Title
题目
Deep learning radiomics can predict axillary lymph node status in early-stage breast cancer
深度学习放射学特征可以预测早期乳腺癌中腋窝淋巴结的情况。
01
文献速递介绍
Accurate identification of axillary lymph node (ALN) involvement in patients with early-stagebreast cancer is important for determining appropriate axillary treatment options andtherefore avoiding unnecessary axillary surgery and complications. Here, we report deeplearning radiomics (DLR) of conventional ultrasound and shear wave elastography of breastcancer for predicting ALN status preoperatively in patients with early-stage breast cancer.Clinical parameter combined DLR yields the best diagnostic performance in predicting ALNstatus between disease-free axilla and any axillary metastasis with areas under the receiveroperating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.902 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.843, 0.961)in the test cohort. This clinical parameter combined DLR can also discriminate between lowand heavy metastatic burden of axillary disease with AUC of 0.905 (95% CI: 0.814, 0.996) inthe test cohort. Our study offers a noninvasive imaging biomarker to predict the metastaticextent of ALN for patients with early-stage breast cancer.
准确识别早期乳腺癌患者腋窝淋巴结(ALN)的受累情况对于确定适当的腋窝治疗选项至关重要,从而避免不必要的腋窝手术和并发症。在这里,我们报告了对于预测早期乳腺癌患者术前腋窝淋巴结(ALN)状况的深度学习放射学(DLR)应用于乳腺癌的常规超声和剪切波弹性成像。临床参数与DLR的结合在预测测试队列中疾病自由腋窝和任何腋窝转移之间的ALN状态方面表现出最佳的诊断性能,曲线下面积(AUC)为0.902(95%置信区间[CI]:0.843,0.961)。这种临床参数与DLR的结合也能够在测试队列中区分腋窝疾病的低和高转移负荷,AUC为0.905(95%CI:0.814,0.996)。我们的研究为早期乳腺癌患者预测腋窝淋巴结的转移程度提供了一种非侵入性成像生物标志物。
Method
方法
Patients. This prospective study was approved by Institutional Review Board ofSun Yat-sen University Cancer Center. The inclusion criteria included the followings: (a) women with US-suspected breast masses; (b) availability of clinicaldata; © patients who underwent breast surgery and sentinel lymph-node biopsy orALN dissection with curative intent. The exclusion criteria included the followings🙁a) preoperative therapy (resection biopsy, neoadjuvant radiotherapy or chemotherapy); (b) patients with multifocal lesions or bilateral disease; © massesdeeper than 3 cm in depth due to the attenuation of SWE or larger than 3.5 cm indiameter due to the limited width of the US probe; (d) unqualified 2D-SWEmeasurements, which means little or no shear wave signal was acquired in the ROIof SWE; (e) benign breast lesions or carcinoma in situ; (f) missing importanthistopathological results (immunohistochemical results or lymph-node results);(g) incomplete information or images. Verbal informed consent was obtained fromall patients.
患者。本前瞻性研究已获得中山大学肿瘤中心机构审查委员会的批准。纳入标准包括:(a)有超声检测到的乳腺肿块的女性;(b)具备临床数据;(c)接受了乳腺手术和具有治愈意图的哨兵淋巴结活检或腋窝淋巴结切除的患者。排除标准包括:(a)术前治疗(切除活检、新辅助放疗或化疗);(b)多发性病变或双侧病变的患者;(c)由于SWE信号衰减或由于超声探头宽度限制而深度大于3厘米或直径大于3.5厘米的肿块;(d)2D-SWE测量不合格,即在SWE感兴趣区域中获得了少量或没有剪切波信号;(e)良性乳腺病变或原位癌;(f)缺少重要的组织病理学结果(免疫组化结果或淋巴结结果);(g)信息或图像不完整。所有患者都获得了口头知情同意。
Results
结果
Baseline characters. Between January 2016 and April 2019, atotal of 1342 women with 1342 breast lesions was studied andfinally 584 women (mean age, 50 years; range, 26–83 years) with584 malignant breast lesions were enrolled for analysis. Figure 1shows the patient recruitment workflow. According to the resultsof SLND or ALN dissection, 337 had disease-free axilla (N0), 150had low metastatic burden of axillary disease (N+(1–2)) and 97had heavy metastatic burden of axillary disease (N+(≥3)).
基线特征。在2016年1月至2019年4月期间,共研究了1342名女性,其乳腺病变总数为1342个,最终有584名女性(平均年龄50岁,范围为26-83岁)患有584个恶性乳腺病变被纳入分析。图1显示了患者招募工作流程。根据SLND或ALN切除的结果,337例患者腋窝无病变(N0),150例患者腋窝疾病的转移负荷较低(N+(1-2)),97例患者腋窝疾病的转移负荷较重(N+(≥3))。
Conclusion
结论
Clinical parameter combined DLR on breast conventional US andSWE images provides a noninvasive and practical way for predicting the extent of ALN involvement preoperatively and havethe potential to determine appropriate axillary treatment optionsfor patients with early-stage breast cancer. Prospective multicenter validation is expected to acquire high-level evidence forclinical use in subsequent studies.
结合乳腺常规超声和SWE图像的临床参数与DLR结合提供了一种非侵入性且实用的方式,可以在术前预测腋窝淋巴结受累的程度,并有潜力确定早期乳腺癌患者适当的腋窝治疗选项。预期未来的多中心前瞻性验证研究将为临床应用提供高水平的证据支持。
Figure
图
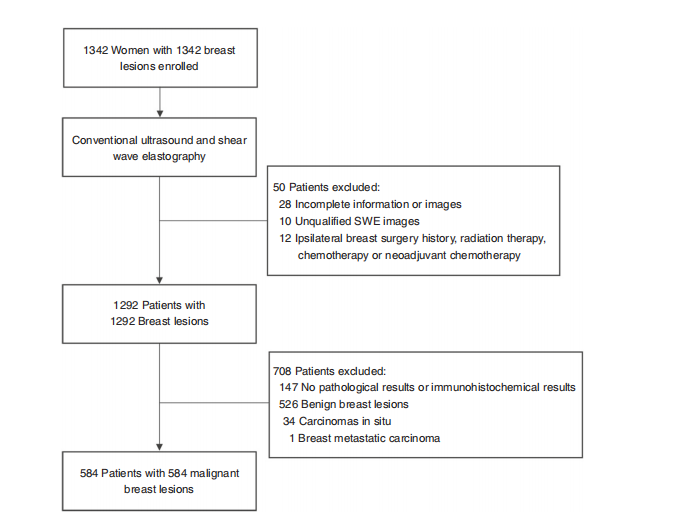
Fig. 1 Patient recruitment workflow. In total, 584 out of 1342 patients were included according to the selection criteria. The included patients wereexamined by conventional US and SWE, and had complete clinical information needed for the study
图1 患者招募工作流程。根据选择标准,共有1342名患者中的584名被纳入研究。被纳入研究的患者接受了常规超声和SWE检查,并且具有研究所需的完整临床信息。
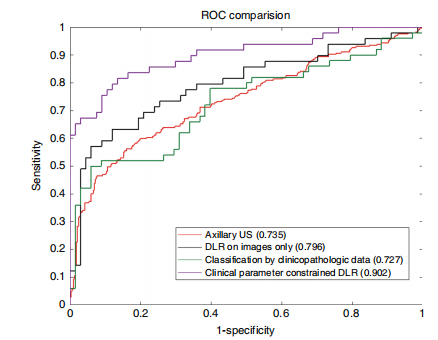
Fig. 2 Comparison of receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curvesbetween different models for predicting disease-free axilla (N0) and anyaxillary metastasis (N+(≥1)). DLR deep learning radiomics. Numbers inparentheses are areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves.Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
图2 不同模型预测疾病自由腋窝(N0)和任何腋窝转移(N+(≥1))的受试者工作特征曲线(ROC曲线)比较。DLR深度学习放射学。括号中的数字是受试者工作特征曲线下面积。源数据已提供,详见源数据文件。
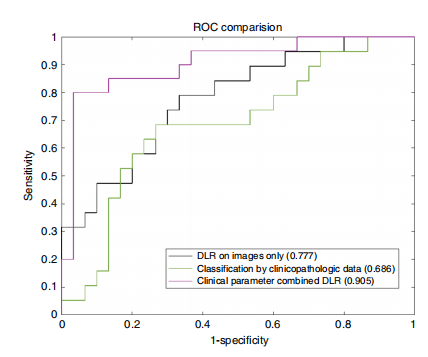
Fig. 3 Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves comparisonbetween different models for predicting low metastatic burden of axillarydisease (N+(1–2)) and heavy metastatic burden of axillary disease(N+(≥3)). DLR deep learning radiomics. Numbers in parentheses are areasunder the receiver operating characteristic curves. Source data are providedas a Source Data file
图3 不同模型预测腋窝疾病的低转移负荷(N+(1–2))和重转移负荷(N+(≥3))的受试者工作特征曲线(ROC曲线)比较。DLR深度学习放射学。括号中的数字是受试者工作特征曲线下面积。源数据已提供,详见源数据文件。
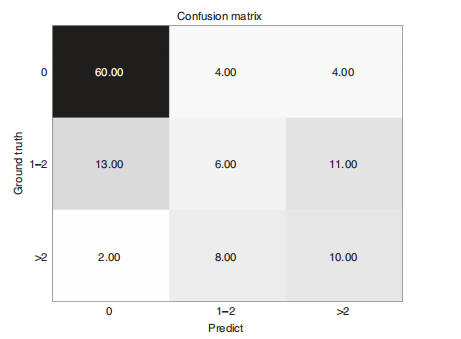
Fig. 4 The confusion matrix of predicting metastasis among disease-freeaxilla (N0), low metastatic burden of axillary disease (N+(1–2)) andheavy metastatic burden of axillary disease (N+(≥3)). Source data areprovided as a Source Data file.
图4 预测疾病自由腋窝(N0)、腋窝疾病的低转移负荷(N+(1–2))和腋窝疾病的重转移负荷(N+(≥3))之间的混淆矩阵。源数据已提供,详见源数据文件。
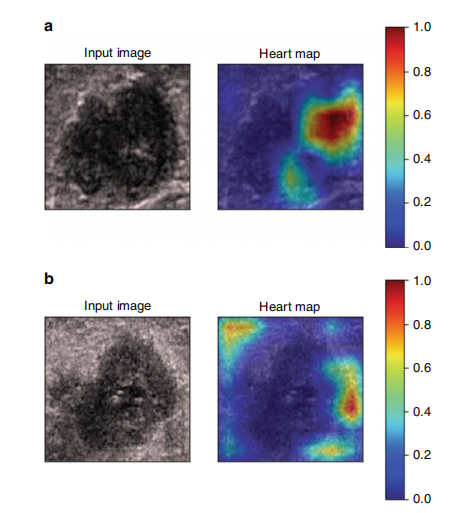
Fig. 5 Visualization of two patient examples. Each example shows thegray-scale US image and corresponding heart map, and the red regionrepresents a larger weight, which can be decoded by the color bar on theright. Image a shows that the low echo area inside the tumor is valuable forpredicting ALN status, while it is the tumor boundary for image b.
图5 两个患者示例的可视化。每个示例显示了灰度超声图像和相应的热力图,红色区域表示较大的权重,可以通过右侧的色条进行解码。图像a显示肿瘤内部的低回声区域对于预测腋窝淋巴结(ALN)状态是有价值的,而图像b则显示肿瘤边界是关键。
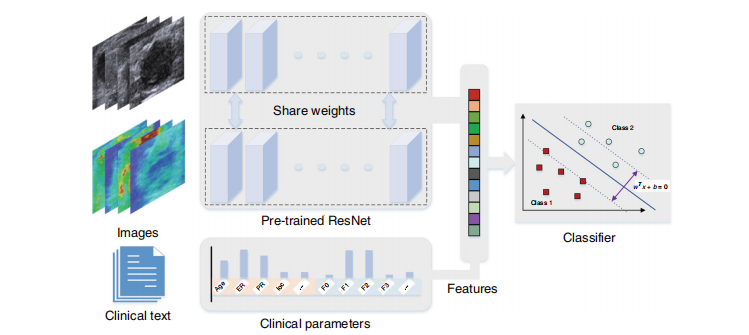
Fig. 6 The overall pipeline of the model. The parallel pre-trained ResNet model encodes the input images to features which be combined with clinicalparameters. Then the combined features be classified by an SVM model.
图6 模型的整体流程。并行预训练的ResNet模型将输入图像编码为特征,然后将这些特征与临床参数结合。接着,将结合后的特征通过SVM模型进行分类。
Table
表
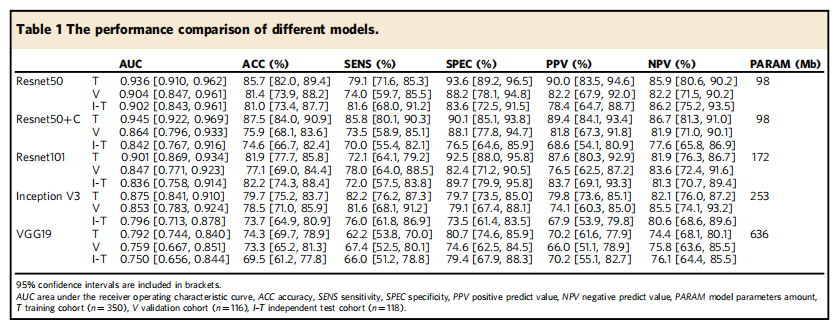
Table 1 The performance comparison of different models.
表1 不同模型的性能比较。
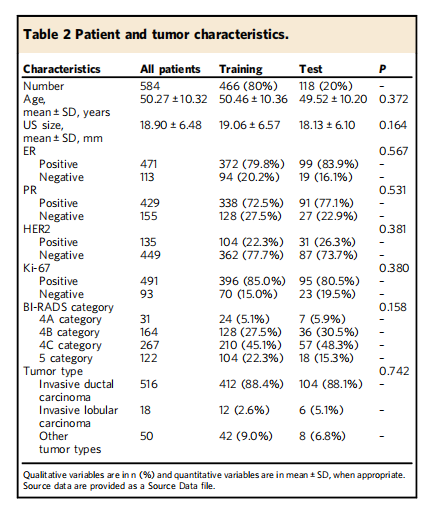
Table 2 Patient and tumor characteristics.
表2 患者和肿瘤特征
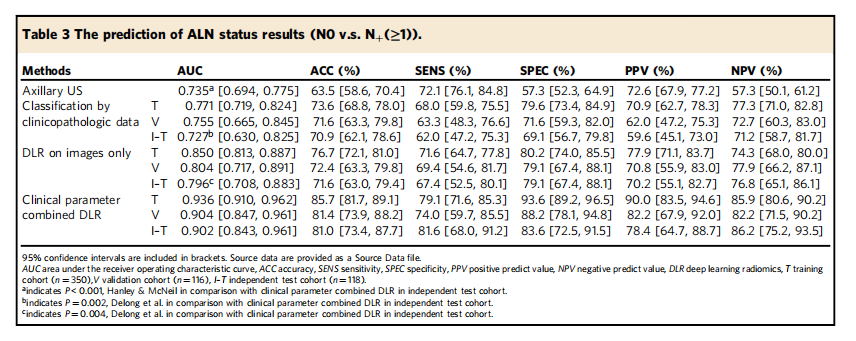
Table 3 The prediction of ALN status results (N0 v.s. N+(≥1))
表3 腋窝淋巴结状态预测结果(N0 vs. N+(≥1))
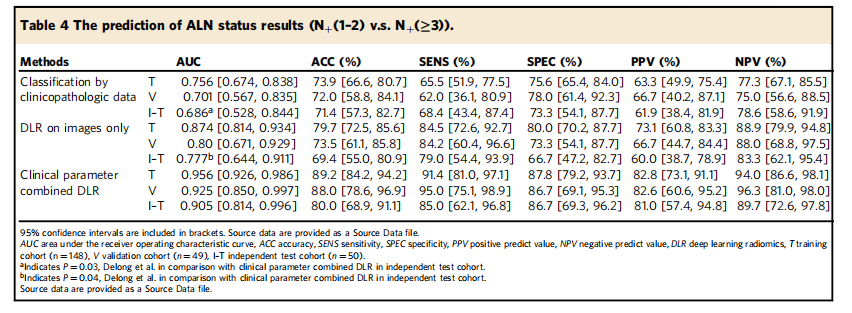
Table 4 The prediction of ALN status results (N+(1–2) v.s. N+(≥3)).
表4 腋窝淋巴结状态预测结果(N+(1–2) vs. N+(≥3))