Title
题目
Model-Driven Deep Learning Method forPancreatic Cancer Segmentation Basedon Spiral-Transformation
基于螺旋变换的胰腺癌分割模型驱动深度学习方法
01
文献速递介绍
胰腺癌是最致命的恶性肿瘤之一,其特点是诊断延迟、治疗困难和高死亡率。患者的总体五年生存率不到9%。在诊断和治疗过程中,胰腺癌的准确分割发挥着重要作用。Attiyeh等人基于准确分割的胰腺癌进行了3D建模,计算了肿瘤大小,提取了纹理特征,并为患者建立了生存预测模型。
磁共振引导的放射治疗在治疗局部晚期胰腺癌方面有潜在的优势。这种方法的关键步骤是轮廓绘制,即在每个治疗阶段开始时生成目标体积。然而,手动分割小尺寸和边界模糊的胰腺癌具有挑战性,因为获取像素级注释数据耗时且费力。鉴于阅读医学图像和进行早期诊断所需的高水平专业知识,数量有限的高级放射科医生面临着手动分割不断增加的病例数量的巨大压力。因此,有必要开发自动化和客观的胰腺癌分割算法,以克服人为错误并及时获得分割结果。
深度学习方法已广泛用于医学图像分割,并取得了显著的成功。然而,据我们所知,关于胰腺癌分割的研究有限。Zhu等人提出了一种搜索模型,即V-NAS,自动在每层之间搜索2D、3D或伪3D卷积,并确定最佳网络架构。该模型在胰腺癌CT数据集上获得了37.78 ± 32.12%的Dice相似性系数(DSC)。作者还提出了一种多尺度3D分割网络,用于胰腺癌CT扫描的粗到细分割。他们在136个胰腺癌样本上获得了最高的DSC,为57.3 ± 28.1%。Zhou等人提出了一个超配对网络(HPN),以整合多相信息。该模型包含了一个双路径网络,两个平行流进行了超连接以进行密集信息交换。HPN在DSC方面的表现为63.94 ± 22.74%。
Abstract-Background
摘要
Pancreatic cancer is a lethal malignant tumor
with one of the worst prognoses. Accurate segmentationof pancreatic cancer is vital in clinical diagnosis and treatment. Due to the unclear boundary and small size of cancers, it is challenging to both manually annotate and automatically segment cancers. Considering 3D infor mation utilization and small sample sizes, we propose a model-driven deep learning method for pancreatic cancer segmentation based on spiral transformation. Specifically,a spiral-transformation algorithm with uniform sampling was developed to map 3D images onto 2D planes while preserving the spatial relationship between textures, thus addressing the challenge in effectively applying 3D contex tual information in a 2D model. This study is the first to intro duce spiral transformationin a segmentation task to provide effective data augmentation, alleviating the issue of small sample size. Moreover, a transformation-weight-corrected module was embedded into the deep learning model to unify the entire framework. It can achieve 2D segmenta tion and corresponding 3D rebuilding constraint to over come non-unique 3D rebuilding results due to the uniform and dense sampling. A smooth regularization based on rebuilding prior knowledge was also designed to optimize segmentation results. The extensive experiments showed that the proposed method achieved a promising segmen tation performance on multi-parametric MRIs, where T2, T1, ADC, DWI images obtained the DSC of 65.6%, 64.0%, 64.5%, 65.3%, respectively. This method can provide a novel paradigm to efficiently apply 3D information and augment sample sizes in the development of artificial intelligence for cancer segmentation.
具有最糟糕预后之一的胰腺癌,准确的癌症分割在临床诊断和治疗中至关重要。由于癌症边界不清晰和体积小,手动注释和自动分割癌症都非常具有挑战性。考虑到3D信息的利用和小样本量,我们提出了一种基于螺旋变换的胰腺癌分割的模型驱动深度学习方法。具体来说,开发了一种带有均匀采样的螺旋变换算法,将3D图像映射到2D平面上,同时保持纹理间的空间关系,因此解决了在2D模型中有效应用3D上下文信息的挑战。这项研究首次在分割任务中引入螺旋变换,以提供有效的数据增强,缓解小样本量问题。此外,一个转换权重修正模块被嵌入到深度学习模型中,以统一整个框架。它可以实现2D分割和相应的3D重建约束,以克服由于均匀和密集采样导致的非唯一3D重建结果。基于重建先验知识的平滑正则化也被设计来优化分割结果。广泛的实验表明,提出的方法在多参数MRI上实现了有希望的分割性能,其中T2、T1、ADC、DWI图像分别获得了65.6%、64.0%、64.5%、65.3%的DSC。这种方法可以提供一个新的范式,有效地应用3D信息和增加样本量,在癌症分割的人工智能开发中。
Conclusions
结论
This study developed a combined spiral-transformation and model-driven deep learning method for pancreatic cancer segmentation. A novel spiral-transformation algorithm was developed to enable a 2D model to achieve 3D image seg mentation with affordable computational resources. It also provided various 2D-transformed images to realize an effective data augmentation for alleviating the problem of insufficient samples. Besides, a transformation-weight-corrected module was designed to combine with the 2D model in a unified framework for the 2D segmentation and 3D rebuilding. The extensive experiments conducted on internal multi-parametric MRI datasets and an external CT dataset demonstrated that the proposed method exhibits promising segmentation perfor mance with strong robustness and generality, while reaching a good balance between the performance and the computational resources. Overall, this combined spiral-transformation and model-driven segmentation scheme can serve as a new method for 3D cancer segmentation.
本研究开发了一种结合螺旋变换与模型驱动的深度学习方法用于胰腺癌分割。开发了一种新颖的螺旋变换算法,使2D模型能够以可承受的计算资源实现3D图像分割。它还提供了各种2D变换图像,以实现有效的数据增强,以缓解样本不足的问题。此外,设计了一个转换权重校正模块,与2D模型在统一框架中结合,用于2D分割和3D重建。在内部多参数MRI数据集和一个外部CT数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,所提出的方法展现出有希望的分割性能,具有强大的鲁棒性和普适性,同时在性能和计算资源之间达到了良好的平衡。总的来说,这种结合螺旋变换和模型驱动的分割方案可以作为一种新的3D癌症分割方法。
Method
方法
In this section, we introduce a model-driven deep learning method for 3D pancreatic cancer segmentation based on spiral transformation. Fig. 2 shows the transformation of a 3D image as input into a 2D plane using the spiral-transformation algorithm. A transformation-weight-corrected module was proposed to embed the 3D rebuilding process into the deep learning model and unify the segmentation framework of 2D segmentation and 3D rebuilding constraint. Moreover, a smooth regularization improved the rebuilding performance.
在本节中,我们介绍了一种基于螺旋变换的3D胰腺癌分割的模型驱动深度学习方法。图2展示了使用螺旋变换算法将3D图像作为输入转换为2D平面的过程。提出了一个转换权重校正模块,将3D重建过程嵌入到深度学习模型中,并统一了2D分割和3D重建约束的分割框架。此外,平滑正则化改进了重建性能。
Figure
图

Fig. 1. Example of MRI pancreatic cancer. The two images on the left are entire original images, whereas the two images on the right are enlarged regions. The cancer is closely surrounded by other tissues that have a similar intensity, and the boundary is unclear
图1. MRI胰腺癌的例子。左边的两幅图像是完整的原始图像,而右边的两幅图像是放大的区域。癌症被其他具有相似强度的组织紧密包围,且边界不清晰。

Fig. 2. Combined spiral-transformation and model-driven segmentation scheme for 3D segmentation
图2. 用于3D分割的螺旋变换与模型驱动分割方案的结合

Fig. 3.Examples of spiral transformation: (a) Coordinate system of spiral transformation, (b) Area density simulation, © Volume density simulation.
图3.螺旋变换的例子:(a) 螺旋变换的坐标系统, (b) 面密度模拟, © 体密度模拟。

Fig. 4.Examples of spiral transformation with different directions of coordinate systems for an identical MRI. The first to third rows show the spiral transformation with different directions, the transformed results, and the enlarged regions of the four identical areas, respectively
图4.相同MRI的不同坐标系统方向的螺旋变换示例。第一到第三行分别展示了不同方向的螺旋变换、变换结果和四个相同区域的放大区域。

Fig. 5. Simulation of non-unique 3D rebuilding results. Three blue points with non-integer coordinates are obtained using uniform and dense sampling. In the reverse transformation, these three points correspond to the same rebuilding 3D voxel, i.e., the red point. The pixels with the same color in I and K have the same 3D rebuilding voxels and weights.
图5. 非唯一3D重建结果的模拟。使用均匀且密集的采样得到三个非整数坐标的蓝点。在反向变换中,这三个点对应于同一个重建的3D体素,即红点。I和K中相同颜色的像素具有相同的3D重建体素和权重。

Fig. 6.Visualization segmentation examples of Spiral-ResUNet with three performance groups: (a) Excellent (DSC ≥ 0.80), (b) Good (0.60 ≤ DSC < 0.80), and © Poor (DSC < 0.60). For each case, the images from left to right are the entire original image, an enlarged region with reference truth in red and segmentation boundary in green, and the segmentation result with white DSC value for this slice, respectively. The red parts indicate correct segmentation (true positive), yellow parts indicate under segmentation (false negative), and blue parts indicate over segmentation (false positive).
图6.螺旋-ResUNet分割示例的可视化,分为三个性能组:(a) 优秀(DSC ≥ 0.80),(b) 良好(0.60 ≤ DSC < 0.80),和 © 较差(DSC < 0.60)。对于每个案例,从左到右的图像分别是完整的原始图像、带有参考真实情况(红色)和分割边界(绿色)的放大区域,以及带有此切片白色DSC值的分割结果。红色部分表示正确的分割(真阳性),黄色部分表示分割不足(假阴性),蓝色部分表示过度分割(假阳性)。

Fig. 7.Variation ratio of DSC with and without smooth regularization of Spiral-ResUNet. The x-axis represents the number of ten repeated experiments, and the y-axis represents the variation rate of the DSC after adding smooth regularization. T-test is used for statistical analysis.
图7.螺旋-ResUNet的DSC变异比率,包括使用和不使用平滑正则化。x轴代表重复实验的次数,y轴代表添加平滑正则化后DSC的变异率。使用T检验进行统计分析。
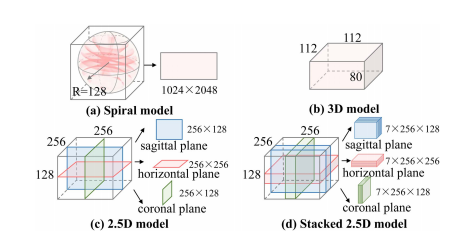
Fig. 8. Examples of different inputs. (a) The spiral model input is spiral transformation result which contains 3D spatial information. (b) The 3D model input is original 3D data. ©-(d) The inputs of 2.5D and stacked 2.5D model are the slices from the horizontal, coronal, and sagittal planes, which only contain information from three views.
图8. 不同输入的例子。(a) 螺旋模型输入是包含3D空间信息的螺旋变换结果。(b) 3D模型输入是原始3D数据。©-(d) 2.5D和堆叠2.5D模型的输入是来自水平面、冠状面和矢状面的切片,这些切片只包含三个视图的信息。

Fig. 9. Performance of four models under a small sample size setting.
图9. 在小样本设置下四个模型的性能。

Fig. 10. Reliability analysis of Spiral-ResUNet by repetitions of five-fold CV experiments.
图10. 通过重复五折交叉验证实验对螺旋-ResUNet的可靠性分析。

Fig. 11. Sensitivity analysis: (a) Relationship between the DSC variation rate and loss coefficient. The horizontal and vertical axes are μ and ν, respectively. (b) The relationship between the DSC variation rate and the origin coordinates of the spiral transformation. The x-, y-, and z-axes represent the percentage of the origin offset along the coronal, sagittal, and vertical axes, respectively. The higher the variation rate, the larger the size of the scatter.
图11. 敏感性分析:(a) DSC变异率与损失系数之间的关系。水平轴和垂直轴分别是μ和ν。(b) DSC变异率与螺旋变换原点坐标之间的关系。x轴、y轴和z轴分别代表沿冠状面、矢状面和垂直轴的原点偏移百分比。变异率越高,散点的大小越大。

Fig. 12. Performance of Spiral-ResUNet on the ADC, DWI, and T1w datasets, with 10 repetitions of the five-fold CV.
图12.在ADC、DWI和T1w数据集上,螺旋-ResUNet通过五折交叉验证的10次重复的性能。
Table
表
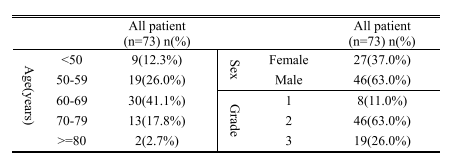
TABLE I theinfor on patints and pscreatic caner progessions
表I 患者及胰腺癌进展情况的信息

TABLE II segmentaion results of our method based on different backbone segmentaion netwprks
表II基于不同基础分割网络的我们方法的分割结果

TABLE III ablation experiments with backbone segmentaion networks
表III基础分割网络的消融实验
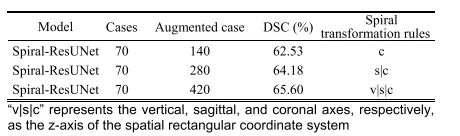
TABLE IV results spiral-resunet with different augmentation times
表IV不同增强次数下螺旋-ResUNet的结果

TABLE V evaluation performance of different inputs
表V不同输入的评估性能

TABLE VI comparison with other state-of-the-art segmentaion models
表VI与其他最先进分割模型的比较

TABLE VII theDSC (%) value when the origin point offset 40%-100% along x-and y-axes
表VII当原点沿X轴和Y轴偏移40%-100%时的DSC(%)值
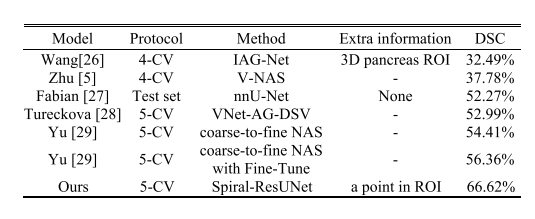
TABLE VIII revi state-of-the-art methods on msd pancreas cancer dataset
表VIII在MSD胰腺癌数据集上回顾最先进方法

TABLE IX reiew existing methods of pancreatic cancer segmentation
表IX回顾现有的胰腺癌分割方法