01
文献速递介绍
在2019年底,一种称为2019冠状病毒病(COVID-19)的新型冠状病毒肺炎出现,迅速成为全球性大流行。感染COVID-19可以引起肺部气囊发炎,导致胸膜积液,这可能使患者经历呼吸困难和其他类似流感的症状,如发热和咳嗽,同时影响多个组织和器官。新冠病毒能够建立人与人之间的传播,并在全世界迅速传播。它对世界各国的医疗卫生系统和经济活动产生了巨大影响。同时,如何保护人类的健康和生命安全也将经受严峻考验目前,临床上诊断肺部疾病的医学影像学方法主要包括X线、计算机断层扫描(CT)和磁共振成像(MRI)。由于价格相对便宜,成像质量较好,X线和CT已成为主要的检查方法。然而,基于X线和CT图像的人工分析和诊断过程对专业知识的依赖性较高,图像特征的分析需要较长时间。通过算法处理,利用深度学习技术可以自动将视觉图像信息抽象成相关特征信息,进行端到端的自动分类。与计算机视觉领域的传统图像处理算法相比,深度学习算法抛弃了手工提取特征的繁琐过程,通过输入到输出的映射直接获得检测结果。使用深度学习算法对CT上的肺炎进行分类,在一定程度上减少了误诊和漏诊,也为缺乏放射科医生的偏远地区提供了专业的分类技术。基于GAN的医学图像翻译算法是一种条件生成方法,将图像和疾病标签信息一起作为条件约束翻译生成过程,旨在完成一种类型的医学图像到另一种类型的医学图像的转换。根据翻译模型中涉及转换的图像域的数量,可分为双域图像翻译模型和多域图像翻译模型,利用深度神经网络寻找两个域图像或多个域图像之间迁移产生的映射关系,CycleGAN[7]和StarGAN[8]等翻译模型已被证明在双域和多域图像翻译中表现良好。基于生成对抗网络的医学图像翻译方法可以有效生成合成所需的医学图像,解决标注数据的稀缺问题,对后续基于深度神经网络的疾病分类和网络性能的提升具有重要的价值和意义。通过分析研究发现,基于GAN的医学图像翻译方法仍存在一些问题,如现有图像翻译模型对现有数据利用不足、注意力不强、关键点转移和生成能力不足、生成图像数量不足、细节特征缺乏等问题限制了合成图像在基于深度学习的肺部图像分类网络中的应用,根本原因是图像生成过程中对网络缺乏约束。针对上述问题提出新思路,为网络建立关键迁移分支,并施加特征约束,以保证翻译模型合成图像的能力,提高真实性和多样性。基于CT图像数据集,完成了正常无病图像和肺炎图像的转换和生成,验证了合成图像数据扩展用于肺炎分类的有效性,体现了基于生成对抗网络的医学图像翻译方法的重要价值。而且,合成的医学图像并非来自真实的患者,因此增强后的数据集可以在不侵犯个人隐私的情况下提供给医院以外的医学图像研究团队和研究学者,让更多的研究者可以开展深度学习医学研究
Title
题目
Multi-domain medical image translation generation for lung image classification based on generative adversarial networks
基于生成对抗网络的肺部图像分类的多域医学图像翻译生成
Methods
方法
This paper proposes a medical image multi-domain translation algorithm MI-GAN based on the key migration branch. After the actual analysis of the imbalanced medical image data, the key target domain images are selected, the key migration branch is established, and a single generator is used to complete the medical image multi-domain translation. The conversion between domains ensures the attention performance of the medical image multi-domain translation model and the quality of the synthesized images. At the same time, a lung image classification model based on synthetic image data augmentation is proposed. The synthetic lung CT medical images and the original real medical images are used as the training set together to study the performance of the auxiliary diagnosis model in the classification of normal healthy subjects, and also of the mild and severe COVID-19 patients.
本文提出了一种基于关键迁移分支的医学图像多域翻译算法MI-GAN。在实际分析了不平衡的医学图像数据后,选择了关键目标域图像,建立了关键迁移分支,并使用单个生成器完成医学图像多域翻译。域之间的转换保证了医学图像多域翻译模型的注意力性能和合成图像的质量。同时,提出了一种基于合成图像数据增强的肺部图像分类模型。
Results
结果
Based on the chest CT image dataset, MI-GAN has completed the mutual conversion and generation of normal lung images without disease, viral pneumonia and Mild COVID-19 images. The synthetic images GAN-test and GAN-train indicators reached, respectively 92.188% and 85.069%, compared with other generative models in terms of authenticity and diversity, there is a considerable improvement. The accuracy rate of pneumonia diagnosis of the lung image classification model is 93.85%, which is 3.1% higher than that of the diagnosis model trained only with real images; the sensitivity of disease diagnosis is 96.69%, a relative improvement of 7.1%. 1%, the specificity was 89.70%; the area under the ROC curve (AUC) increased from 94.00% to 96.17%.
基于胸部CT图像数据集,MI-GAN完成了无病正常肺部图像、病毒性肺炎图像和轻度COVID-19患者图像的相互转换和生成,合成图像GAN-test和GAN-train指标分别达到92.188%和85.069%,与其他生成模型相比在真实性和多样性方面有相当大的提升,肺部图像分类模型的肺炎诊断准确率为93.85%,比仅用真实图像训练的诊断模型高3.1%;疾病诊断的敏感度为96.69%,相对提升7.1%.1%,特异度为89.70%;ROC曲线下面积(AUC)从94.00%提升至96.17%。
Conclusions
结论
In this paper, a multi-domain translation model of medical images based on the key transfer branch is proposed, which enables the translation network to have key transfer and attention performance. It is verified on lung CT images and achieved good results. The required medical images are synthesized by the above medical image translation model, and the effectiveness of the synthesized images on the lung image classification network is verified experimentally
本文提出了一种基于关键转移分支的医学图像多域翻译模型,使翻译网络具有关键转移和注意力性能,在肺CT图像上进行了验证,取得了较好的效果。通过上述医学图像翻译模型合成了所需的医学图像,并实验验证了合成图像在肺部图像分类网络上的有效性。
Figure
图
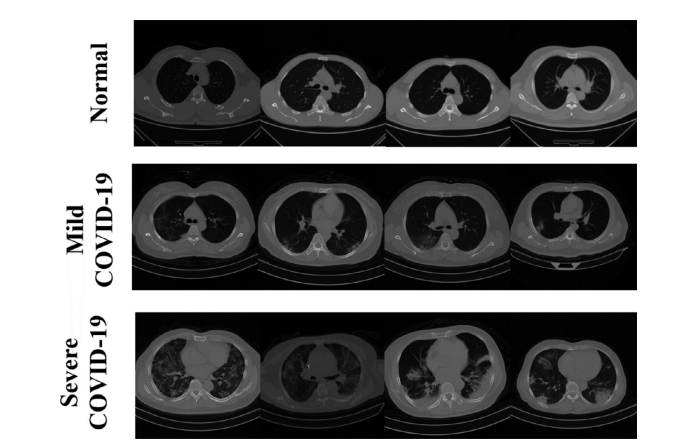
Fig. 1. Partial sample of the dataset.
图1. 数据集的部分样本。
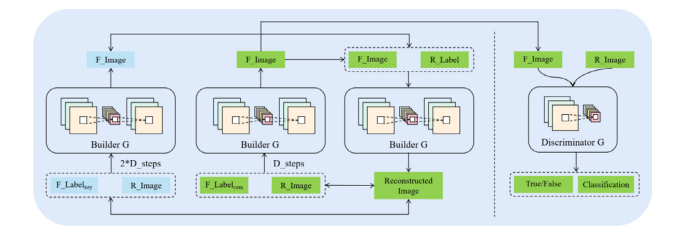
Fig. 2. The overall structure of the multi-domain translation model MI-GAN.
图2. 多域翻译模型MI-GAN的总体结构。
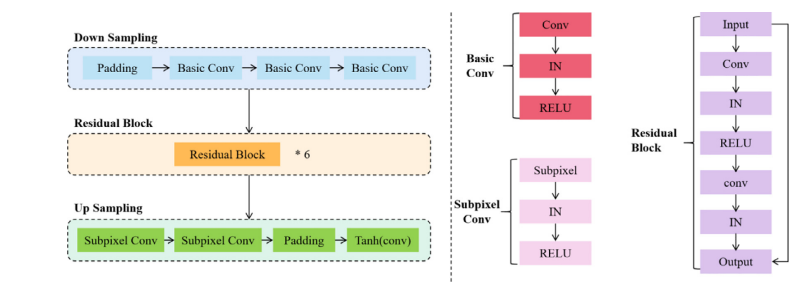
Fig. 3. Generator network structure diagram.
图3. 生成器网络结构图。
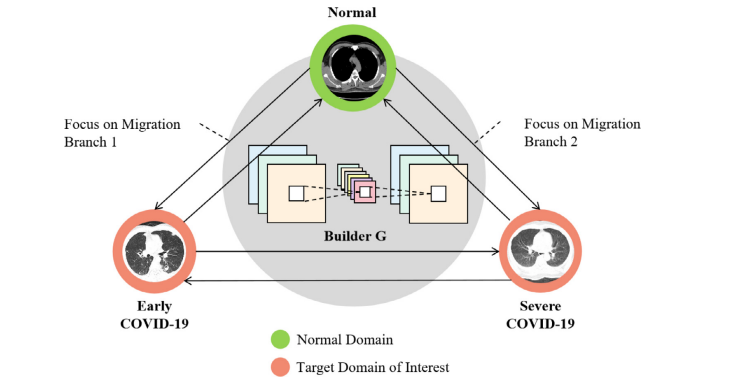
Fig. 4. Schematic diagram of MI-GAN key migration branch structure
图4. MI-GAN关键迁移分支结构示意图。
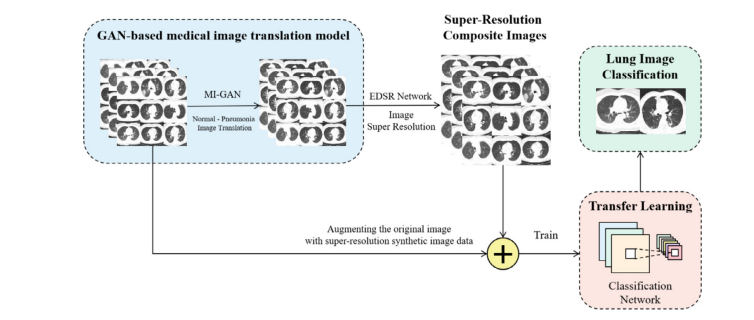
Fig. 5. Structure diagram of lung image classification model based on synthetic image data augmentation.
图5. 基于合成图像数据增强的肺部图像分类模型结构图。
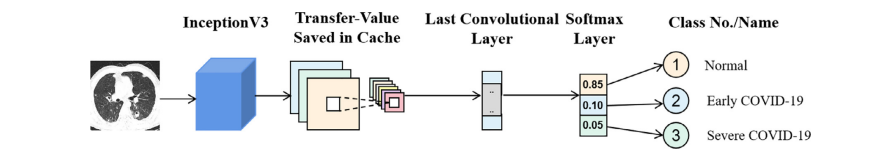
Fig. 6. Schematic diagram of transfer learning of InceptionV3 model
图6. InceptionV3模型迁移学习的示意图。
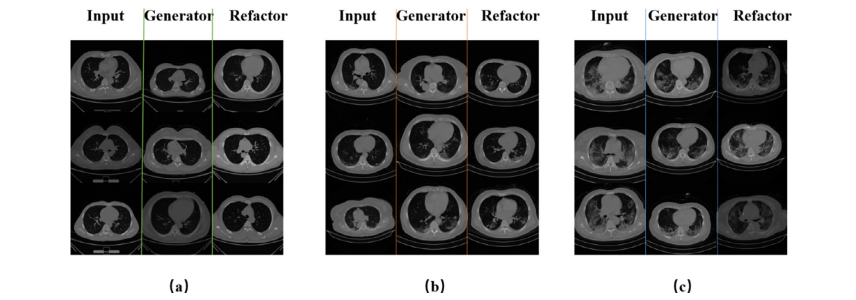
Fig. 7. MI-GAN single attribute test results based on (a) Normal, (b) EarlyMild COVID-19 and © Severe COVID-19.
图7. 基于(a) 正常,(b) 早期轻症COVID-19和© 重症COVID-19的MI-GAN单属性测试结果。
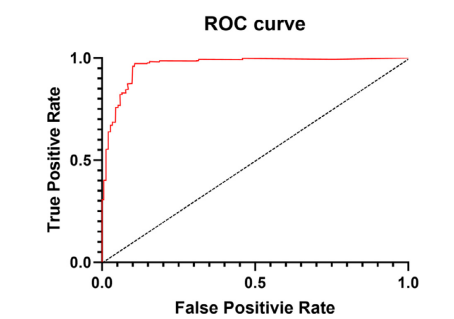
Fig. 8. ROC curves of viral and MildCOVID-19.
图8. 病毒性和轻症COVID-19的ROC曲线。
Table
表
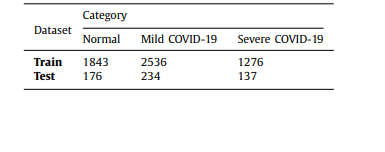
Table 1 The composition of real image dataset of lung image classification network
表1 肺部图像分类网络真实图像数据集的组成
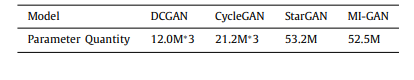
Table 2 Comparison of parameters of generative models
表2 生成模型参数比较
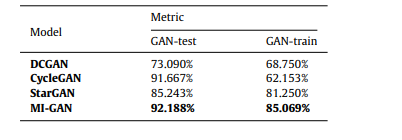
Table 3 Comparison of metrics between generative models based on GAN-test and GAN-Train.
表3 基于GAN-test和GAN-Train的生成模型之间的指标比较。
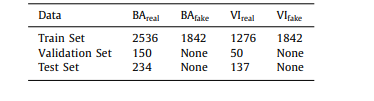
Table 4 Index comparison between GAN-test and Gan-train of the generated model.
表4 生成模型的GAN-test和Gan-train之间的指标比较。
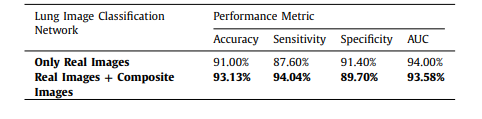
Table 5 Classification results of lung images.
表5 肺部图像分类结果。