Title
题目
Deep Learning–based Image Conversion of CT Reconstruction Kernels Improves Radiomics Reproducibility for Pulmonary Nodules or Masses
基于深度学习的 CT 重建核的图像转换改进了肺部结节或肿块的放射组学再现性
Background
背景
Intratumor heterogeneity in lung cancer may influence outcomes. CT radiomics seeks to assess tumor features to provide detailed imaging features. However, CT radiomic features vary according to the reconstruction kernel used for image
generation.肺癌的肿瘤内部异质性可能会影响预后。CT放射组学旨在评估肿瘤特征,以提供详细的成像特征。然而,CT放射组学特征根据用于图像生成的重建核而变化。
Method
方法
In this retrospective analysis, patients underwent non–contrast material–enhanced and contrast material–enhanced axial chest CT with soft kernel (B30f) and sharp kernel (B50f) reconstruction using a single CT scanner from April to JuneTo convert different kernels without sinogram, the CNN model was developed using residual learning and an end-to-end way. Kernel-converted images were generated, from B30f to B50f and from B50f to B30f. Pulmonary nodules or masses were semiautomatically segmented and 702 radiomic features (tumor intensity, texture, and wavelet features) were extracted. Measurement variability in radiomic features was evaluated using the concordance correlation coefficient (CCC).
在这项回顾性分析中,患者在2017年4月至6月期间接受了非对比物质增强和对比物质增强的胸部CT检查,采用单台CT扫描仪进行软核(B30f)和锐核(B50f)重建。为了在没有正弦图的情况下转换不同的核,使用了残差学习和端到端的方式开发了CNN模型。生成了核转换图像,从B30f到B50f,从B50f到B30f。肺部结节或肿块被半自动分割,并提取了702个放射组学特征(肿瘤强度、纹理和小波特征)。利用一致性相关系数(CCC)评估了放射组学特征的测量变异性
Results
结果
A total of 104 patients were studied, including 54 women and 50 men, with pulmonary nodules or masses (mean age, 63.2 years 6 10.5). The CCC between two readers using the same kernel was 0.92, and 592 of 702 (84.3%) of the radiomic features were reproducible (CCC 0.85); using different kernels, the CCC was 0.38 and only 107 of 702 (15.2%) of the radiomic features were reliable. Texture features and wavelet features were predominantly affected by reconstruction kernel (CCC, from 0.88 to 0.61 for texture features and from 0.92 to 0.35 for wavelet features). After applying image conversion, CCC improved to 0.84 and 403 of 702 (57.4%) radiomic features were reproducible (CCC, 0.85 for texture features and 0.84 for wavelet features).
共研究了104名患者,包括54名女性和50名男性,患有肺部结节或肿块(平均年龄为63.2岁,标准偏差为10.5)。在使用相同核的两个读者之间,CCC为0.92,702个放射组学特征中的592个(84.3%)具有再现性(CCC ≥ 0.85);而在使用不同核时,CCC为0.38,仅有107个放射组学特征中的702个(15.2%)是可靠的。纹理特征和小波特征主要受重建核的影响(纹理特征的CCC从0.88降至0.61,小波特征的CCC从0.92降至0.35)。在应用图像转换后,CCC提高到0.84,有402个702个(57.4%)放射组学特征具有再现性(纹理特征的CCC为0.85,小波特征的CCC为0.84)。
Conclusion
结论
Chest CT image conversion using a convolutional neural network effectively reduced the effect of two different reconstruction kernels and may improve the reproducibility of radiomic features in pulmonary nodules or masses.
胸部CT图像转换利用卷积神经网络有效地减少了两种不同重建核的影响,并可能提高肺部结节或肿块的放射组学特征的再现性。
Figure
图
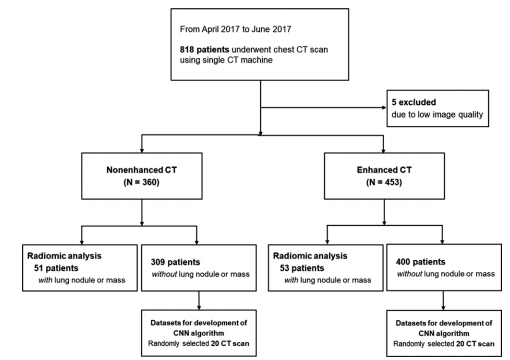
Figure 1: Flow diagram of patient inclusion. CNN = convolutional neural network.
图 1:患者纳入流程图。CNN = 卷积神经网络。
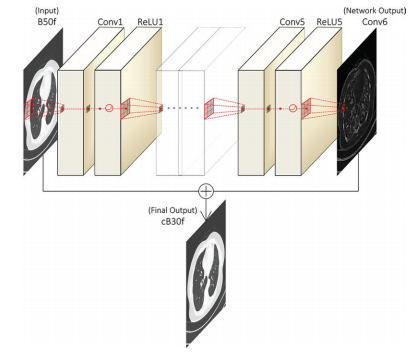
Table 2: Operational Parameters for Training the Proposed Convolutional Neural Network
表 2:训练所提出的卷积神经网络的操作参数
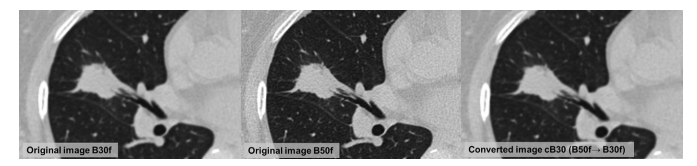
Figure 3: Example of nonenhanced CT image conversion among different reconstruction kernels using convolutional neural network (CNN). Images in a 55-year-old woman with a 24-mm nodule in right middle lobe; the nodule was found to be lung cancer upon pathologic examination. Patient underwent axial nonenhanced chest CT. Regarding the value of texture feature, glcm_homogeniety was 0.782 on original axial B30f image and 0.697 on original B50f image. Regarding the value of wavelet feature, avelet_LHH_glrlm_RunLengthNonUniformity was 2643 on original axial B30f image and 3727 on original B50f image. CNN architecture was applied to convert reconstruction kernels from B30 to B50. The texture is almost similar in the converted image compared with that in the original images under visual assessment. glcm_homogeniety was 0.789 and wavelet_LHH_ glrlm_RunLengthNonUniformity was 2638 on converted B30 image (cB30), which was close to the value of original B30f image.
图 3:利用卷积神经网络(CNN)在不同重建核之间进行无增强CT图像转换的示例。这是一位55岁女性的图像,右中叶有一个直径为24毫米的结节;病理检查证实该结节为肺癌。患者接受了胸部轴位无增强CT检查。关于纹理特征的值,原始轴位B30f图像上的glcm_homogeniety为0.782,原始B50f图像上为0.697。关于小波特征的值,原始轴位B30f图像上的avelet_LHH_glrlm_RunLengthNonUniformity为2643,原始B50f图像上为3727。CNN架构被应用于将重建核从B30转换为B50。在视觉评估下,转换后的图像中的纹理与原始图像几乎相似。转换后的B30图像(cB30)上的glcm_homogeniety为0.789,wavelet_LHH_glrlm_RunLengthNonUniformity为2638,接近原始B30f图像的值。
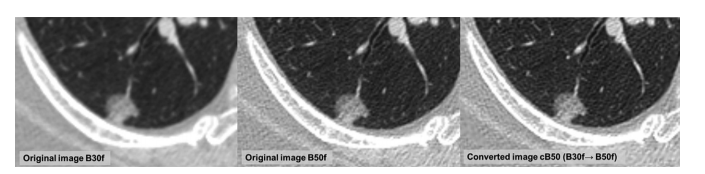
Figure 4: Example of contrast-enhanced CT image conversion among different reconstruction kernels using convolutional neural network. Images in a 68-year-old woman with a 16-mm ground-glass nodule in right lower lobe. Patient underwent axial contrast-enhanced chest CT. Regarding the value of radiomic features, glcm_contrast was 1.100 on original axial B30f image and 2.146 on original B50f image. wavelet_HHH_glrlm_HighGrayLevelRunEmphasis was 2.507 on original axial B30f image and 6.513 on original B50f image. After applying image conversion, glcm_contrast was 2.397 and wavelet_HHH_glrlm_HighGrayLevelRunEmphasis was 6.572 on converted B50 image (cB50) which was close to the value of original B50f image
图 4:利用卷积神经网络进行不同重建核之间对比增强CT图像转换的示例。这是一位68岁女性的图像,右下叶有一个直径为16毫米的地玻璃结节。患者接受了胸部轴位对比增强CT检查。关于放射组学特征的值,原始轴位B30f图像上的glcm_contrast为1.100,原始B50f图像上为2.146。wavelet_HHH_glrlm_HighGrayLevelRunEmphasis在原始轴位B30f图像上为2.507,在原始B50f图像上为6.513。应用图像转换后,转换后的B50图像(cB50)上的glcm_contrast为2.397,wavelet_HHH_glrlm_HighGrayLevelRunEmphasis为6.572,与原始B50f图像的值接近。
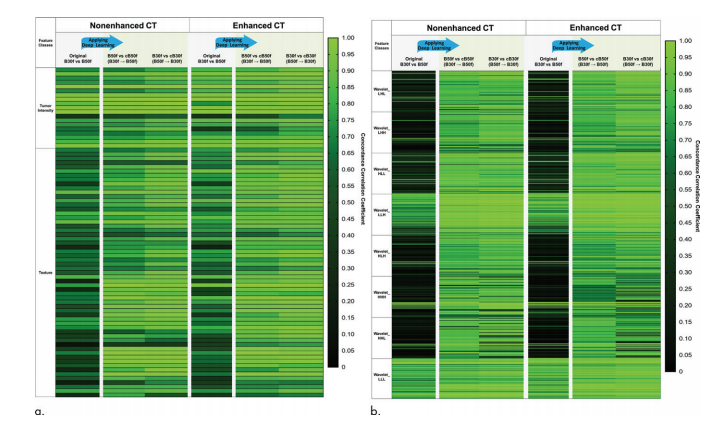
Figure 5: Concordance correlation coefficient (CCC) heat map of radiomic features. The heat map of CCCs for the 702 radiomics features between the different comparisons is shown. Texture features and wavelet features are dominantly affected by different kernels of CT images showing low CCC under different kernels in both nonenhanced and contrast-enhanced CT scans. After applying image conversion, CCC improved in all radiomic features. The results were similar in both nonenhanced and contrast-enhanced CT images. CCC of (a) tumor intensity and texture features and (b) wavelet features.
图 5:放射组学特征的一致性相关系数(CCC)热力图。显示了702个放射组学特征在不同比较之间的CCC热力图。在无增强和对比增强的CT扫描中,纹理特征和小波特征主要受到不同核的影响,在不同核下CCC较低。应用图像转换后,所有放射组学特征的CCC都有所提高。结果在无增强和对比增强的CT图像中相似。(a)肿瘤强度和纹理特征的CCC,以及(b)小波特征的CCC。
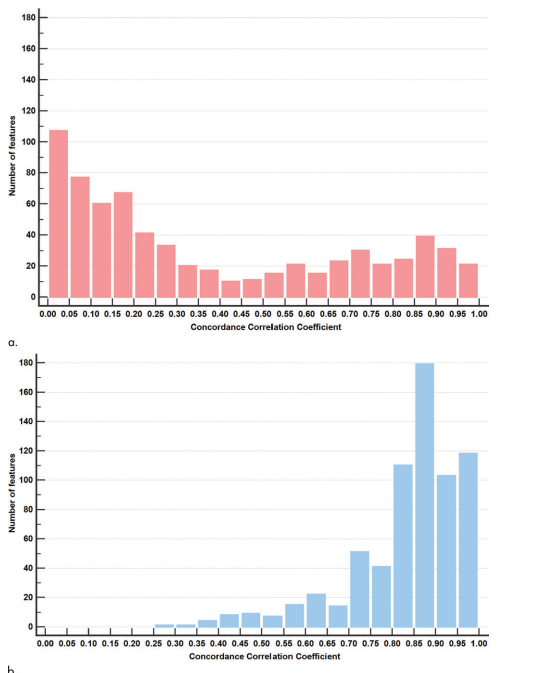
Figure 6: Results of changes in distributions of concordance correlation coefficient (CCC) between two readers with different kernels before and after applying image conversion (texture and wavelet features). (a) When the pulmonary nodule or mass was evaluated by different readers under different kernels of images, only 96 out of 683 texture and wavelet features were reproducible, showing CCC of 0.85 or higher, and most of the features showed CCC below 0.85 (left side deviation of the histogram, pink). (b) After the application of image conversion, 391 out of 683 texture and wavelet features showed CCC of 0.85 or higher under different readers and kernels, and the improvement in CCC was observed as a right shift of the CCC distribution histogram (blue). X-axis indicates the value of CCC, reproducibility of radiomic features, and Y-axis indicates the number of features in each range of CCC.
图 6:在应用图像转换前后,不同核下两位读者对纹理和小波特征的一致性相关系数(CCC)分布的变化结果。(a) 当肺部结节或肿块在不同核的图像下由不同读者进行评估时,仅有96个纹理和小波特征中的683个具有CCC为0.85或更高,大多数特征显示的CCC低于0.85(直方图的左偏,粉色)。(b) 在应用图像转换后,683个纹理和小波特征中的391个显示出不同读者和核下的CCC为0.85或更高,CCC的改善表现为CCC分布直方图向右移动(蓝色)。X轴表示CCC的值,放射组学特征的再现性,Y轴表示每个CCC范围内的特征数量。
Table
表
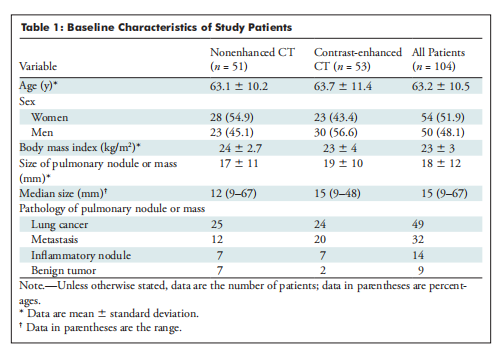
Table 1: Baseline Characteristics of Study Patients
表 1:研究患者的基线特征
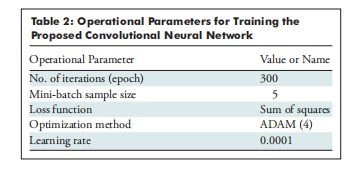
Table 2: Operational Parameters for Training the Proposed Convolutional Neural Network
表 2:训练所提出的卷积神经网络的操作参数
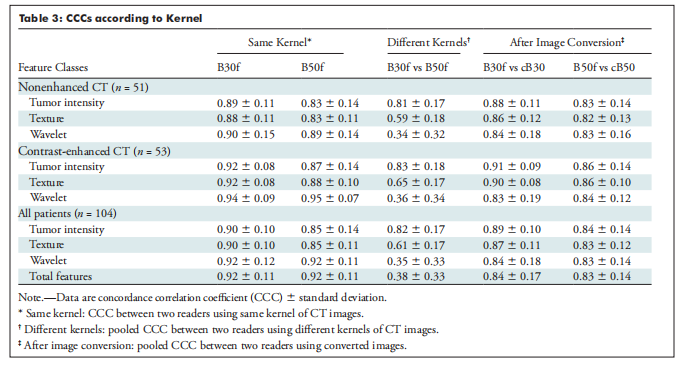
Table 3: CCCs according to Kernel
表 3:根据核的CCC值
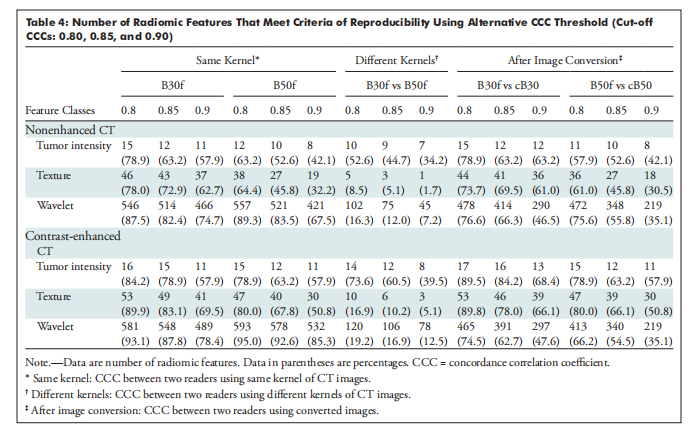
Table 4: Number of Radiomic Features That Meet Criteria of Reproducibility Using Alternative CCC Threshold (Cut-off CCCs: 0.80, 0.85, and 0.90)
表 4:满足替代CCC阈值(截断CCC:0.80、0.85和0.90)再现性标准的放射组学特征数量