Title
题目
Deep Learning to Simulate Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI of Invasive Breast Cancer
深度学习模拟增强对比剂的乳腺癌MRI
01
文献速递介绍
Background: There is increasing interest in noncontrast breast MRI alternatives for tumor visualization to increase the accessibility of
breast MRI.
人们越来越感兴趣于非对比剂乳腺MRI替代方案,用于肿瘤可视化,以提高乳腺MRI的可及性。
Purpose: To evaluate the feasibility and accuracy of generating simulated contrast-enhanced T1-weighted breast MRI scans from precontrast MRI sequences in biopsy-proven invasive breast cancer with use of deep learning.
评估使用深度学习从未经对比增强的MRI序列生成模拟对比增强T1加权乳腺MRI扫描在经活检证实的侵袭性乳腺癌中的可行性和准确性。
Results
结果
Ninety-six MRI examinations in 96 women (mean age, 52 years ± 12 [SD]) were evaluated. The readers assessed all simulated MRI scans as having the appearance of a real MRI scan with tumor enhancement. Index mass sizes on real and simulated MRI scans demonstrated good to excellent agreement (intraclass correlation coefficient, 0.73–0.86; P < .001) without significant differences (mean differences, −0.8 to 0.8 mm; P = .36–.80). Almost all simulated MRI scans (84 of 88 [95%]) were considered of diagnostic quality (ratings of excellent, acceptable, or good). Quantitative analysis demonstrated strong similarity (structural similarity index, 0.88 ± 0.05), low voxel-wise error (symmetric mean absolute percent error, 3.26%), and Dice coefficient of enhancing tumor overlap of 0.75 ± 0.25.
评估了96名女性(平均年龄52岁±12 [SD])的96次MRI检查。读者评估所有模拟MRI扫描具有真实MRI扫描的外观和肿瘤增强。真实和模拟MRI扫描上的指数质量大小显示了良好到优秀的一致性(类内相关系数,0.73-0.86;P < .001)没有显著差异(平均差异,-0.8到0.8毫米;P = .36-.80)。几乎所有模拟MRI扫描(88中的84个[95%])被认为是诊断质量(优、可接受或良好的评级)。定量分析显示了强相似性(结构相似性指数,0.88 ± 0.05),低体素级误差(对称平均绝对百分比误差,3.26%),和增强肿瘤重叠的Dice系数为0.75 ± 0.25。
Methods
方法
Women with invasive breast cancer and a contrast-enhanced breast MRI examination that was performe for initial evaluation of the extent of disease between January 2015 and December 2019 at a single academic institution were ret rospectively identified. A three-dimensional, fully convolutional deep neural network simulated contrast-enhanced T1-weighted breast MRI scans from five precontrast sequences (T1-weighted non–fat-suppressed [FS], T1-weighted FS, T2-weighted FS, apparent diffusion coefficient, and diffusion-weighted imaging). For qualitative assessment, four breast radiologists (with 3–15 years of expe rience) blinded to whether the method of contrast was real or simulated assessed image quality (excellent, acceptable, good, poor,or unacceptable), presence of tumor enhancement, and maximum index mass size by using 22 pairs of real and simulated contrast enhanced MRI scans. Quantitative comparison was performed using whole-breast similarity and error metrics and Dice coefficient analysis of enhancing tumor overlap.
本研究回顾性地识别了在单一学术机构2015年1月至2019年12月间接受对比增强乳腺MRI检查的初始疾病范围评估的有侵袭性乳腺癌的女性。一个三维全卷积深度神经网络从五个预对比序列(非脂肪抑制的T1加权、脂肪抑制的T1加权、脂肪抑制的T2加权、表观扩散系数和扩散加权成像)模拟了对比增强的T1加权乳腺MRI扫描。为了定性评估,四位乳腺放射科医师(有3-15年经验)在盲测条件下评估了图像质量(优、可接受、良好、差或不可接受)、肿瘤增强的存在以及使用22对真实和模拟对比增强MRI扫描的最大指数质量大小。定量比较使用整个乳腺的相似性和错误指标以及增强肿瘤重叠的Dice系数分析进行。
Conclusion
结论
It is feasible to generate simulated contrast-enhanced breast MRI scans with use of deep learning. Simulated and real contrast-enhanced MRI scans demonstrated comparable tumor sizes, areas of tumor enhancement, and image quality without significant qualitative or quantitative differences.
使用深度学习生成模拟的对比增强乳腺MRI扫描是可行的。模拟和真实的对比增强MRI扫描在肿瘤大小、肿瘤增强区域和图像质量方面显示了可比性,没有显著的定性或定量差异。
Fig
图
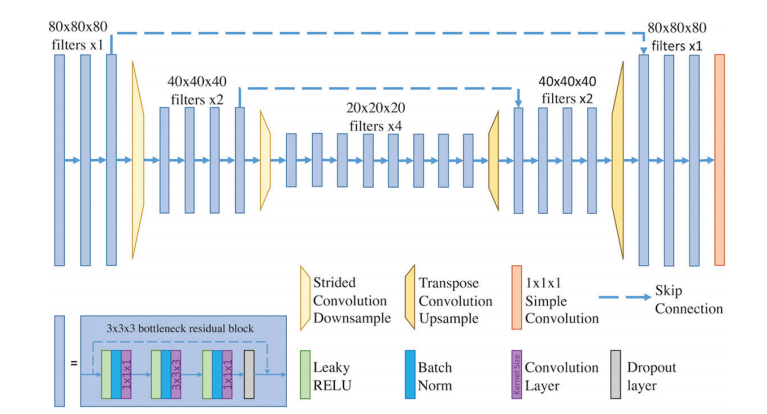
Figure 1: Schematic of the deep learning fully convolutional neural network architecture. The deep learning convolutional neural network was trained on 80 × 80 × 80–voxel training patches from preprocessed images. Our network architecture consisted of a deep learning convolutional neural network with three-dimensional convolution bottleneck residual blocks (blue blocks), strided convolution downsampling (yellow trapezoids), transpose convolution upsampling (orange trapezoids), and long-range skip connections with feature concatenation (dashed lines). A 1 × 1 × 1 convolutional layer (orange block) mapped features to final output image patches. A schematic of the 3 × 3 × 3 bottleneck residual block is included (bottom left). RELU = rectified linear unit.
图1:深度学习全卷积神经网络架构示意图。深度学习卷积神经网络是在预处理图像的80 × 80 × 80体素训练补丁上训练的。我们的网络架构由一个深度学习卷积神经网络组成,包括三维卷积瓶颈残差块(蓝色块)、跨步卷积下采样(黄色梯形)、转置卷积上采样(橙色梯形)以及长距离跳跃连接与特征连接(虚线)。一个1 × 1 × 1卷积层(橙色块)将特征映射到最终输出图像补丁。包括了一个3 × 3 × 3瓶颈残差块的示意图(左下角)。RELU = 线性整流单元。
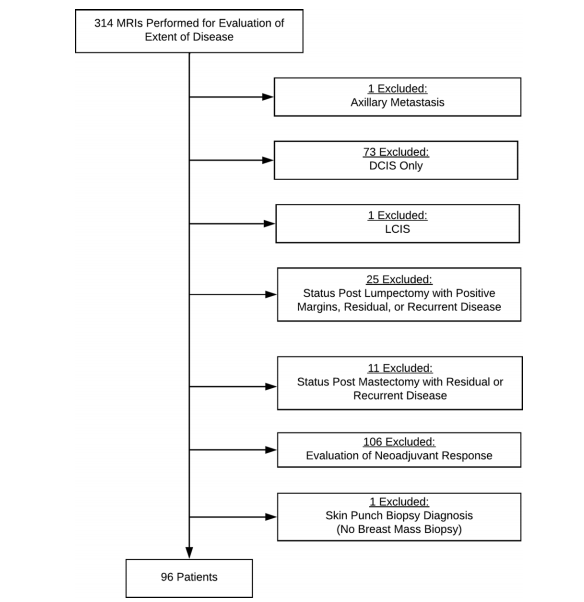
Figure 2: Study flowchart. DCIS = ductal carcinoma in situ, LCIS = lobular carcinoma in situ.
图2: 研究流程图。DCIS = 原位导管癌,LCIS = 原位小叶癌。
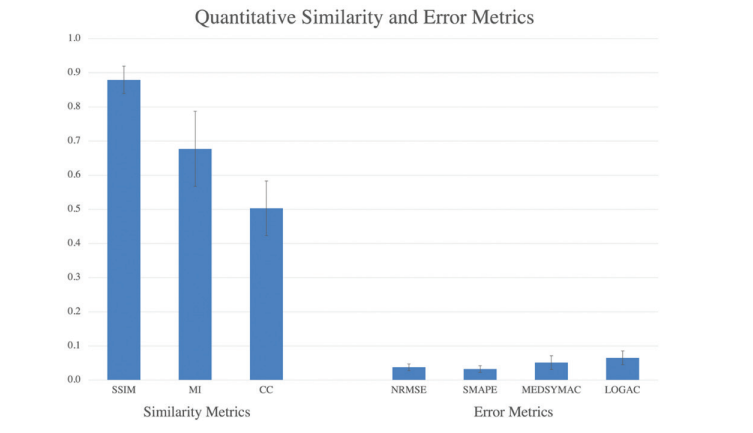
Figure 3: Bar graph shows quantitative similarity and error metrics for real versus simulated contrast-enhanced MRI across the whole breast. Overall, there was strong similarity and low voxel-wise error across the whole breast. Similarity metrics included structural similarity index (SSIM), histogram mutual information (MI), and normalized neighborhood cross correlation (CC). The four error metrics were normalized root mean square error (NRMSE), symmetric mean absolute per cent error (SMAPE), median symmetric accuracy (MEDSYMAC), and log accuracy ratio (LOGAC). Error bars represent the SD above and below the mean.
图3: 条形图显示了整个乳腺的真实对比增强MRI与模拟对比增强MRI之间的定量相似性和误差指标。总体而言,整个乳腺具有强相似性和低体素级误差。相似性指标包括结构相似性指数(SSIM)、直方图互信息(MI)和标准化邻域交叉相关性(CC)。四个误差指标为标准化均方根误差(NRMSE)、对称平均绝对百分比误差(SMAPE)、中位对称准确度(MEDSYMAC)和对数准确率比(LOGAC)。误差条代表平均值以上和以下的标准差。
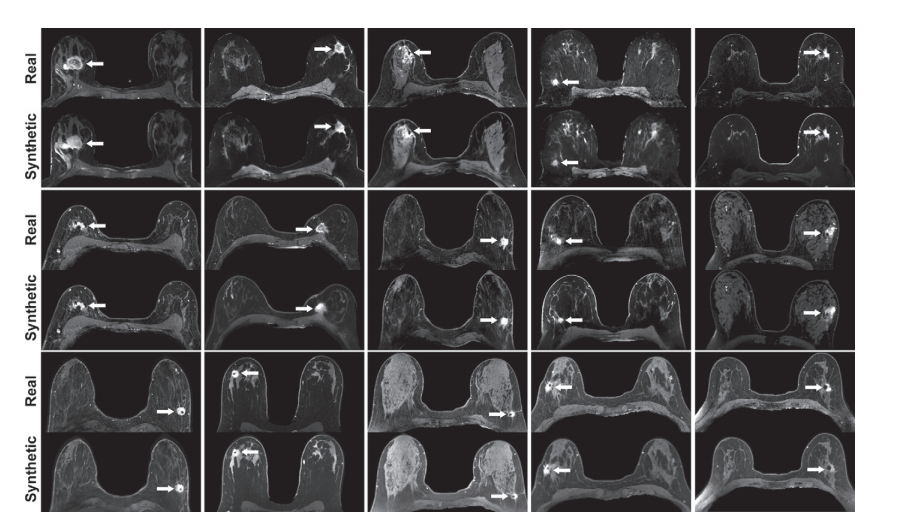
Figure 4: Real versus simulated (ie, synthetic) contrast-enhanced T1-weighted axial breast MRI scans of patients with invasive breast cancer. Pairs of real and simulated contrast-enhanced breast MRI scans from 15 patients with invasive breast cancer (arrows). Intrathoracic and extramammary structures were masked in all images.
图4: 侵袭性乳腺癌患者的真实对比增强T1加权轴向乳腺MRI扫描与模拟(即合成)对比增强T1加权轴向乳腺MRI扫描。15位侵袭性乳腺癌患者的真实和模拟对比增强乳腺MRI扫描对(箭头)。所有图像中的胸内和乳腺外结构均被遮挡。
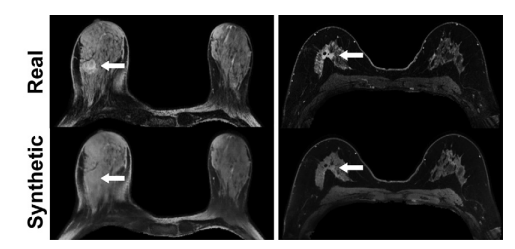
Figure 5: MRI scans in a 55-year-old woman with right invasive ductal carcinoma (left panel) and a 67-year-old woman with right invasive ductal carcinoma (right panel) show failed enhance ment of the index lesion (arrow) on the simulated (ie, synthetic) contrast-enhanced MRI scans.
图5: 一位55岁女性(左侧面板)和一位67岁女性(右侧面板)的右侧侵袭性导管癌MRI扫描显示,在模拟(即合成)的对比增强MRI扫描中指数病灶(箭头)未显示增强。
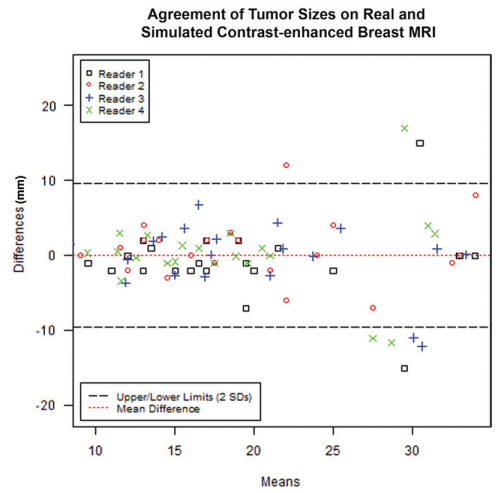
Figure 6: Agreement of tumor sizes on real and simulated contrast-enhanced breast MRI scans. Modified Bland-Altman plot shows agreement of tumor sizes on real versus simulated contrast enhanced breast MRI scans. The dotted red line and black dashed lines represent bias and limits of agreement lines (2 SDs above and below the mean), respectively.
图6: 真实和模拟对比增强乳腺MRI扫描上肿瘤大小的一致性。 修改后的布兰德-奥特曼图显示了真实与模拟对比增强乳腺MRI扫描上肿瘤大小的一致性。红色点线和黑色虚线分别代表偏差和一致性限度线(平均值以上和以下2个标准差)。
Table
1
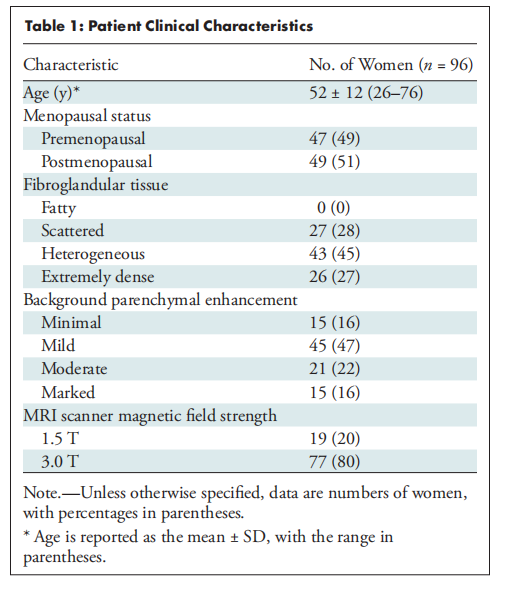
Table 1: Patient Clinical Characteristics
表1: 患者临床特征
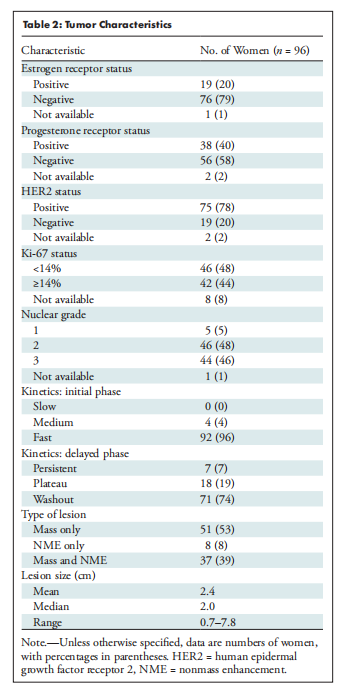
Table 2: Tumor Characteristics
表2: 肿瘤特征
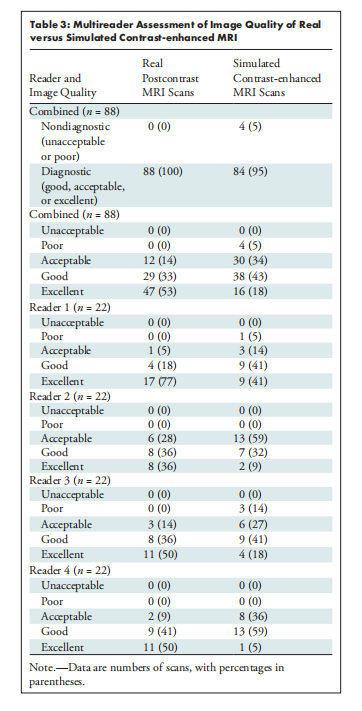
Table 3: Multireader Assessment of Image Quality of Real versus Simulated Contrast-enhanced MRI
表3: 多读者评估真实对比增强MRI与模拟对比增强MRI的图像质量