01
文献速递介绍
Rectal cancer is the second most prevalent form of cancer in the large intestine, and its primary
treatment modalities include radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and surgery (1,2). Radiotherapy, in
particular, can lead to various early and late effects on the rectum and bladder, potentially causingproctitis, cystitis, and a range of toxicities such as bowel obstruction, fistula, perforation, dysuria,hematuria, and a significant decrease in quality of life. These complications are contingent onmultiple clinical factors, including radiation dose and the patient’s clinical, biological, and genomiccharacteristics (3–5).
直肠癌是大肠中第二常见的癌症形式,其主要治疗方式包括放射治疗、化疗和手术(1,2)。特别是放射治疗,可能会对直肠和膀胱产生各种早期和晚期效应,潜在地导致直肠炎、膀胱炎以及如肠梗阻、瘘管、穿孔、排尿困难、血尿和生活质量显著下降等一系列毒性。这些并发症取决于多种临床因素,包括放射剂量和患者的临床、生物和基因组特征(3-5)
Title
题目
Multimodality radiomics prediction of radiotherapy-induced theearly proctitis and cystitis in rectal cancer patients: A machinelearning study
多模态放射组学预测直肠癌患者放疗引发的早期直肠炎和膀胱炎:一项机器学习研究
Abstract
摘要
This study aims to predict radiotherapy-induced rectal and bladder toxicity usingcomputed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) radiomics features incombination with clinical and dosimetric features in rectal cancer patients.
本研究旨在通过结合临床和剂量学特征,使用计算机断层扫描(CT)和磁共振成像(MRI)放射组学特征,预测直肠癌患者放疗引起的直肠和膀胱毒性。
Methods
方法
A total of sixty-three patients with locally advanced rectal cancer who underwent threedimensional conformal radiation therapy (3D-CRT) were included in this study. Radiomicsfeatures were extracted from the rectum and bladder walls in pretreatment CT and MR-T2Wweighted images. Feature selection was performed using various methods, including Least
Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (Lasso), Minimum Redundancy Maximum Relevance
(MRMR), Chi-square (Chi2), Analysis of Variance (ANOVA), Recursive Feature Elimination(RFE), and SelectPercentile. Predictive modeling was carried out using machine learningalgorithms, such as K-nearest neighbor (KNN), Support Vector Machine (SVM), LogisticRegression (LR), Decision Tree (DT), Random Forest (RF), Naive Bayes (NB), Gradient Boosting(XGB), and Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA). The impact of the Laplacian of Gaussian (LoG)
filter was investigated with sigma values ranging from 0.5 to 2. Model performance was evaluatedin terms of the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), accuracy, precision,sensitivity, and specificity.
本研究纳入了63名接受三维适形放射治疗(3D-CRT)的局部晚期直肠癌患者。从治疗前的CT和MR-T2W加权图像中提取了直肠和膀胱壁的放射组学特征。特征选择采用了多种方法,包括最小绝对收缩和选择算子(Lasso)、最小冗余最大相关性(MRMR)、卡方检验(Chi2)、方差分析(ANOVA)、递归特征消除(RFE)和SelectPercentile。预测建模采用了机器学习算法,如K最近邻(KNN)、支持向量机(SVM)、逻辑回归(LR)、决策树(DT)、随机森林(RF)、朴素贝叶斯(NB)、梯度提升(XGB)和线性判别分析(LDA)。探讨了高斯拉普拉斯(LoG)滤波器的影响,sigma值范围从0.5到2。模型性能以接收者操作特性曲线下面积(AUC)、准确度、精确度、灵敏度和特异性来评估。
Results
结果
A total of 479 radiomics features were extracted, and 59 features were selected. The preMRI T2W model exhibited the highest predictive performancewithanAUC:91.0/96.57%,accuracy:90.38/96.92%, precision:90.0/97.14%,sensitivity:93.33/96.50%,andspecificity:88.09/97.14%. These results were achieved with both original image and LoG filter (sigma=0.5-1.5) based on LDA/DT-RF classifiers for proctitis and cystitis, respectively. Furthermore, for the CT data, AUC: 90.71/96.0%, accuracy: 90.0/96.92%, precision: 88.14/97.14%, sensitivity:93.0/96.0%, and specificity: 88.09/97.14% were acquired. The highest values were achieved usingXGB/DT-XGB classifiers for proctitis and cystitis with LoG filter (sigma=2)/LoG filter(sigma=0.5-2), respectively. MRMR/RFE-Chi2 feature selection methods demonstrated the best
performance for proctitis and cystitis in the pre-MRI T2W model. MRMR/MRMR-Lasso yieldedthe highest model performance for CT.
提取了479个放射组学特征,并选取了59个特征。MRI T2W模型展示出了最高的预测性能,其AUC为91.0/96.57%,准确度为90.38/96.92%,精确度为90.0/97.14%,灵敏度为93.33/96.50%,特异性为88.09/97.14%。这些结果是在原始图像和LoG滤波器(sigma=0.5-1.5)的基础上,通过LDA/DT-RF分类器分别针对直肠炎和膀胱炎实现的。此外,对于CT数据,获得的AUC为90.71/96.0%,准确度为90.0/96.92%,精确度为88.14/97.14%,灵敏度为93.0/96.0%,特异性为88.09/97.14%。使用XGB/DT-XGB分类器结合LoG滤波器(sigma=2)/LoG滤波器(sigma=0.5-2),分别针对直肠炎和膀胱炎获得了最高值。MRMR/RFE-Chi2特征选择方法在MRI T2W模型中对直肠炎和膀胱炎展示了最佳性能。MRMR/MRMR-Lasso为CT数据提供了最高的模型性能。
Conclusions
结论
Radiomics features extracted from pretreatment CT and MR images can effectivelypredict radiation-induced proctitis and cystitis. The study found that LDA, DT, RF, and XGBclassifiers, combined with MRMR, RFE, Chi2, and Lasso feature selection algorithms, along withthe LoG filter, offer strong predictive performance. With the inclusion of a larger training dataset,these models can be valuable tools for personalized radiotherapy decision-making.
从治疗前CT和MR图像中提取的放射组学特征可以有效预测放射治疗引起的直肠炎和膀胱炎。研究发现,结合MRMR、RFE、Chi2和Lasso特征选择算法以及LoG滤波器的LDA、DT、RF和XGB分类器,提供了强大的预测性能。随着更大训练数据集的纳入,这些模型可以成为个性化放射治疗决策的有价值工具。
Figure
图

Figure 1 provides an overview of the methods employed in this study, which can be divided into two main phases: Data Acquisition, and Model Building and Evaluation. Each phase is explained in detail separately.
图1展示了本研究所采用的方法概览,可分为两个主要阶段:数据获取,以及模型构建和评估。每个阶段都有单独详细的解释。
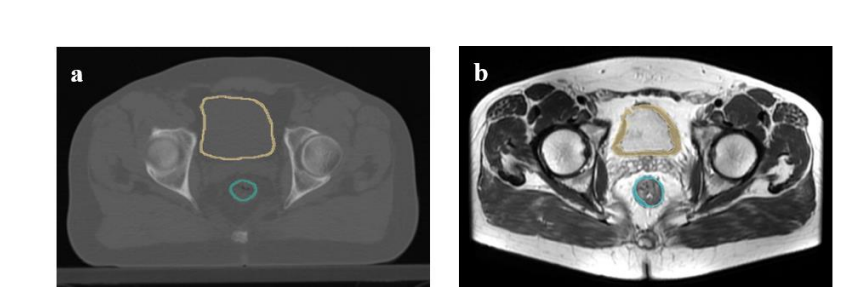
Figure2. Segmentation of the rectum and bladder walls on a) planning CT, b) pre-MRI T2W of therectal cancer patient in 3D-slicer.
图2. 在a) 规划CT、b) 直肠癌患者前MRI T2W上对直肠和膀胱壁的分割,使用3D切片器 Figure 3. Comparison of the mean dosimetric parameters in patients with proctitis and cystitis toxicities.
Figure 3. Comparison of the mean dosimetric parameters in patients with proctitis and cystitis toxicities.
图3. 患有直肠炎和膀胱炎毒性反应患者平均剂量参数的比较。 Figure 4. Intraclass correlation coefficients of the two observers for the different radiomics feature categories
Figure 4. Intraclass correlation coefficients of the two observers for the different radiomics feature categories
图 4. 两位观察员对不同放射组学特征类别的组内相关系数

Figure 5. Heatmap of the AUC value of the individual model and combined model for (a) proctitis,and (b) cystitis. “SP: select percentile, C: clinical, RCT (O): radiomics CT of the original image, RCT+C+D (O): radiomics CT +clinical+ dosimetric of the original image, and RMRI (O):radiomics MRI of original image”.
图 5. 针对(a)直肠炎和(b)膀胱炎的个体模型和组合模型的AUC值热图。“SP:选择百分位数,C:临床,RCT(O):原始图像的放射CT,RCT+C+D(O):原始图像的放射CT+临床+剂量,以及RMRI(O):原始图像的放射MRI”。
 Figure 6. The most significant radiomics features that correlated with proctitis.
Figure 6. The most significant radiomics features that correlated with proctitis.
图 6. 与直肠炎相关的最显著的放射组学特征。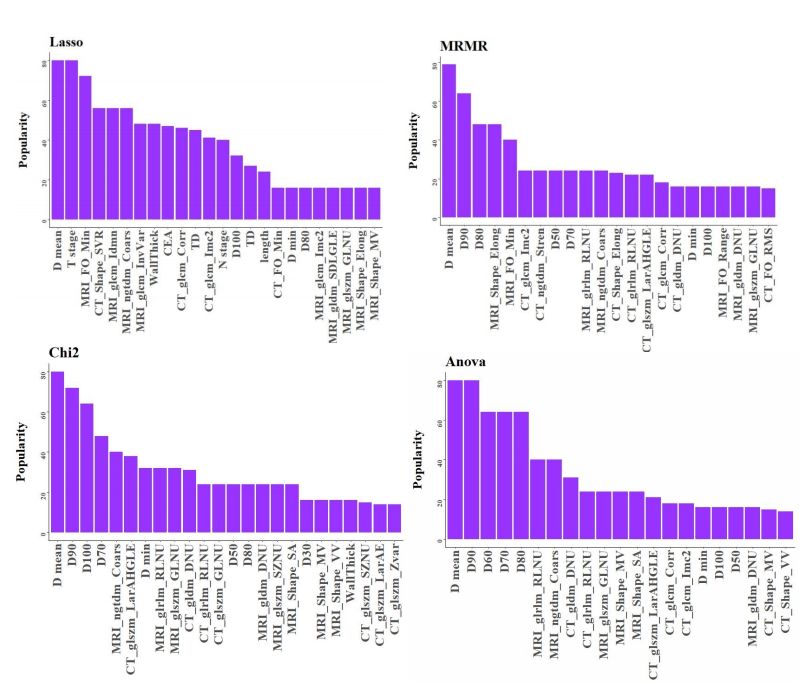
 Figure 7. The most significant radiomics features that correlated with cystitis.
Figure 7. The most significant radiomics features that correlated with cystitis.
图 7. 与膀胱炎相关的最显著的放射组学特征。
Table
表
 Table1. Feature selection and classification methods
Table1. Feature selection and classification methods
表1. 特征选择与分类方法 Table 2. The patient demographic and clinical information
Table 2. The patient demographic and clinical information
表2. 患者人口统计及临床信息 Table 3. Selected methods of individual and combined models for the proctitis and cystitisprediction
Table 3. Selected methods of individual and combined models for the proctitis and cystitisprediction
表 3. 针对直肠炎和膀胱炎预测的个体和组合模型的选定方法