Title
题目
Prognostic Value of Deep Learning PET/CT-BasedRadiomics: Potential Role for Future IndividualInduction Chemotherapy in AdvancedNasopharyngeal Carcinoma
基于深度学习PET/CT放射学的预后价值:未来在晚期鼻咽癌个体化诱导化疗中的潜在作用
01
文献速递介绍
鼻咽癌(NPC)是一种特殊类型的头颈部癌症,主要流行于南亚。尽管放疗技术和化疗策略的进步已经改善了NPC的预后,但晚期患者的预后仍然不尽人意,近30%的病例存在治疗失败的情况。不幸的是,超过70%的患者在初诊时已经表现为局部区域晚期疾病。对于晚期疾病的管理仍然是临床医生面临的挑战。
在进行根治放疗之前给予诱导化疗(IC)已在过去十年被广泛证明是一种可行的新辅助治疗,对晚期NPC具有满意的疗效和低毒性。因此,IC已被常规推荐用于晚期NPC。然而,值得指出的是,晚期疾病包括许多亚组,并非所有患者都能从额外的IC中受益。因此,识别可以从IC中受益的高风险亚组是改善晚期NPC管理的关键。尽管一些回顾性研究发现,治疗前血浆Epstein-Barr病毒DNA(pre-DNA)可能作为IC的指标,但这些证据并不强有力。最重要的是,血浆EBV DNA的检测标准化限制了其广泛应用,因为不同实验室使用不同的聚合酶链反应检测方法,因此产生了不一致的结果。因此,值得寻找新的、有力的因素来指导IC
Abstract
摘要
Purpose目的: We aimed to evaluate the value of deep learningon positron emission tomography with computed tomography (PET/CT)–based radiomics for individual induction chemotherapy (IC) in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma(NPC).
Experimental Design实验设计:
We constructed radiomics signaturesand nomogram for predicting disease-free survival (DFS)based on the extracted features from PET and CT images ina training set (n ¼ 470), and then validated it on a test set (n ¼237). Harrell’s concordance indices (C-index) and time-independent receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis wereapplied to evaluate the discriminatory ability of radiomicsnomogram, and compare radiomics signatures with plasmaEpstein–Barr virus (EBV) DNA.
我们旨在评估基于深度学习的正电子发射计算机断层扫描(PET/CT)放射学在晚期鼻咽癌(NPC)个体化诱导化疗(IC)中的价值。
我们在一个训练集(n=470)中基于PET和CT图像提取的特征构建了预测无病生存(DFS)的放射学标志和诊断图。然后,在一个测试集(n=237)上进行验证。我们应用Harrell的一致性指数(C-index)和与时间无关的接收器工作特性(ROC)分析来评估放射学诊断图的区分能力,并将放射学标志与血浆Epstein-Barr病毒(EBV)DNA进行比较。
Results
结果
A total of 18 features were selected to constructCT-based and PET-based signatures, which were signifi-cantly associated with DFS (P < 0.001). Using these signatures, we proposed a radiomics nomogram with aC-index of 0.754 [95% confidence interval (95% CI),0.709–0.800] in the training set and 0.722 (95% CI,0.652–0.792) in the test set. Consequently, 206 (29.1%)patients were stratified as high-risk group and the other501 (70.9%) as low-risk group by the radiomics nomogram, and the corresponding 5-year DFS rates were 50.1%and 87.6%, respectively (P < 0.0001). High-risk patientscould benefit from IC while the low-risk could not. Moreover, radiomics nomogram performed significantly betterthan the EBV DNA-based model (C-index: 0.754 vs. 0.675in the training set and 0.722 vs. 0.671 in the test set) in riskstratification and guiding IC.
总共选择了18个特征来构建基于CT和PET的标志,这些标志与DFS(P < 0.001)显著相关。利用这些标志,我们提出了一个放射学诊断图,训练集中的C指数为0.754(95%置信区间[95% CI]:0.709–0.800),测试集中的为0.722(95% CI:0.652–0.792)。因此,206名(29.1%)患者被分层为高风险组,另外501名(70.9%)患者被分层为低风险组,放射学诊断图对应的5年DFS率分别为50.1%和87.6%(P < 0.0001)。高风险患者可以从IC中受益,而低风险患者则不能。此外,放射学诊断图在风险分层和指导IC方面表现显著优于基于EBV DNA的模型(C指数:训练集中为0.754 vs. 0.675,测试集中为0.722 vs. 0.671)。
Conclusion
结论
Deep learning PET/CT-based radiomics couldserve as a reliable and powerful tool for prognosis predictionand may act as a potential indicator for individual IC inadvanced NPC.
基于深度学习PET/CT的放射学可以作为一种可靠且强大的预后预测工具,并可能成为晚期NPC中个体化IC的潜在指标。
Figure
图
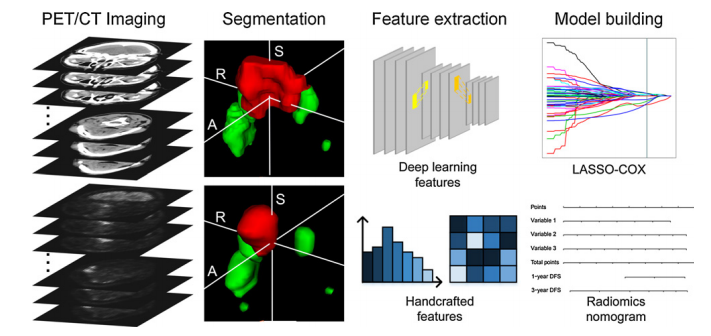
Figure 1. Radiomics workflow in this study.
图1. 本研究中的放射学工作流程。
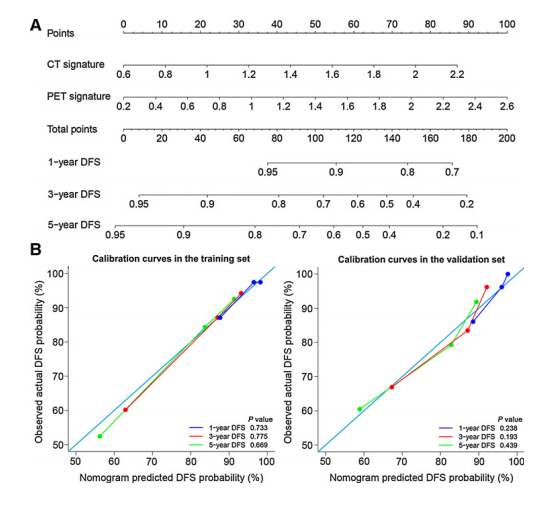
Figure 2.A, Radiomics nomogram; B,Radiomics nomogram calibrationcurves. PET, positron emissiontomography; CT, computedtomography.
图2.A,放射学诊断图;B,放射学诊断图校准曲线。PET,正电子发射断层扫描;CT,计算机断层扫描。
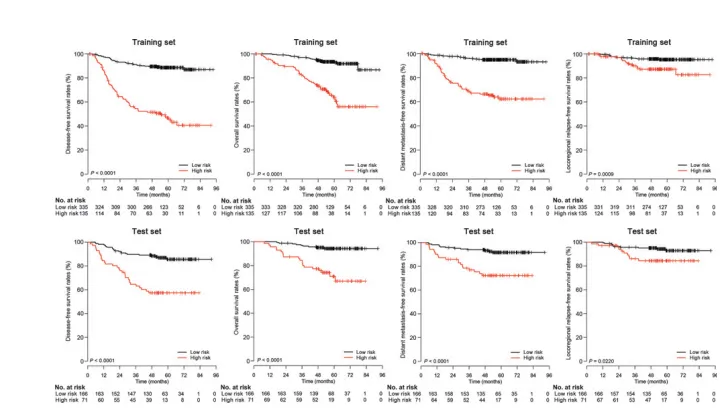
Figure 3.DFS, overall survival, DMFS, and locoregional relapse-free survival Kaplan–Meier curves between the radiomics nomogram–defined high-risk and low-risk groups in the training and test sets.
图3. 训练集和测试集中放射学诊断图定义的高风险和低风险组之间的无病生存(DFS)、总生存率、远处转移无病生存(DMFS)和局部区域复发无病生存的Kaplan-Meier曲线。
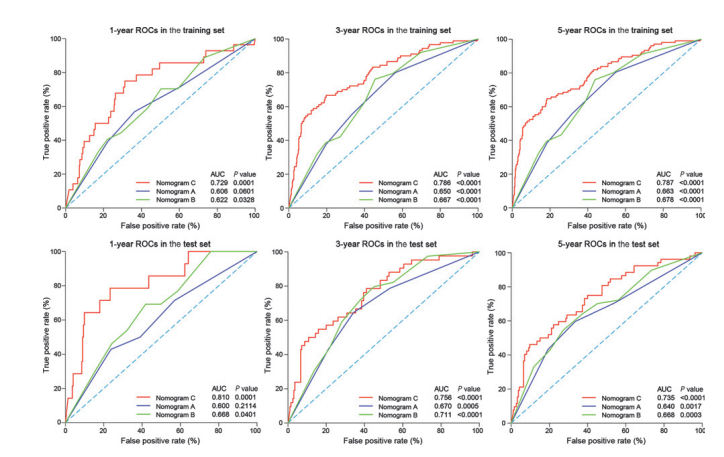
Figure 4.ROC curves comparing the predictive power of three nomograms for DFS in the training and test sets. ROC, receiver operator characteristic; AUC, area under the curve.
图4. 训练集和测试集中三个诊断图对无病生存(DFS)预测能力的ROC曲线比较。ROC,受试者工作特征曲线;AUC,曲线下面积。
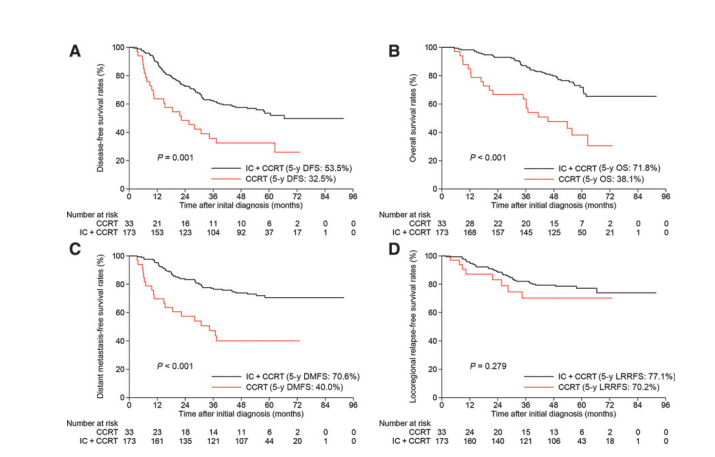
Figure 5.A–D, Kaplan–Meier survival curves between IC þ CCRT and CCRT alone within the radiomics nomogram–defined high-risk group. IC, induction chemotherapy;CCRT, concurrent chemoradiotherapy.
图5.A–D,放射学诊断图定义的高风险组中IC + CCRT和单独CCRT之间的Kaplan-Meier生存曲线。IC,诱导化疗;CCRT,同步化疗放疗。
Table
表
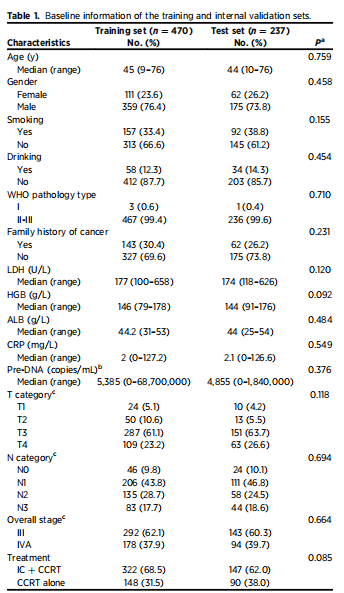
Table 1. Baseline information of the training and internal validation sets
表1. 训练集和内部验证集的基线信息