01
文献速递介绍
淋巴瘤包括多种类型的血液系统恶性肿瘤,包括超过 80 种成熟的淋巴瘤实体,根据细胞起源分为三大类别,即 B 细胞、T 细胞或自然杀手/T 细胞淋巴瘤。作为最常见的淋巴瘤类型,B 细胞淋巴瘤可以进一步分类为霍奇金淋巴瘤(HL)和非霍奇金淋巴瘤(NHL,占 90% 的病例)。HL 是一种罕见的 B 细胞恶性肿瘤,其中大多数(90%)病例归因于 HL(经典霍奇金淋巴瘤,cHL),其特征是 Hodgkin 和毛囊淋巴瘤(FL)分别代表最常见的侵袭性和惰性非霍奇金淋巴瘤(NHL)。霍奇金淋巴瘤(HL)是青少年和年轻成年人(15至29岁)中最常诊断的癌症之一,而非霍奇金淋巴瘤(NHL)则更常见于儿童 。多年来,淋巴瘤的治疗有所改进。放射治疗、化疗、免疫治疗、自体造血细胞移植或这些治疗的组合,可能是基于肿瘤的病理组织学和分期的淋巴瘤管理选择 。治疗前或治疗期间的功能成像可以帮助指导进一步的管理选择,取决于空间异质性以及恶性肿瘤的生物学、病理学和代谢状态。
为了精确调整个体治疗方案,需要考虑影像学方法以最佳化视觉化分期和对治疗的反应,尤其是那些能评估肿瘤的分子和生物学过程的方法,超越了形态学特征。具体来说,2-脱氧-2-[18F] 氟-D-葡萄糖正电子发射断层扫描([18F] FDG PET/CT)已被证明是一种有效且广泛应用于淋巴瘤分期和评估的成像方式 。它对检测基于其磷酸化形式在恶性细胞中积累的葡萄糖代谢的区域差异具有高灵敏度,这是由于沃尔伯格效应 。基线[18F] FDG PET/CT 允许通过全身成像绘制初始肿瘤部位,这对于识别在形态学上无变化的正常大小淋巴结和淋巴外部位(如骨髓)的恶性肿瘤特别有用 。此外,[18F] FDG PET/CT 在淋巴瘤的诊断、分期、治疗分层之外的预后评估中可能扮演重要角色。这种模式最常用的半定量参数包括标准化摄取值(SUV)、总代谢肿瘤体积(MTV)和总病变糖酵解(TLG)。
然而,这些指标仅提供非常基本的成像特征,未能捕捉肿瘤异质性。这一限制代表了恶性肿瘤治疗中的一个重大挑战。
在过去几年中,影像组学的发展在实践范围内提供了潜在的影响,包括诊断、治疗规划和预后,从而推动了精准医疗的进步 。影像组学是一种使用复杂的计算机算法从临床环境中常规获得的图像中提取大量数据的方法,揭示了如何从不同成像模式中派生出肿瘤特征 。这种模式能提供对肿瘤生物学更深入的理解,通过生成基于影像的生物标记物更好地协助临床决策。在淋巴瘤中,放射组学在区分淋巴瘤与其他肿瘤、治疗反应和预后方面显示出前景。例如,[18F] FDG PET/CT 成像模式用于协助快速有效的治疗。此外,通过成像探针的创新,可以获得个体的结构、功能和分子变化 。使用更具体的探针的 PET 成像,如 [18F] FLT、[62Cu] ATSM 和 [68Ga] FAPI,可能使淋巴瘤特征和负荷的更精确表征和评估成为可能。因此,本综述将讨论基于放射组学的基线 PET/CT 成像在淋巴瘤的鉴别诊断、反应评估和预测中的作用。
Title
题目
Role of Radiomics‑Based Baseline PET/CTImaging in Lymphoma: Diagnosis, Prognosis,and Response Assessment
《基于影像组学的基线PET/CT成像在淋巴瘤中的作用:诊断、预后和反应评估》
Abstract
摘要
Radiomic analysis provides information on the underlying tumour heterogeneity in lymphoma, refecting the real-time evolution of malignancy. 2-Deoxy-2-[18F] fuoro-D-glucose positron emission tomog
raphy ([18F] FDG PET/CT) imaging is recommended before, during,and at the end of treatment foralmost all lymphoma patients. This methodology ofers high specifcity and sensitivity, which can aid
in accurate staging and assist in prompt treatment. Pretreatment [ 18F] FDG PET/CT-based radiomicsfacilitates improved diagnostic ability, guides individual treatment regimens, and boosts outcome
prognosis based on heterogeneity as well as the biological, pathological, and metabolic status ofthe lymphoma. This technique has attracted considerable attention given its numerous applications
in medicine. In the current review, we will briefy describe the basic radiomics workfow and typesof radiomic features. Details of current applications of baseline [ 18F] FDG PET/CT-based radiomics in
lymphoma will be discussed, such as diferential diagnosis from other primary malignancies, diagnosisof bone marrow involvement, and response and prognostic prediction. We will also describe how this
technique provides a unique noninvasive platform to assess tumour heterogeneity. Newly emerging PET radiotracers and multimodality technology will improve diagnostic specifcity and further clarify
tumor biology and even genetic variations in lymphoma, potentially promoting the development ofprecision medicine.
影像组学分析能够提供淋巴瘤患者肿瘤异质性的信息,反映了恶性肿瘤的实时进展。2-脱氧-2-[18F]氟-D-葡萄糖正电子发射断层扫描([18F] FDG PET/CT)成像在治疗前、治疗期间和治疗结束时几乎对所有淋巴瘤患者都是推荐的。这种方法提供了高特异性和灵敏度,可以帮助准确分期并协助及时治疗。治疗前基于[18F] FDG PET/CT的影像组学分析,能够提高诊断能力,指导个体化治疗方案,并基于异质性以及淋巴瘤的生物学、病理学和代谢状态提高预后预测。鉴于该技术在医学中的众多应用,它引起了极大的关注。在当前的综述中,我们将简要描述基础影像组学工作流程和影像组学特征类型。我们将讨论基线[18F] FDG PET/CT影像组学在淋巴瘤中当前应用的细节,例如与其他原发性恶性肿瘤的鉴别诊断、骨髓受累的诊断,以及反应和预后预测。我们还将描述这项技术如何提供一个独特的非侵入性平台来评估肿瘤异质性。新兴的PET影像性示踪剂和多模态技术将提高诊断特异性,并进一步阐明淋巴瘤的肿瘤生物学甚至遗传变异,有望促进精准医学的发展。
Conclusions
结论
Taken together, frst-order features in PET imaging, includingMTV and TLG, and second-order texture features, such asGLCM, GLRLM, GLZLM, and NGLDM, appeared to be the most frequently observed signifcant radiomic features in thestudies for prognosis and response assessment of lymphoma.Radiomic analysis of baseline [18F] FDG PET/CT imagingfeatures indicate the promising potential of this methodology in diagnostic and prognostic applications in lymphoma.
Nevertheless, to date, the majority of related studies weresingle-centre, retrospective studies with limited cohort sizesand lacked external validation. Additionally, various SUV threshold setting methods and segmentation approaches couldafect quantitative parameters. Thus, prospective studies with large populations and multiple centres as well as more typesof features extracted from combinations of PET and CTimages should be further investigated to better understandthe ability of radiomics.
Moreover, with the development of artifcial intelligence,exponential increases in computational power and the adventof increasingly advanced algorithms will improve and expandradiomics-based analysis and application. For example, deeplearning neural networks are being developed for automated segmentation and extraction of quantitative data. In addition, technological developments, including hybrid PET-MRI imaging, will provide further information and lesion features and enhance the positive predictive value of PET imaging.Increasing novel radiotracers of PET imaging also representa pivotal factor for the application of PET-based radiomics in combination with various types of biomarkers. Furthermore,radiogenomics linking imaging data to biological knowledge from genomic changes has the potential to accelerate the characterization of tumour behaviour and genetic compo sition. This progress will facilitate PET/CT-based radiom ics in the diagnosis, response, and prognosis prediction of lymphoma and holds promise in further clinical application, particularly in the era of precision medicine. However, this methodology remains in its infancy and requires furtherdevelopment and prospective validation.
总之,PET影像的一级特征,包括MTV和TLG,以及二级纹理特征,如GLCM、GLRLM、GLZLM和NGLDM,似乎是淋巴瘤预后和疗效评估研究中最常观察到的显著影像组学特征。对基线[18F] FDG PET/CT成像特征的影像组学分析表明,该方法在淋巴瘤诊断和预后应用中具有良好的潜力。然而,到目前为止,大多数相关研究都是单中心、回顾性研究,队列规模有限,缺乏外部验证。此外,不同的SUV阈值设置方法和分割方法可能会影响定量参数。因此,应进一步研究具有大人群和多中心的前瞻性研究,以及从PET和CT图像组合中提取更多类型的特征,以更好地理解影像组学的能力。此外,随着人工智能的发展,计算能力的指数增长和日益先进的算法的出现,将改善和扩大影像组学的应用范围。例如,深度学习神经网络正在开发用于定量数据的自动分割和提取。此外,技术发展,包括混合PET-MRI成像,将提供进一步的信息和病变特征,并提高PET成像的阳性预测价值。越来越多的新型PET显像放射性示踪剂也代表了基于PET的影像组学与各种类型的生物标志物相结合的应用的关键因素。此外,将影像数据与来自基因组变化的生物学知识联系起来的放射基因组学有可能加快肿瘤行为和基因组成的表征。这一进展将促进基于PET/CT的放射组学在淋巴瘤的诊断、疗效和预后预测方面的应用,并有望在进一步的临床应用中发挥作用,特别是在精准医疗时代。然而,这种方法仍处于起步阶段,需要进一步的发展和前瞻性验证。
Figure
图

Fig. 1 Radiomics workfow. The workfow involves imaging acquisition and preprocessing, region of interest (ROI) selection and segmentation, radiomics parameter extraction and feature standardization, feature selection and reduction, model construction and clinical application.
图 1 影像组学工作流程。该流程包括影像采集与预处理、感兴趣区域(ROI)的选择与分割、影像组学参数提取与特征标准化、特征选择与减少、模型构建与临床应用。

Fig. 2 Histogram of the areaunder the curve (AUC) radiomicfeatures extracted from baseline[18F] FDG PET/CT images invarious types of carcinoma andlymphoma.
图 2 基线下曲线面积(AUC)放射组学特征的直方图,这些特征是从各种类型的癌症和淋巴瘤中的[18F] FDG PET/CT 影像中提取的。

Fig. 3 Histogram of progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) for metrics extracted from baseline [18F] FDG PET/CTimages in lymphoma patients. Hazard ratio with 95% confdence interval was reported.
图 3 淋巴瘤患者基线[18F] FDG PET/CT影像中提取的无进展生存(PFS)和总生存(OS)指标的直方图。报告了带有 95% 置信区间的风险比。
Table
表



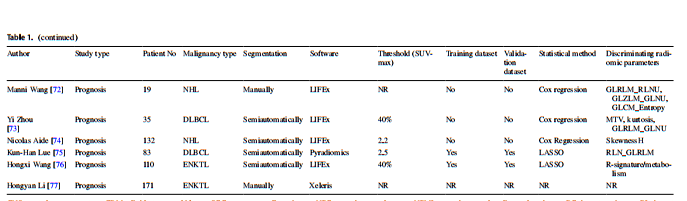
Table 1. Summary of all publications on [18F] FDG PET/CT imaging based radiomics in lymphoma
表 1. 淋巴瘤中基于[18F] FDG PET/CT 影像组学的所有出版物摘要