问题对 (V,Q)(V, Q)(V,Q),其中 QQQ 代表一个与医学相关的问题,VVV 是一张医学图像。一个数据集 {(vi,qi,ai)}i=1N{(v_i, q_i, a_i)}{i=1}N{(vi,qi,ai)}i=1N 由图像 vi∈Vv_i \in Vvi∈V、问题 qi∈Qq_i \in Qqi∈Q 和候选答案 ai∈Aa_i \in Aai∈A 的三元组组成。VQA-Med可以表示为一个问答模型,从候选答案中找到具有最高概率的答案:\hat{a} = \arg\max{a_i \in A} P(a_i | v, q; \theta) \tag{1}其中 θ\thetaθ 是问答模型中的参数。如图1所示,所提出的CCIS-MVQA由四个主要组件组成。
Conclusion
结论
This paper proposed a novel CCIS-MVQA framework to discuss how to mitigate the influence of language bias and enhance the interpretability of the VQA-Med model in mixed causal data. The proposed CCIS-MVQA framework consists of image feature extraction, question feature extraction, BAN, and interpretation generator. This paper focused on theinterpretation generator to explore the interpretability and language bias of VQA-Med. We incorporated counterfactual interpretation and causal-effect reasoning into CCIS-MVQA to explore how the VQA-Med system responds to causal intervention strategy (such as the covered image of a given focus, how the model generates predictive answers), and quantify the effects of such intervention strategies.
本文提出了一种新颖的CCIS-MVQA框架,旨在讨论如何减轻语言偏差的影响并增强VQA-Med模型在混合因果数据中的可解释性。所提出的CCIS-MVQA框架包括图像特征提取、问题特征提取、BAN(双线性注意网络)和解释生成器。本文重点研究了解释生成器,以探索VQA-Med的可解释性和语言偏差。我们将反事实解释和因果推理引入CCIS-MVQA,探讨VQA-Med系统如何响应因果干预策略(例如,给定焦点的覆盖图像,模型如何生成预测答案),并量化这些干预策略的效果。
Figure
图

Fig. 1. The proposed CCIS-MVQA framework based on counterfactual causal-effect intervention strategy
图1:基于反事实因果干预策略的CCIS-MVQA框架

Fig. 2. Factual and counterfactual interpretations on VQA-Med dataset.
图2:VQA-Med数据集上的事实和反事实解释。
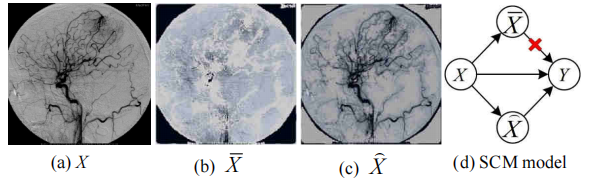
Fig. 3. Causal graph model based on counterfactual samples. (a) Original image X; Answer Y: Vascular malformation. (b) Counterfactual imageX ; Answer Y: NOT Vascular malformation. © Counterfactual imageX⌢; Answer Y: Vascular malformation. (d) SCM model.
图3:基于反事实样本的因果图模型。(a) 原始图像X;答案Y:血管畸形。(b) 反事实图像X;答案Y:非血管畸形。© 反事实图像X⌢;答案Y:血管畸形。(d) SCM模型。

Fig. 4 Training and optimization process of CCIS-MVQA at epoch i
图4:CCIS-MVQA在第i个epoch的训练和优化过程

Fig. 5. Examples of counterfactual samples between the causal and non-causal correlations.
图5:因果相关和非因果相关之间反事实样本的示例。

Fig.6. Examples for interpretable causal saliency map.
图6:可解释因果显著性图示例。

Fig.7. Visualization results of the debiasing ability with CCIS-MVQA.
图7:CCIS-MVQA去偏能力的可视化结果。

Fig. 8. Ablation studies on batch size and parameter k
图8:关于批处理大小和参数k的消融研究

Fig.9. The confusion matrix of Plane
图9:平面的混淆矩阵
Table
表
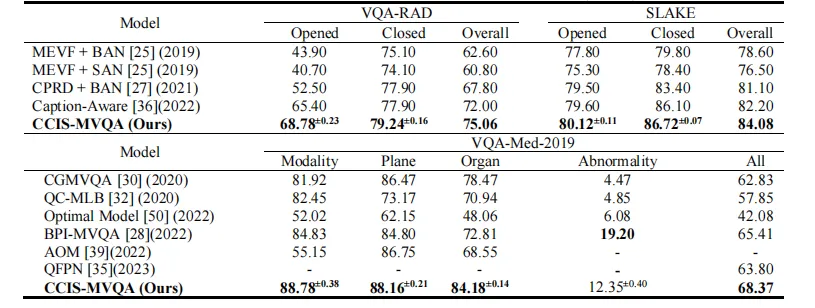
TABLE I quantitative verification results of model overall performance (acc. %)
表 I 模型整体性能的定量验证结果(准确率%)

TABLE II effect of different k value on ccis-mvqa performance (acc. %)
表 II不同K值对CCIS-MVQA性能的影响(准确率%)

TABLE IIIthe quantitative verification results of model debiasing ability (acc. %)
表 III模型去偏能力的定量验证结果(准确率%)

TABLE IV effect of pre-training process on ccis-mvqa
表 IV 预训练过程对CCIS-MVQA的影响