Title
题目
Artificial intelligence-aided CT segmentation for body composition analysis: a validation study
人工智能辅助的CT分割用于体成分分析:一项验证研究
Abstract -Background
摘要-背景
Body composition is associated with survival outcome in oncological patients, but it is not routinely calculated. Manual segmentation of subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) and muscle is time-consuming and therefore limited to a single CT slice. Our goal was to develop an artificial-intelligence (AI)-based method for automated quantification of three-dimensional SAT and muscle volumes from CT images.
体成分与肿瘤患者的存活结果有关,但通常不会进行常规计算。皮下脂肪组织(SAT)和肌肉的手动分割既耗时又因此仅限于单个CT切片。我们的目标是开发一种基于人工智能(AI)的方法,用于从CT图像中自动量化三维SAT和肌肉体积。
Methods
方法
Ethical approvals from Gothenburg and Lund Universities were obtained. Convolutional neural networks were trained to segment SAT and muscle using manual segmentations on CT images from a training group of 50 patients. The method was applied to a separate test group of 74 cancer patients, who had two CT studies each with a median interval between the studies of 3 days. Manual segmentations in a single CT slice were used for comparison. The accuracy was measured as overlap between the automated and manual segmentations.
从哥德堡和隆德大学获得了伦理批准。使用来自50名患者训练组的CT图像上的手动分割,训练了卷积神经网络来分割SAT和肌肉。该方法应用于另一个由74名癌症患者组成的测试组,这些患者每人进行了两次CT检查,两次检查之间的中位间隔为3天。用单个CT切片中的手动分割进行了比较。准确性通过自动和手动分割之间的重叠来测量。
Results
结果
The accuracy of the AI method was 0.96 for SAT and 0.94 for muscle. The average differences in volumes were significantly lower than the corresponding differences in areas in a single CT slice: 1.8% versus 5.0% (p < 0.001) for SAT and 1.9% versus 3.9% (p < 0.001) for muscle. The 95% confidence intervals for predicted volumes in an individual subject from the corresponding single CT slice areas were in the order of ± 20%.
AI方法的准确性对于SAT为0.96,对于肌肉为0.94。平均体积差异显著低于单个CT切片中相应面积的差异:对于SAT为1.8%对比5.0%(p < 0.001),对于肌肉为1.9%对比3.9%(p < 0.001)。在单个受试者中,根据相应单个CT切片面积预测体积的95%置信区间大约为±20%。
Conclusions
结论
The AI-based tool for quantification of SAT and muscle volumes showed high accuracy and reproducibility and provided a body composition analysis that is more relevant than manual analysis of a single CT slice.
用于SAT和肌肉体积量化的基于AI的工具展现了高准确性和可重复性,并提供了比单个CT切片的手动分析更具相关性的体成分分析。
Figure
图
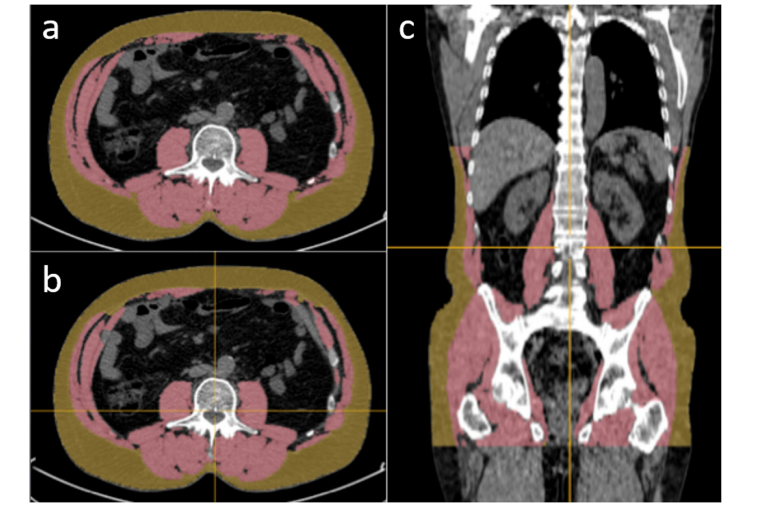
Fig. 1 Manual and AI-based segmentations of SAT and muscle. Left: segmentation on a CT slice at L3 level: manual (a) and AI-based (b). Coronal slice showing the AI-based 3D segmentation from T11 to the hip bone ©. Measurements: manual areas, 186 cm2 (SAT) and 170 cm2 (muscle); AI-based areas, 184 cm2 (SAT) and 158 cm2 (muscle); AI-based volumes 6,832 cm3 (SAT) and 8,253 cm3 (muscle). AI Artificial intelligence, SAT Subcutaneous fat
图1 SAT和肌肉的手动和基于AI的分割。左侧:L3水平的CT切片上的分割:手动(a)和基于AI的(b)。冠状切片展示了从T11到髋骨的基于AI的3D分割(c)。测量:手动面积,186平方厘米(SAT)和170平方厘米(肌肉);基于AI的面积,184平方厘米(SAT)和158平方厘米(肌肉);基于AI的体积6832立方厘米(SAT)和8253立方厘米(肌肉)。AI人工智能,SAT皮下脂肪。
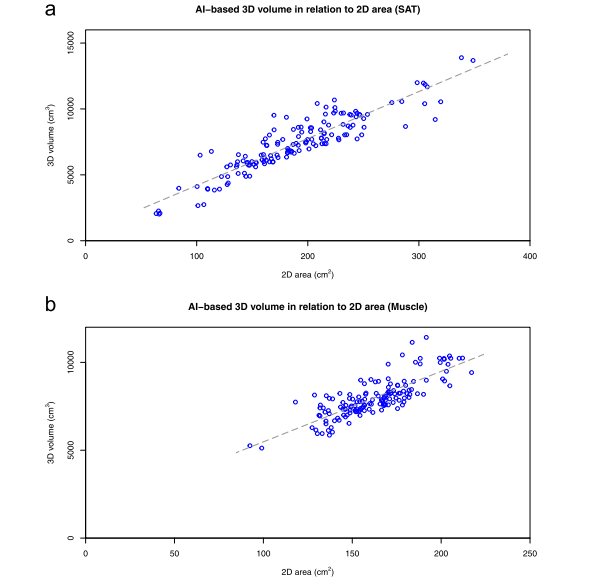
Fig. 2 Relation between AI-based 3D volume and L3 slice 2D area for SAT (a) and muscle (b) for 148 computed tomography studies in 74 patients. 2D Two-dimensional, 3D Three-dimensional, AI Artificial intelligence, SAT Subcutaneous fat
图2 在74名患者的148个计算机断层扫描研究中,基于AI的3D体积与L3切片2D面积之间的关系,针对SAT(a)和肌肉(b)。2D 二维,3D 三维,AI 人工智能,SAT 皮下脂肪。
Table
表
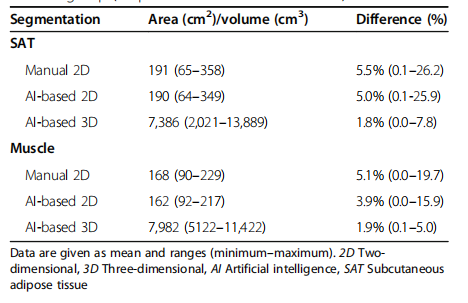
Table 1 Subcutaneous adipose tissue and muscle areas and volumes calculated from manual and AI-based segmentations in the test group (74 patients and two studies each)
表1 测试组(74名患者,每人进行两次研究)中的皮下脂肪组织和肌肉面积及体积,根据手动和基于AI的分割计算得出