01
文献速递介绍
作为世界上最常见的癌症,乳腺癌对人们的健康和生存构成了严重威胁(1)。鉴于其高转移倾向和高死亡率(2, 3),加之良性和恶性乳腺肿瘤治疗方式的显著差异,早期明确诊断是乳腺病变治疗管理中的关键第一步,这对于改善患者预后和生存率起着至关重要的作用(3-5)。随着超声成像技术的最新进展,超声在乳腺病变检测中扮演着越来越重要的角色。应变弹性成像(SE)允许通过彩色编码成像快速直观地显示病变内部的弹性系数差异,因此,它作为一种强大的诊断辅助工具,为病变诊断提供了宝贵的参考值(6, 7)。自动乳腺体积扫描仪(ABVS)由于其标准化操作程序,提供了良好的诊断结果可重复性(8),它可以获取整个乳腺体积信息并对获取的信息进行多平面成像。研究表明,ABVS在检测乳腺病变方面展现出了与手持式超声扫描仪相当的诊断准确性,同时还提供了额外信息(9, 10)。在常规超声检查中,常常遇到固态低回声乳腺病变的患者,医生可以根据ABVS图像上的形态表现和SE图像上的弹性表现,对乳腺病变的恶性风险进行初步评估。ABVS和SE成像技术的结合在评估乳腺病变方面显示出显著的诊断效能(11)。然而,传统成像技术产生的诊断结果的可靠性在很大程度上取决于检查医生的熟练程度,并且极易受到观察者间变异性的影响(12)。
放射组学符合精准医疗的当前趋势,它通过深入挖掘医学图像,将普通视觉图像转化为高通量数据,以非侵入性方式捕捉整个肿瘤的内部异质性(13-15)。因此,它可能提供新的生物标志物,以促进更好的临床决策。已经有几项关于超声(US)、乳房X光摄影术和磁共振(MR)在乳腺癌诊断中的放射组学研究取得了有希望的结果(16-29)。然而,目前还没有关于结合ABVS和UE放射组学特征与临床超声因素进行乳腺癌诊断的研究。因此,我们对SE和ABVS图像进行了放射组学分析,然后将这些特征与传统成像风险评估和其他临床风险因素结合,形成了一种新的诺莫图,以帮助医生准确诊断固态低回声乳腺病变。
Title
题目
A clinical-radiomics nomogram based on multimodal ultrasound for predicting the malignancy
risk in solid hypoechoic breast lesions
基于多模式超声的临床放射学诺莫图,用于预测实质性低回声乳腺病变的恶性风险
Background
背景
In routine clinical examinations, solid hypoechoic breast lesions are frequently encountered, but accurately distinguishing them poses a challenge.
This study proposed a clinical-radiomics nomogram based on multimodal ultrasound that enhances the diagnostic accuracy for solid hypoechoic breast lesions.
在常规临床检查中,实质性低回声乳腺病变经常会遇到,但准确区分它们是一项挑战。本研究提出了一种基于多模式超声的临床放射学诺莫图,可以提高对实质性低回声乳腺病变的诊断准确性。
methods
方法
This retrospective study analyzed ultrasound strain elastography (SE) and automated breast volume scanner images (ABVS) of 423 solid hypoechoic
breast lesions from 423 female patients in our hospital between August 2019 and
May 2022. They were assigned to the training (n=296) and validation (n=127) groups in a 7:3 ratio by generating random numbers. Radiomics features were extracted and screened from ABVS and SE images, followed by the calculation of the radiomics score (Radscore) based on these features. Subsequently, a nomogram was constructed through multivariate logistic regression to assess
the malignancy risk in breast lesions by combining Radscore with Breast Imaging
Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) scores and clinical risk factors associated
with breast malignant lesions. The diagnostic performance, calibration performance, and clinical usefulness of the nomogram were assessed by the
area under the curve (AUC) of the receiver operating characteristic curve, the calibration curve, and the decision analysis curve, respectively.
这项回顾性研究分析了我们医院2019年8月至2022年5月间423名女性患者共423个实性低回声乳腺病变的超声应变弹性成像(SE)和自动化乳腺体积扫描仪(ABVS)图像。他们按7:3的比例通过生成随机数被分配到训练组(n=296)和验证组(n=127)。从ABVS和SE图像中提取并筛选放射组学特征,然后根据这些特征计算放射组学评分(Radscore)。随后,通过多变量逻辑回归构建了一个诺模图,以结合Radscore、乳腺影像报告和数据系统(BI-RADS)评分及与乳腺恶性病变相关的临床风险因素,评估乳腺病变的恶性风险。诺模图的诊断性能、校准性能和临床实用性分别通过接受者操作特征曲线下面积(AUC)、校准曲线和决策分析曲线进行评估。
Results
结果
The diagnostic performance of the nomogram is significantly superior to hat of both the clinical diagnostic model (BI-RADS model) and the multimodal radiomics model (SE+ABVS radiomics model) in training (AUC: 0.972 vs 0.930 vs
0.941) and validation group (AUC:0.964 vs 0.916 vs 0.933). In addition, the nomogram also exhibited a favorable goodness-of-fit and could lead to greater net benefits for patients.
该诺模图的诊断性能显著优于临床诊断模型(BI-RADS模型)和多模态放射组学模型(SE+ABVS放射组学模型),无论是在训练组(AUC:0.972 vs 0.930 vs 0.941)还是在验证组(AUC:0.964 vs 0.916 vs 0.933)。此外,该诺模图还展现了良好的适应性,并可能为患者带来更大的净益处。
Conclusions
结论
The nomogram enables a more effective assessment of the malignancy risk of solid hypoechoic breast lesions; therefore, it can serve as a
new and efficient diagnostic tool for clinical diagnosis.
该诺莫图可以更有效地评估实质性低回声乳腺病变的恶性风险,因此,它可以作为临床诊断的新的高效工具。
Figure
图
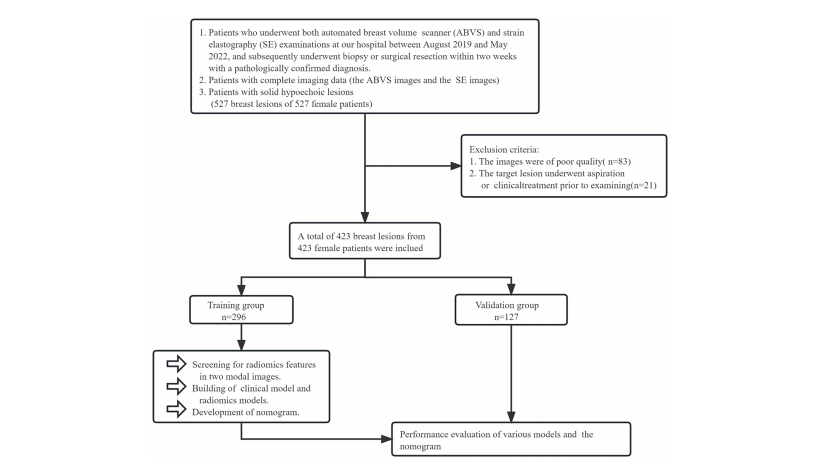
FIGURE 1 The grouping process of this study.
图1 本研究的分组流程
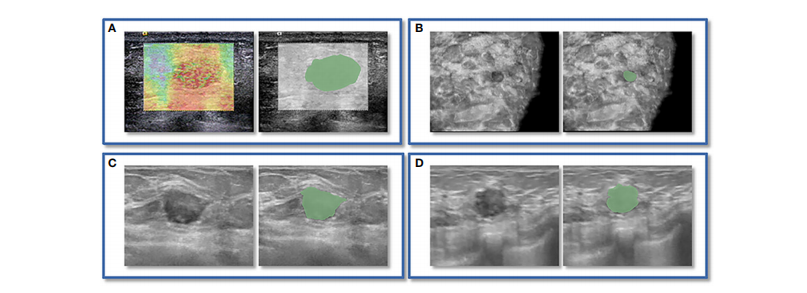
FIGURE 2 An instance of manually delineating a region of interest (ROI). The strain elastography (SE) and automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) images of a 41-year-old female with a solid hypoechoic lesion measuring approximately 16×11×12mm on her left breast. The lesion was irregular in shape, parallel in position, with still well-defined borders, sharp margins, and scattered microcalcifications visible internally, and exhibited no significant posterior echogenicity change or retraction in the coronal plane, and the ultrasound elasticity score was 4, finally, the lesion was classified as BI
RADS category 4a. Pathological examination confirmed it as invasive ductal carcinoma. ROI segmentation was performed on both the SE image (A)and ABVS coronal image (B), with delineation along the boundary of the lesion followed by uniform outward expansion of its edges by 3 mm to
encompass some surrounding tissue.ROI segmentation was performed on ABVS transverse © and sagittal (D) images, respectively, and meticulous
delineation was performed along the lesion’s contour and borders on these two views.
图2手动绘制感兴趣区域(ROI)的示例。这是一位41岁女性的左乳房上有一个约16×11×12mm的实质性低回声病变的应变弹性成像(SE)和自动乳腺体积扫描仪(ABVS)图像。该病变呈不规则形状,位置平行,边界清晰,边缘锐利,内部可见分散的微钙化,冠状位上没有明显的后方声明显改变或回缩,超声弹性评分为4,最终被分类为BI-RADS类别4a。病理检查确认为浸润性导管癌。ROI分割分别在SE图像(A)和ABVS冠状图像(B)上进行,沿病变边界绘制,然后将边缘均匀向外扩展3毫米以包围一些周围组织。ROI分割分别在ABVS横断面(C)和矢状面(D)图像上进行,对这两个视图上的病变轮廓和边界进行了精细细致的绘制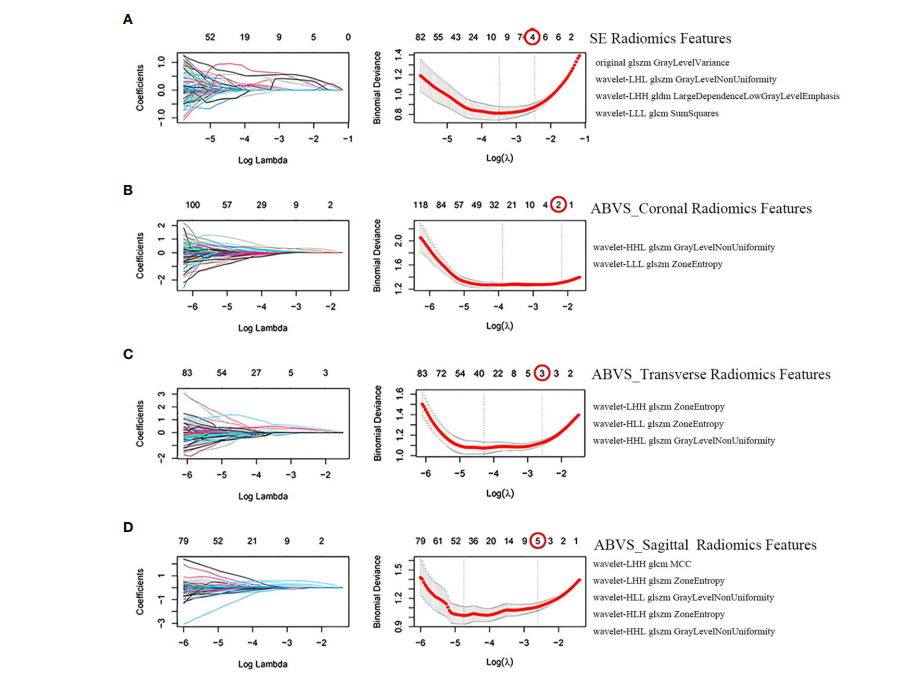
FIGURE 3 Screening of radiomics features. Selection of strain elastography (SE) radiomics features (A), automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) coronal plane radiomics features (B), ABVS transverse plane radiomics features ©, and ABVS sagittal plane radiomics features (D) using the least absolute
shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression model. The coefficient profiles of LASSO for each modal radiomics feature are presented on
the left. The right shows that the tuning parameter l (lambda) in the LASSO model was selected using tenfold cross-validation, and the binomial
deviance was plotted as a function of log(l), with vertical dashed lines drawn at the minimum deviation (log(l.min)) and the 1 standard error of the
minimum deviation (log(l.1se)). Selected the non-zero coefficient features in the model when the horizontal coordinate was log(l.1se).
图3 放射学特征的筛选。使用最小绝对收缩和选择算子(LASSO)回归模型选择应变弹性成像(SE)放射学特征(A)、自动乳腺体积扫描仪(ABVS)冠状平面放射学特征(B)、ABVS横断面放射学特征(C)和ABVS矢状面放射学特征(D)。左侧呈现了每种模态放射学特征的系数轮廓。右侧显示,使用十折交叉验证选择了LASSO模型中的调整参数l(lambda),并且将二项式偏差作为log(l)的函数绘制,垂直虚线标在最小偏差(log(l.min)) 和最小偏差的1个标准误差(log(l.1se)) 处。当横坐标为log(l.1se)时,选择了模型中的非零系数特征。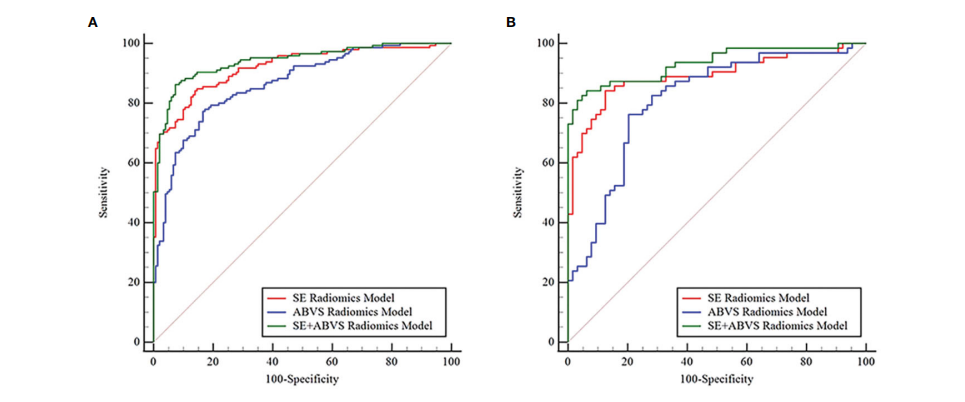
FIGURE 4 The receiver operator characteristic curves for various radiomics models in the training (A) and validation groups (B).
图4 在训练组(A)和验证组(B)中,各种放射学模型的受试者工作特征曲线。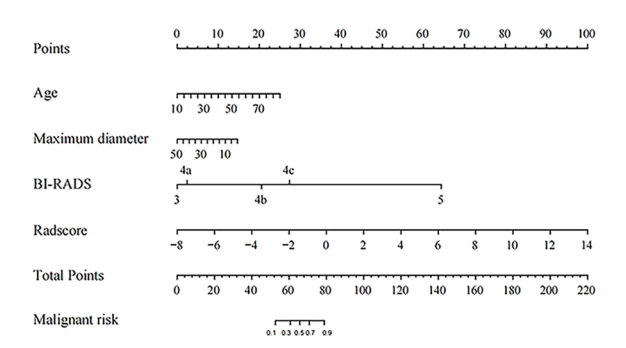
FIGURE 5 The Nomogram for predicting the malignant risk of solid hypoechoic breast lesions.
图5 用于预测实质性低回声乳腺病变恶性风险的诺莫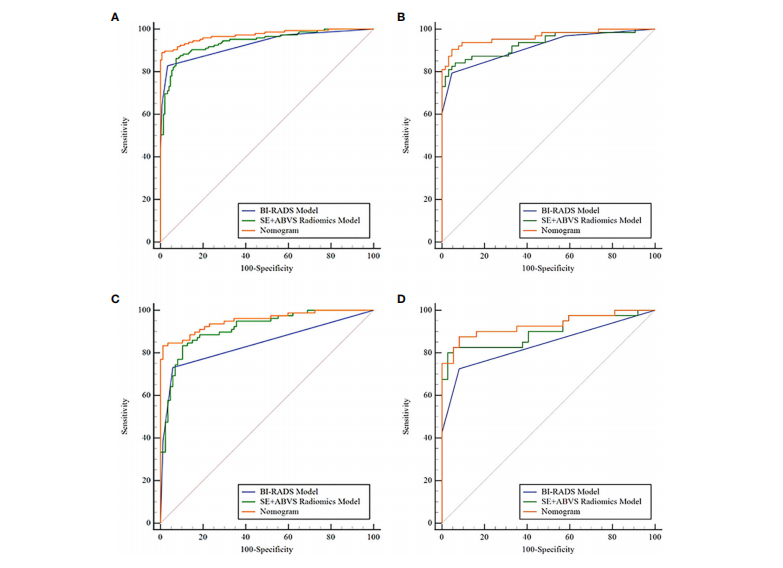
FIGURE 6 The receiver operator characteristic curves of the BI-RADS model, SE+ABVS radiomics model, and Nomogram in the training group (A), the
validation group (B), the BI-RADS category 4 lesions in the training group ©, and the BI-RADS category 4 lesions in the validation group (D).
图6 在训练组(A)、验证组(B)、训练组中的BI-RADS类别4病变(C)和验证组中的BI-RADS类别4病变(D)中,展示了BI-RADS模型、SE+ABVS放射学模型和诺莫图的受试者工作特征曲线。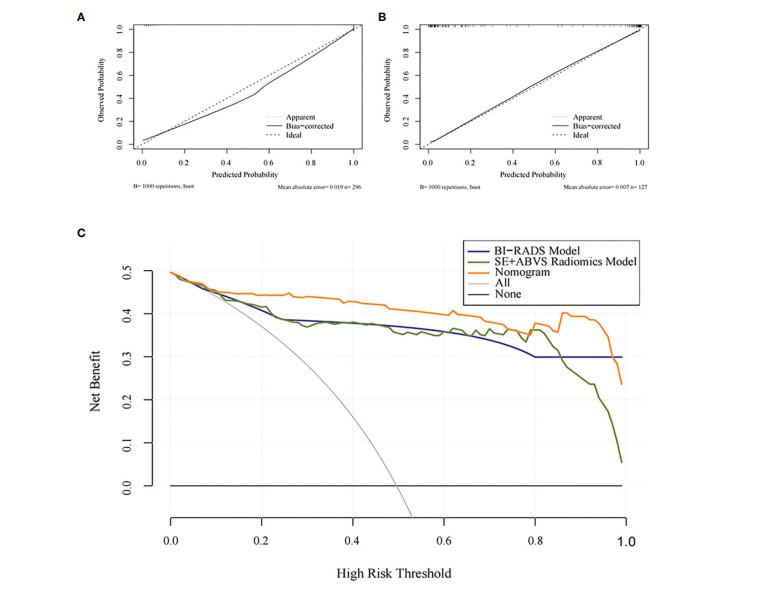
FIGURE 7 The calibration curves for the Nomogram in the training group (A) and the validation group (B).The decision analysis curves of the BI-RADS mode, SE+ABVS radiomics model, and Nomogram in the validation group ©.
图7 诺莫图在训练组(A)和验证组(B)中的校准曲线。BI-RADS模型、SE+ABVS放射学模型和诺莫图在验证组中的决策分析曲线(C)。
**
Table**
表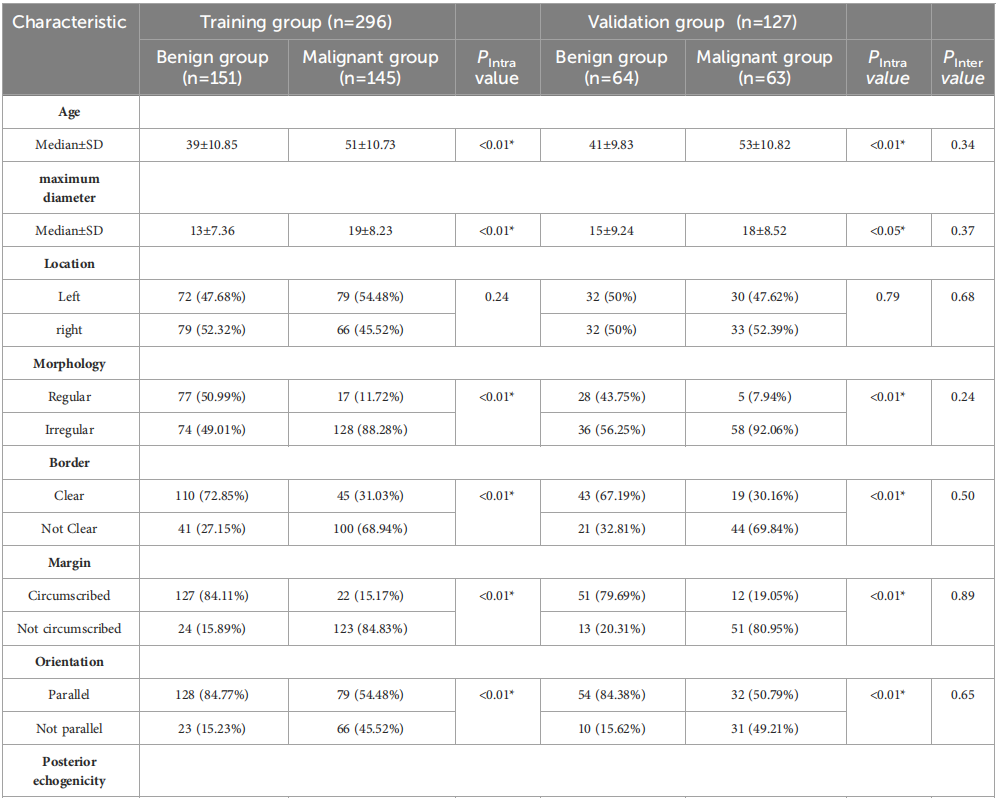
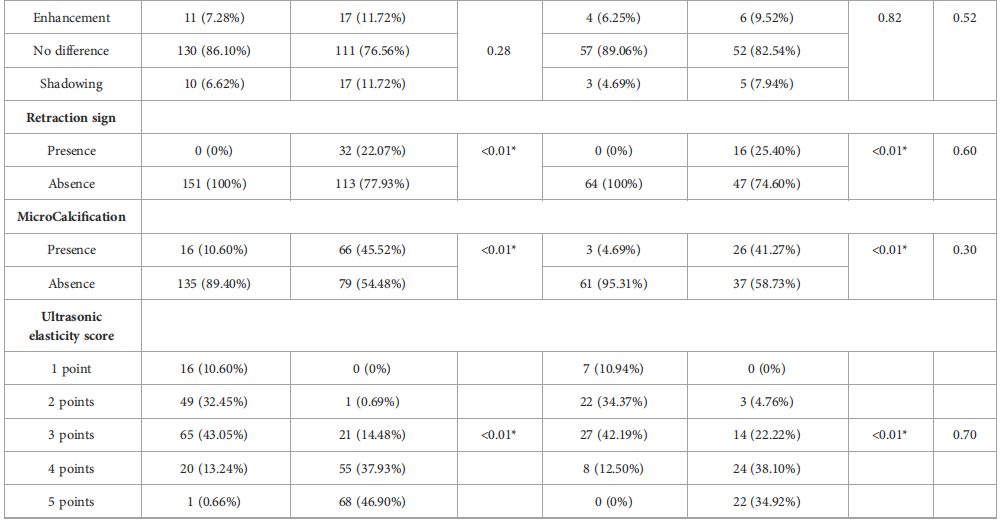
 TABLE 1 Clinical basis information and sonographic features of patients with breast lesions.
TABLE 1 Clinical basis information and sonographic features of patients with breast lesions.
表1 乳腺病变患者的临床基本信息和超声特征。
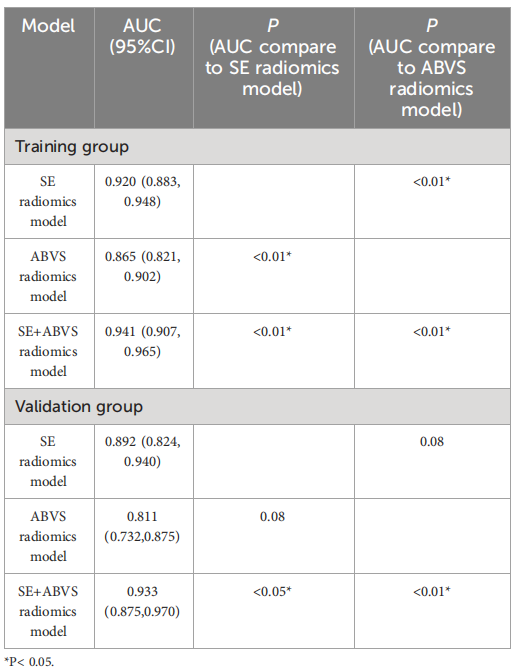
TABLE 2 The AUC values of radiomics models in the training andvalidation groups.
表2 训练组和验证组中放射学模型的AUC值
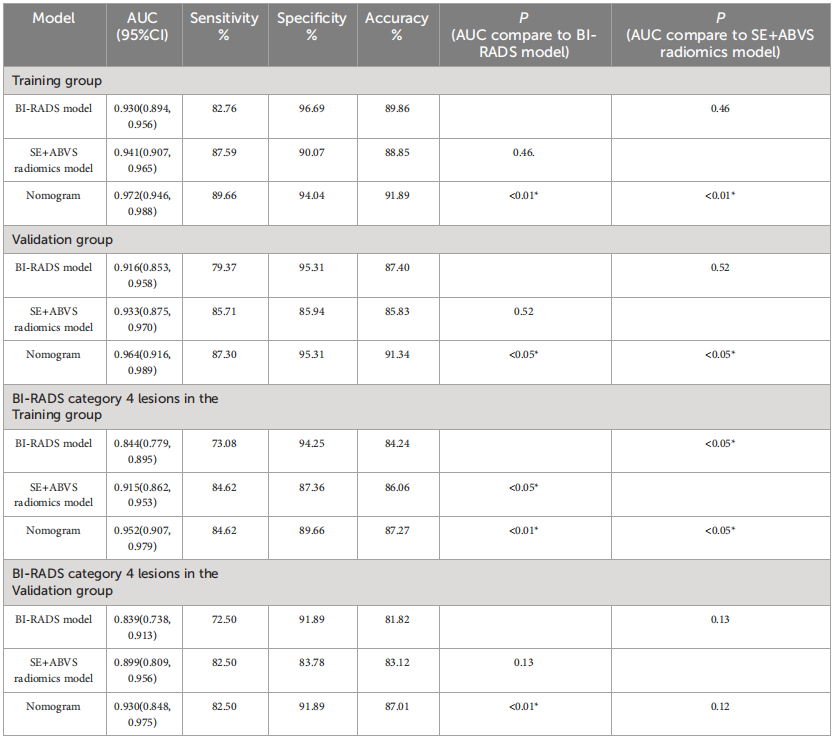
TABLE 3 The diagnostic parameters of the BI-RADS model, SE+ABVS radiomics model, and Nomogram in each group
表3 BI-RADS模型、SE+ABVS放射学模型和诺莫图在每个组中的诊断参数。