文献速递介绍**
本文综述了超声影像组学在甲状腺疾病研究中的应用及其局限性。近年来,甲状腺疾病的发病率逐渐增加,传统超声是最关键的甲状腺成像方法之一,但仍存在一定局限性。超声影像组学基于超声图像来勾画感兴趣区域(ROI),然后提取特征以量化图像中包含的疾病信息,有助于分析图像与疾病的临床病理之间的相关性。通过构建强大的模型,可以用于诊断良恶性甲状腺结节、预测甲状腺癌的淋巴结状态、分析分子生物学特征,以及预测甲状腺癌患者的生存情况。目前,超声影像组学在甲状腺领域的应用非常广泛。
超声影像组学的工作流程 包括数据收集、ROI分割、特征提取、特征选择和建模。数据收集阶段,需要大量的医学图像数据。ROI分割是影像组学的基本步骤,目标区域可以是肿瘤病变或病变周围的正常组织。特征提取阶段,从医学图像中提取与患者疾病状态相关的高通量特征。特征选择是在ROI的组学特征中进一步选择包含关键信息的特征。建模是许多影像组学项目的最终目标,通常包括有监督学习、无监督学习和半监督学习。
超声影像组学在甲状腺成像中的应用 主要包括:利用超声影像组学诊断良恶性甲状腺结节、评估甲状腺癌的侵袭性和淋巴结转移、预测甲状腺癌与分子生物学特性之间的关联,以及评估甲状腺癌患者的生存情况。
然而,超声影像组学也存在局限性。首先,大多数研究样本量不足,可能导致提取的图像特征不具代表性。其次,超声成像组的数据收集和目标分割过程受到临床经验的影响,这是影像组学研究中可重复性的最大挑战之一。此外,大多数基于超声影像组学的甲状腺研究使用了回顾性收集的数据,未来需要更多的前瞻性研究来确认超声影像组学在临床上的可行性。
Title
题目
A Review of the Role of Ultrasound Radiomics and Its Application and Limitations in the Investigation of Thyroid Disease
超声影像组学在甲状腺疾病调查中的作用及其应用和局限性的综述
Abstract-Background
摘要
The incidence of thyroid disease has gradually increased in recent years. Conventional ultrasound is one of the most critical thyroid imaging methods, but it still has certain limitations. The use of B-model ultrasound (BMUS) diagnosis of thyroid disease will be affected by a doctors’ clinical experience. The ultrasound radiomics is based on ultrasound images to delineate the region of interest (ROI), and then extract features to quantify the disease information contained in the image, which helps to analyze the correlation between the image and the clinical pathology of the disease. By building a powerful model, it can be used to diagnose benign and malignant thyroid nodules, predict lymph node status in thyroid cancer, analyze molecular biological characteristics, and predict the survival of thyroid cancer patients. At present, the application of ultrasound radiomics in the thyroid is pervasive. These ultrasound radiomics studies have further promoted the progress of ultrasonic technology in the field of thyroid disease. Clinicians should be familiar with the workflow of ultrasound radiomics and understand the application of this technology to the thyroid. In this article, we first describe the workflow of ultrasound radiomics, followed by an overview of the application of ultrasound radiomics to the thyroid. Finally, some current limitations of the technology and areas for future improvement are discussed. This article aims to review the role of ultrasound radiomics and its application and limitations in the investigation of thyroid disease.
近年来,甲状腺疾病的发病率逐渐增加。传统超声是最重要的甲状腺成像方法之一,但仍有一定的局限性。B模超声(BMUS)诊断甲状腺疾病会受到医生临床经验的影响。超声影像组学基于超声图像来勾画感兴趣区域(ROI),然后提取特征以量化图像中所含的疾病信息,有助于分析图像与疾病的临床病理之间的相关性。通过构建强大的模型,可以用来诊断良恶性甲状腺结节,预测甲状腺癌的淋巴结状态,分析分子生物学特性,以及预测甲状腺癌患者的生存率。目前,超声影像组学在甲状腺的应用非常广泛。这些超声放射组学研究进一步推动了甲状腺疾病领域超声技术的进步。临床医生应熟悉超声影像组学的工作流程,并理解这项技术对甲状腺的应用。在本文中,我们首先描述超声影像组学的工作流程,然后概述超声影像组学在甲状腺的应用。最后,讨论了该技术的一些当前局限性和未来改进的领域。本文旨在综述超声影像组学在甲状腺疾病调查中的作用及其应用和局限性。
Conclusions
结论
In conclusion, ultrasound radiomics, as a technique for extracting image data, plays an important role in the evaluation of medical images of related diseases. However, there are some deficiencies, and more efforts are needed to standardize the discipline of ultrasound radiomics and to apply ultrasound radiomics to clinical work.
总之,超声影像组学作为一种提取图像数据的技术,在评估相关疾病的医学图像方面发挥着重要作用。然而,该技术存在一些不足之处,需要更多努力来规范超声放射组学这一学科,并将超声影像组学应用于临床工作中。
Table
表
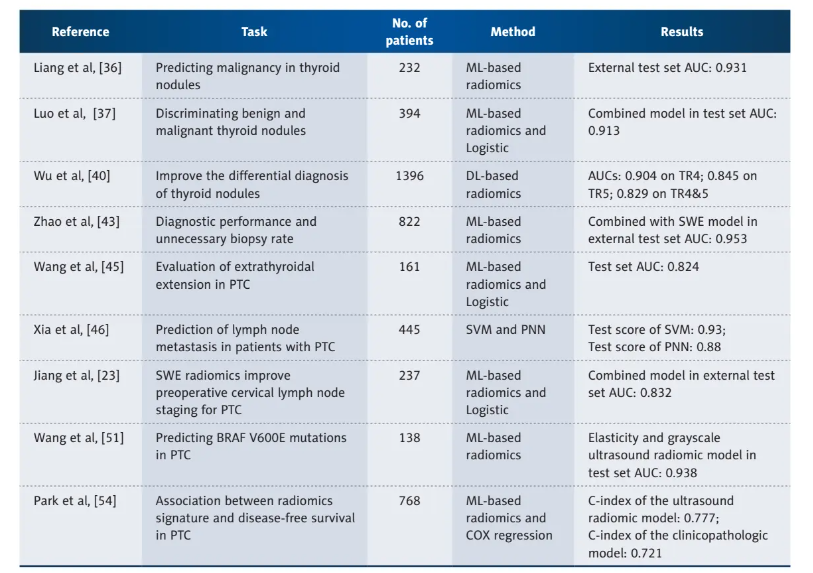
Table 1. Application of ultrasound radiomics in thyroid imaging.
表1. 超声影像组学在甲状腺成像中的应用。
Figure
图
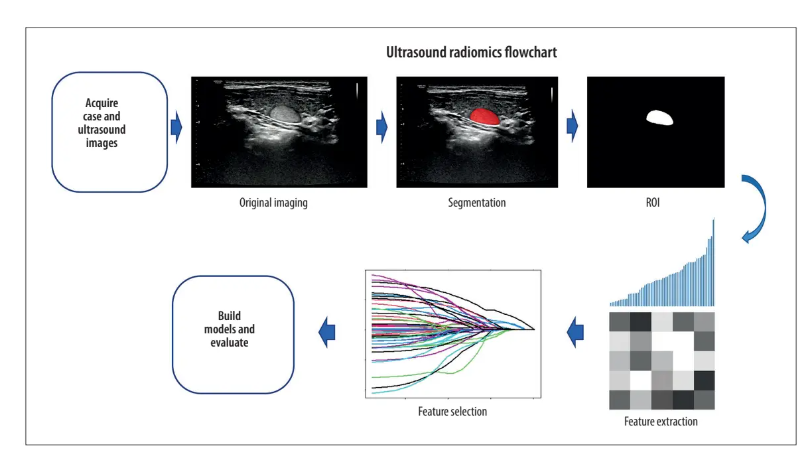
Figure 1. The picture uses an ultrasound image case of a thyroid nodule, showing the workflow of the ultrasound radiomics. Region of interest (ROI) segmentation was conducted on the largest diameter of the thyroid nodule. Radiomics features were extracted from ROI, including features such as shape, grayscale, texture, and wavelets. The feature selection process is shown with LASSO as an example.
wavelets. The feature selection process is shown with LASSO as an example.*
图1. 该图片使用了一个甲状腺结节的超声图像案例,展示了超声影像组学的工作流程。在甲状腺结节的最大直径上进行了感兴趣区域(ROI)的分割。从ROI中提取了影像组学特征,包括形状、灰度、纹理和小波等特征。以LASSO为例展示了特征选择过程。