Title
题目
Deep-LIBRA: An artificial-intelligence method for robust quantification of breast density with independent validation in breast cancer risk assessment
Deep-LIBRA:一种用于可靠量化乳腺密度的人工智能方法,并在乳腺癌风险评估中进行了独立验证
01
文献速递介绍
研究表明,乳腺密度,即乳腺内纤维腺体组织的程度,不仅限制了筛查乳腺X光检查的敏感性,而且还是一个独立的乳腺癌风险因素(Engmann 等,2017;Freer,2015;Brentnall 等,2018)。乳腺密度可以通过全视野数字乳腺X光片(FFDM)图像进行估算,通常使用美国放射学会乳腺影像报告和数据系统(BI-RADS)进行评估(D’orsi 等,2003)。然而,BI-RADS密度评估高度主观,并且未能提供乳腺密度的定量、连续测量,这将有助于更精细的风险分层和乳腺密度变化的评估(Irshad 等,2016;Sprague 等,2016)。
可以通过市售软件(Hartman 等,2008;Regini 等,2014)和基于研究的工具(Keller 等,2012;Mustra 等,2016;Li 等,2013;Shi 等,2018;Anitha 等,2017;Ferrari 等,2004;Kwok 等,2004)对FFDM图像中的乳腺密度进行自动定量测量。尽管这些工具有用,但仍存在重要的局限性。大多数市售软件包(如Quantra和Volpara)基于X射线束交互模型计算乳腺密度(Hartman 等,2008;Regini 等,2014)。这些软件包基于特定元数据进行假设,以简化各种估算,包括识别脂肪组织。因此,当所需元数据缺失时,这些假设可能导致估算不准确。此外,商业工具不提供相应的致密组织分割空间图,同时它们也很昂贵,难以普及。另一方面,除了少数例外(如公开的LIBRA软件,Keller 等,2012;Gastounioti 等,2020),基于研究的方法通常不是免费提供的,难以广泛采用并严格比较其性能。大多数基于研究的工具也是使用小型、单机构数据集开发的,缺乏独立验证(Keller 等,2012;Li 等,2013;Shi 等,2018;Anitha 等,2017)。
Abstract
摘要
乳腺密度是乳腺癌的重要风险因素,也影响筛查乳腺X光检查的特异性和敏感性。目前的联邦立法要求对所有进行乳腺癌筛查的女性报告乳腺密度。在临床上,乳腺密度是通过美国放射学会乳腺影像报告和数据系统(BI-RADS)评分进行视觉评估的。本文介绍了一种人工智能(AI)方法,用于从数字乳腺X光片中估算乳腺密度。我们的方法利用深度学习,使用两种卷积神经网络架构来准确分割乳腺区域。然后应用结合超像素生成和放射组学机器学习的AI算法,区分乳腺内的致密和非致密组织区域,从而估算乳腺密度。我们的方法在包含不同种族和多机构的15,661张图像(4,437名女性)的数据集上进行了训练和验证,并在一个独立的匹配病例对照数据集(6368张数字乳腺X光片,414例病例;1178例对照)上进行了乳腺密度估算和病例对照区分测试。在独立数据集上,Deep-LIBRA和专家读片者的乳腺密度百分比(PD)估算高度相关(Spearman相关系数=0.90)。此外,在调整年龄和体重指数(BMI)的模型中,Deep-LIBRA在病例对照区分性能方面表现更优(ROC曲线下面积,AUC=0.612 [95%置信区间(CI):0.584,0.640]),相比于四种广泛使用的研究和商业乳腺密度评估方法(AUC=0.528到0.599)。我们的结果表明,Deep-LIBRA与专家读片者的金标准评估之间的乳腺密度估算高度一致,并且在乳腺癌风险评估中表现优于最先进的开源和商业方法。
Method
方法
Deep-LIBRA is a pipeline of AI modules sequentially performing all three key computational steps involved in automated breastdensity quantification from FFDM. Through these steps, DeepLIBRA provides estimates of the total dense tissue area (DA), aswell as the relative amount of dense tissue within the breast, alsoknown as breast percent density (PD). This section describes thestudy datasets and the experiments used to develop and evaluateeach AI module of Deep-LIBRA (Table 1, Fig. 1 and SupplementaryFigure 1).
Deep-LIBRA是一系列AI模块的管道,按顺序执行FFDM自动乳腺密度量化涉及的所有三个关键计算步骤。通过这些步骤,Deep-LIBRA提供了总致密组织面积(DA)的估算,以及乳腺内致密组织的相对量,即乳腺密度百分比(PD)。本节描述了用于开发和评估Deep-LIBRA每个AI模块的研究数据集和实验(表1,图1和补充图1)。
Results
结果
3.1. Evaluation on development datasets
3.1.1. Background and pectoralis muscle removal
The evaluation curves in the development phase of Deep-LIBRAshow sufficient training and high performance in breast segmentation (Fig. 4). The highest weighted dice score achieved by thebackground removal module on the validation set was 99.4% after35 epochs, with a value of 99.5% on the training set at the sameepoch (Fig. 4 (a)). The pectoralis muscle removal module achievedthe highest weighted dice of 95.0% on the validation set after 158epochs, with a valueof 96.3% on the training set at the same epoch(Fig. 4 (b)).
3.1. 评估开发数据集
3.1.1. 背景和胸肌去除
Deep-LIBRA开发阶段的评估曲线显示了在乳腺分割中的充分训练和高性能(图4)。背景去除模块在验证集上的最高加权Dice得分在第35轮后达到了99.4%,在训练集上的值在同一轮达到了99.5%(图4(a))。胸肌去除模块在第158轮后在验证集上达到了最高加权Dice得分95.0%,在训练集上的值在同一轮达到了96.3%(图4(b))。
Figure
图
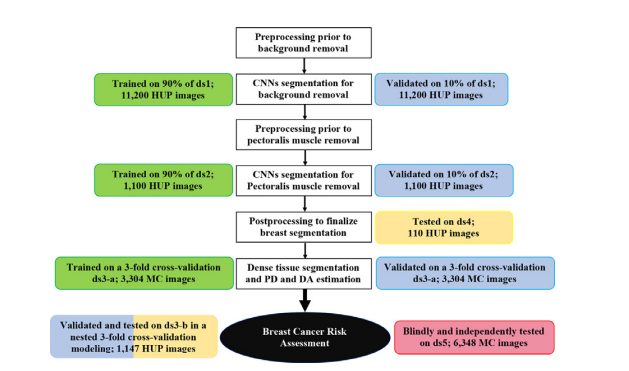
Fig. 1. Development and evaluation experiments. White boxes: workflow of theDeep-LIBRA algorithm. Green, blue, yellow, and red boxes: training, validation, independent testing, and blinded independent testing, respectively. HUP: Hospital ofthe University of Pennsylvania; MC: Mayo Clinic.
图1. 开发和评估实验。白色框:Deep-LIBRA算法的工作流程。绿色、蓝色、黄色和红色框分别表示训练、验证、独立测试和盲独立测试。HUP:宾夕法尼亚大学医院;MC:梅奥诊所。
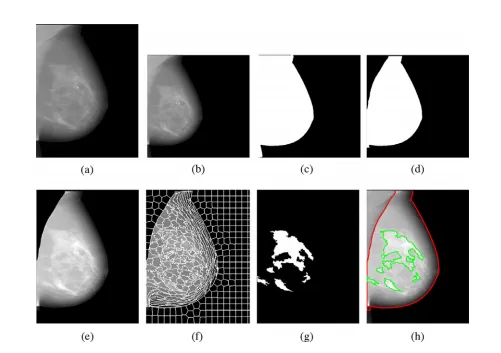
Fig. 2. Detailed illustration of the Deep-LIBRA algorithm operation. Panel (a) showsthe original FFDM image in 16-bit resolution, and panel (b) is the zero-padded image in an 8-bit intensity resolution. The zero-padded image is used by the background segmentation U-Net, which generates the image shown in panel ©. Panel(d) is the output of the module of pectoralis muscle removal using the second UNet resulting to the final breast segmentation shown in panel (e). The image frompanel (e) is used to generate superpixels as shown in panel (f) and perform radiomic feature analysis. Finally, the SVM classifies the superpixels based on the extracted features, resulting in dense tissue segmentation, as shown in panel (g). Thepanel (h) shows the final dense tissue segmentation overlaid on the original image. Note: The image sizes are different in this figure because the panels (a), (e)-(h)show images in the original image resolution, while the panels (b)-(d) are downsampled images of size 512 × 512 pixels used in U-Net segmentation.
图2. Deep-LIBRA算法操作的详细说明。面板(a)显示了16位分辨率的原始FFDM图像,面板(b)是零填充的8位强度分辨率图像。零填充图像被背景分割U-Net使用,生成面板©中显示的图像。面板(d)是使用第二个U-Net去除胸肌模块的输出,结果为面板(e)中显示的最终乳腺分割图像。面板(e)中的图像用于生成如面板(f)所示的超像素,并进行放射组学特征分析。最后,SVM根据提取的特征对超像素进行分类,结果为致密组织分割,如面板(g)所示。面板(h)显示了覆盖在原始图像上的最终致密组织分割图像。注意:此图中的图像大小不同,因为面板(a)和面板(e)-(h)显示的是原始图像分辨率,而面板(b)-(d)是用于U-Net分割的512 × 512像素的下采样图像。
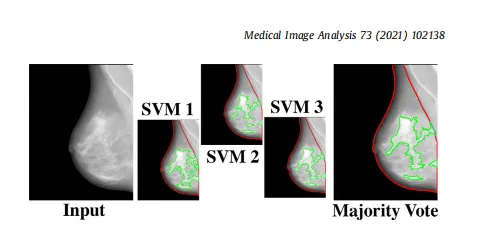
Fig. 3. The majority voting approach. The majority voting approach uses the outcome of three SVM models, each trained on two folds of ds3-a, to make the finaldense tissue segmentation. The majority voting scheme assigns the dense or nondense label to each superpixel based on at least two SVM models agreeing on thelabel.
图3. 多数投票方法。多数投票方法使用三个SVM模型的结果,每个模型在ds3-a的两个折叠上训练,以进行最终的致密组织分割。多数投票方案根据至少两个SVM模型对标签的同意情况,将致密或非致密标签分配给每个超像素。
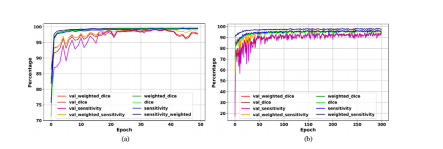
Fig. 4. Deep-LIBRA evaluation curves in the development phase. Panels (a) and(b) show the training and validation (noted as “val_”) results for background andpectoral muscle segmentation CNNs, respectively. As the panel (b) shows, there isno sign of overfitting for pectoralis muscle segmentation while panel (a) indicatessome possible signs of overfitting after epoch 40 shown by a wider fluctuation onthe validation set.
图4. Deep-LIBRA在开发阶段的评估曲线。面板(a)和面板(b)分别显示了背景和胸肌分割CNN的训练和验证(标记为“val_”)结果。如面板(b)所示,胸肌分割没有出现过拟合的迹象,而面板(a)显示出在第40轮后验证集上的波动较大,可能存在一些过拟合的迹象。
Table
表
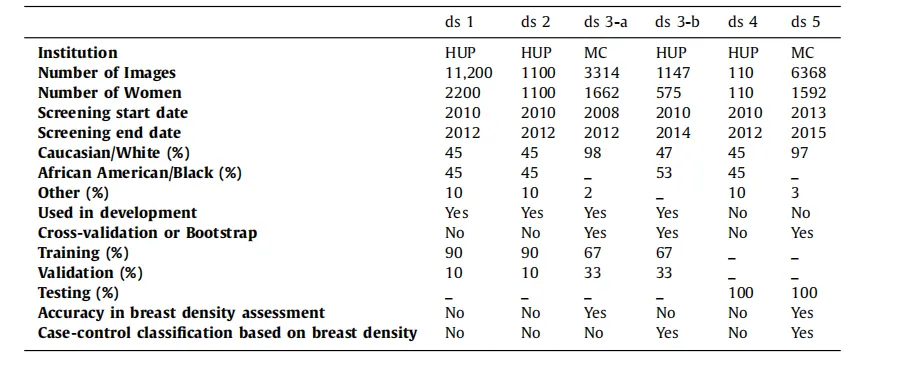
Table 1General characteristics of the six study datasets. For each dataset, this table shows the institution where images werecollected, the number of images and individual women, the range of screening dates, the racial distribution, andinformation about the dataset usage in this study. The case-control datasets (ds3-b and ds5) include any availablecancer case from the HUP and MC screening cohorts as long as a negative FFDM exam acquired prior to breastcancer diagnosis was available for analysis.
表1 六个研究数据集的一般特征。对于每个数据集,本表显示了图像收集的机构、图像和个体女性的数量、筛查日期范围、种族分布以及在本研究中数据集的使用信息。病例对照数据集(ds3-b和ds5)包括HUP和MC筛查队列中的所有可用癌症病例,只要有乳腺癌诊断前获得的阴性FFDM检查可供分析。
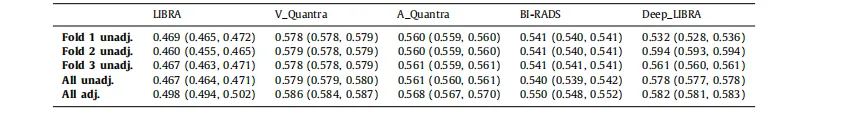
Table 2Case-control discrimination performance on the dataset ds3-b for breast percent density (PD) values generated by Deep-LIBRA and LIBRA,area-based (A_Quantra) and volumetric (V_Quantra) PD values by Quantra, and clinical BI-RADS density assessments. Results correspond tomean AUCs and 95% CIs in parentheses. Folds 1, 2 and 3 are the held-out folds used for the evaluation of the corresponding Deep-LIBRASVM. Unadj. and adj. indicate unadjusted logistic regression models and logistic regression models adjusted for age and BMI, respectively.
表2 ds3-b数据集上Deep-LIBRA和LIBRA生成的乳腺密度百分比(PD)值的病例对照区分性能,Quantra生成的基于面积(A_Quantra)和体积(V_Quantra)的PD值,以及临床BI-RADS密度评估。结果对应于平均AUC和95%置信区间(CI)括号内的值。折叠1、2和3是用于评估相应Deep-LIBRA SVM的保留折叠。Unadj.和adj.分别表示未调整的逻辑回归模型和调整年龄和BMI的逻辑回归模型。
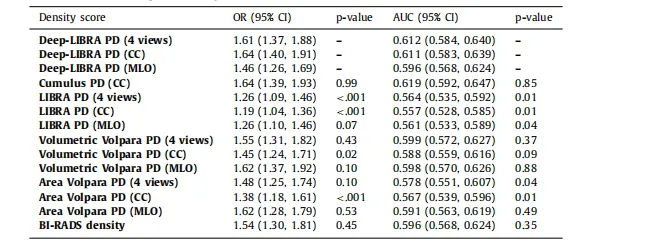
Table 3Associations of percent density (PD) measures with breast cancer and case-control discriminatory performance on ds5, using logistic regression models adjusted for age and BMI. P-values for both AUCs and ORswere obtained from 1000 bootstrap samples to test for the null hypothesis of no difference from the AUCor OR derived from Deep-LIBRA using the same breast views.
表3使用调整年龄和BMI的逻辑回归模型,在ds5数据集上乳腺密度百分比(PD)测量与乳腺癌的关联及病例对照区分性能。AUC和OR的P值是通过1000次自举样本获得的,以检验与使用相同乳腺视图的Deep-LIBRA得到的AUC或OR之间无差异的零假设。
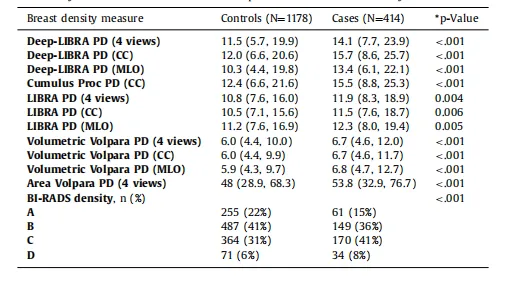
Table 4Breast density distributions on ds5. Except for BI-RADS density, data corresponds to medianand interquartile range in parentheses. For BI-RADS density, data corresponds to number ofwomen and percentage in parentheses. P-values from Wilcoxon Rank-sum tests for continuous density measures and from Pearson chi-squared test for BI-RADS density.
表4 ds5数据集上的乳腺密度分布。除BI-RADS密度外,数据对应于中位数和括号中的四分位数范围。对于BI-RADS密度,数据对应于括号中的女性数量和百分比。*P值来自Wilcoxon秩和检验(用于连续密度测量)和Pearson卡方检验(用于BI-RADS密度)。