Title
题目
Adaptive mix for semi-supervised medical image segmentation
半监督医学图像分割的自适应混合方法
01
文献速递介绍
医学图像分割旨在从不同成像模态中勾勒出组织、器官和病变区域,这对于预后评估、术前规划等计算机辅助临床应用至关重要。深度学习凭借其强大的表征能力和大量标记数据,极大地推动了医学图像分割的发展(Ronneberger 等人, 2015; Milletari 等人, 2016; Chen 等人, 2021a; Wang 等人, 2022; Wu 等人, 2024a)。然而,医学图像的像素级标注既耗时又昂贵,因为这需要专业知识。半监督学习(SSL)有望通过利用大量未标记数据来缓解标签稀缺问题(Van Engelen 和 Hoos, 2020)。 一致性正则化是应用最广泛的半监督学习技术之一,它促使模型预测对输入扰动具有不变性,旨在从未标记数据中挖掘监督信息(Rasmus 等人, 2015; Laine 和 Aila, 2016; Tarvainen 和 Valpola, 2017)。基于一致性正则化的思想,强弱伪监督(Sohn 等人, 2020)要求对强扰动和弱扰动的未标记图像的预测伪标签保持一致,从而充分从未标记数据中提取监督信号(Sohn 等人, 2020; Chen 等人, 2023, 2021b; Wu 等人, 2022; Shen 等人, 2023; Wang 等人, 2023b)。强弱伪监督的核心挑战在于确定合适的强扰动策略以生成强扰动图像。不当的扰动无法匹配训练模型的能力,会误导训练过程(Shen 等人, 2023)。近年来,结合图像颜色空间变换的 CutMix(Yun 等人, 2019)被广泛用于构建强扰动(French 等人, 2019; Chen 等人, 2021b; Yang 等人, 2022, 2023a)。如图 1(b) 所示,CutMix 通过随机混合原始图像和辅助图像之间的图像块来合成强扰动样本。然而,这种扰动程度不可控的随机混合操作会导致一致性正则化过程振荡且不稳定(图 1(f)),模型容易过拟合到随机扰动样本,进而在验证集上表现出不佳的泛化能力(图 1(g))。为解决随机混合操作的不稳定性,我们之前的工作 UMix(Shen 等人, 2023)(图 1©)合成了包含更多高置信度区域的强扰动图像,使模型能够对这些样本产生高质量预测。如图 1(f-g) 所示,使用 UMix 图像训练的模型展现出更平滑且更低的训练损失,但由于一致性正则化的效果有限,其验证和测试性能并不理想。此外,我们还研究了逆 UMix(I-UMix)策略(图 1(d))。由于该操作生成的新样本扰动过强,模型的训练损失出现严重振荡,验证性能也较差(图 1(f-g))。可以看出,随机扰动往往难以控制,而基于固定规则的混合操作会导致扰动微弱或过强,两者均限制了一致性正则化的效果。因此,开发适用于半监督医学图像分割的自适应扰动/增强策略具有重要意义。 从概念上讲,随着训练轮数的增加,模型性能会动态变化;因此,合适的混合操作也应根据分割模型的能力状态动态调整扰动程度。基于这一假设,我们提出了一种新颖的动态可学习扰动算法——自适应混合(AdaMix),该算法基于模型的学习状态自适应地执行图像混合,以更好地在半监督医学图像分割中实现一致性正则化。我们的核心思想是将自步学习(Kumar 等人, 2010; Jiang 等人, 2014; Ma 等人, 2017)的概念引入混合算法设计,为强弱伪监督提供样本复杂度逐步提升的更合理强扰动图像,如图 1(e) 所示。具有不同扰动程度的混合算法能够生成不同样本复杂度的强扰动图像。对于分割模型而言,包含更多高置信度区域的图像被视为较简单样本,因为模型更容易从这类图像中产生准确预测;相反,混合更多高置信度图像块会得到更难的样本(扰动强度更强)。具体来说,AdaMix 基于训练损失:1)生成自步掩码,用于确定图像是与高置信度图像块还是低置信度图像块混合;同时 2)生成自步权重,用于确定混合图像块的数量。从图 1(f-g) 可以看出,与随机和固定规则的混合方法(即 CutMix(Yun 等人, 2019)和 UMix(Shen 等人, 2023))相比,AdaMix 能够在训练过程中保持稳定的收敛能力,并在验证和测试阶段实现更好的泛化性能。我们通过实验证明,AdaMix 可以无缝集成到自训练、均值教师和协同训练等半监督学习范式中(即 FixMatch(Sohn 等人, 2020)、MT(Tarvainen 和 Valpola, 2017)和 CPS(Chen 等人, 2021b)),分别形成 AdaMix-ST、AdaMix-MT 和 AdaMix-CT 框架,这些框架在半监督医学图像分割任务中取得了最先进的性能。我们在三个公开的医学图像分割数据集(涵盖 2D 和 3D 模态)上对所提框架进行了评估,结果验证了我们方法各组件的有效性及其相对于现有最先进方法的优越性。 综上所述,我们的主要贡献如下: • 新视角:我们从动态模型训练的角度指出了现有混合方法的局限性:它们要么以随机方式执行图像混合,要么基于预定义的固定规则,导致扰动图像的扰动程度不可控、微弱或过强,严重影响了一致性正则化的效果。我们认为,结合模型学习状态的自适应混合方案对于一致性正则化至关重要。 • 新方法:我们提出了一种新颖的自步式图像混合算法 AdaMix。据我们所知,这是首个基于模型状态自适应执行混合扰动的工作,其中分割模型和 AdaMix 算法相互协作学习。此外,AdaMix 具有高度灵活性,可无缝集成到自训练、均值教师和协同训练等半监督学习范式中。 • 新发现:我们得出了新的见解:将高置信度图像块融入图像可生成较简单样本,这有利于分割模型在训练初期的学习;相反,低置信度区域(通常出现在分割边界)在训练后期融入图像时,会迫使分割模型关注这些难样本区域,从而增强模型的判别能力。我们还发现,对于一致性正则化而言,扰动策略比学习范式更为重要。
Aastract
摘要
Mix-up is a key technique for consistency regularization-based semi-supervised learning methods, blending twoor more images to generate strong-perturbed samples for strong-weak pseudo supervision. Existing mix-up operations are performed either randomly or with predefined fixed rules, such as replacing low-confidence patcheswith high-confidence ones. The former lacks control over the perturbation degree, leading to overfitting on randomly perturbed samples, while the latter tends to generate images with trivial perturbations, both of whichlimit the effectiveness of consistency regularization. This paper aims to answer the following question: How canimage mix-up perturbation be adaptively performed during training? To this end, we propose an Adaptive Mixalgorithm (AdaMix) for image mix-up in a self-paced learning manner. Given that, in general, a model’s performance gradually improves during training, AdaMix is equipped with a self-paced curriculum that, in the initialtraining stage, provides relatively simple perturbed samples and then gradually increases the difficulty of perturbed images by adaptively controlling the perturbation degree based on the model’s learning state estimatedby a self-paced regularizer. We develop three frameworks with our AdaMix, i.e., AdaMix-ST, AdaMix-MT, andAdaMix-CT, for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. Extensive experiments on three public datasets,including both 2D and 3D modalities, show that the proposed frameworks are capable of achieving superiorperformance. For example, compared with the state-of-the-art, AdaMix-CT achieves relative improvements of2.62 % in Dice similarity coefficient and 48.25 % in average surface distance on the ACDC dataset with 10 %labeled data. The results demonstrate that mix-up operations with dynamically adjusted perturbation strengthbased on the segmentation model’s state can significantly enhance the effectiveness of consistency regularization.
Mix-up是基于一致性正则化的半监督学习方法的核心技术,通过混合两张或多张图像生成强扰动样本,用于强弱伪监督。现有Mix-up操作要么随机执行,要么遵循预定义的固定规则(例如用高置信度补丁替换低置信度补丁)。前者对扰动程度缺乏控制,导致模型在随机扰动样本上过拟合;后者则容易生成扰动微弱的图像,两者均限制了一致性正则化的效果。本文旨在解决以下问题:如何在训练过程中自适应地执行图像Mix-up扰动?为此,我们提出一种自适应混合算法(AdaMix),以自步学习的方式实现图像混合。考虑到模型性能通常在训练过程中逐步提升,AdaMix设计了自步课程:在训练初期提供相对简单的扰动样本,随后通过自步正则化器估计模型的学习状态,自适应控制扰动程度,逐步增加图像扰动的难度。我们基于AdaMix构建了三个框架(即AdaMix-ST、AdaMix-MT和AdaMix-CT),用于半监督医学图像分割。在三个公开数据集(涵盖2D和3D模态)上的大量实验表明,所提框架能够实现更优性能。例如,在ACDC数据集10%标记数据的设置下,与当前最优方法相比,AdaMix-CT在Dice相似系数上实现了2.62%的相对提升,在平均表面距离上实现了48.25%的相对提升。实验结果证实,基于分割模型状态动态调整扰动强度的Mix-up操作,可显著增强一致性正则化的效果。
Method
方法
3.1. Problem statement
Before delving into the proposed method, we first provide the notations that will be used subsequently. The training set = {𝐿, 𝑈 }contains a labeled set 𝐿 = {(𝑥 𝑙 𝑖 , 𝑦𝑙 𝑖 ) 𝑁 𝑖=1 𝐿 } and an unlabeled set 𝑈 ={(𝑥 𝑢 𝑗 ) 𝑁𝑈𝑗=1 }, where 𝑥 𝑙 𝑖 /𝑥 𝑢 𝑗 denotes the 𝑖 𝑡ℎ/𝑗 𝑡ℎ labeled/unlabeled image, 𝑦 𝑙 𝑖 isthe ground truth for the labeled image, and 𝑁𝐿 and 𝑁𝑈 (𝑁𝑈 >> 𝑁𝐿)are the numbers of labeled and unlabeled samples. Given the trainingdata , semi-supervised semantic segmentation aims to learn a model𝑓(⋅; 𝜃) that performs well on unseen test sets
3.1 问题陈述 在深入介绍所提方法之前,首先明确后续将使用的符号定义。训练集(\mathcal{D} = {\mathcal{D}L, \mathcal{D}U})包含标记集(\mathcal{D}L = {(x_il, y_il)}{i=1}^{NL})和未标记集(\mathcal{D}U = {(x_ju)}{j=1}^{NU}),其中(x_il/x_ju)分别表示第(i)个标记图像/第(j)个未标记图像,(y_il)是标记图像对应的真实标签,(NL)和(NU)((NU \gg NL))分别为标记样本和未标记样本的数量。给定训练数据(\mathcal{D}),半监督语义分割的目标是学习一个模型(f(\cdot; \theta)),使其在未见过的测试集(\mathcal{T})上表现优异。 要不要我帮你整理一份全文核心符号对照表,涵盖数据集、模型、参数等关键符号的定义和用途?
Conclusion
结论
This paper explores adaptive mix-up techniques for semi-supervisedmedical image segmentation. We propose a novel Adaptive Mix algorithm that features a self-paced curriculum, which initially providesrelatively simple mixed samples and then gradually increases the diffi-culty of the mixed images by adaptively controlling the mix-up strengthbased on the model’s learning state. AdaMix can be seamlessly integrated as a plug-and-play module into self-training, mean-teacher, andco-training semi-supervised learning paradigms, achieving superior performance. Experiments on three public medical image datasets validatethe effectiveness of the proposed method and demonstrate its superiorityover state-of-the-art approaches. Moreover, we reveal that incorporating more high-confidence patches into images generates easier samples,which benefits the segmentation model during the initial training stage;in contrast, replacing high-confidence regions with low-confidence onesproduces harder examples that are effective for the later training stage.Since low-confidence regions often appear in segmentation boundaries,forcing the model to learn from these regions helps enhance its discriminative capability. Our analysis also demonstrates that, in strong-weakpseudo supervision for semi-supervised learning, perturbation strategiesare more critical than learning paradigms.
本文探讨了适用于半监督医学图像分割的自适应混合技术。我们提出一种新颖的自适应混合(Adaptive Mix)算法,该算法采用自步学习课程:训练初期提供相对简单的混合样本,随后基于模型的学习状态自适应控制混合强度,逐步增加混合图像的难度。AdaMix可作为即插即用模块无缝集成到自训练、均值教师和协同训练等半监督学习范式中,实现更优性能。在三个公开医学图像数据集上的实验验证了所提方法的有效性,并证明其相较于现有最优方法的优越性。此外,我们发现:将更多高置信度图像块融入图像可生成较简单样本,有利于分割模型在训练初期的学习;相反,用低置信度区域替换高置信度区域会产生较难样本,对训练后期有效。由于低置信度区域通常出现在分割边界,迫使模型从这些区域学习有助于增强其判别能力。我们的分析还表明,在半监督学习的强弱伪监督中,扰动策略比学习范式更为关键。
Results
结果
4.1. Datasets
ACDC3 (Bernard et al., 2018) contains 200 short-axis cine-MRIs from100 subjects, and the corresponding annotations with the left ventricle,right ventricle, and myocardium labels. Following (Luo, 2020), we splitthe dataset into the training, validation, and testing sets, respectivelyincluding 70, 10, and 20 patients’data.LA4 (Xiong et al., 2021) consists of 100 3D gadolinium-enhancedmagnetic resonance scans and left atrial segmentation ground truths.Following (Yu et al., 2019), we divide the 100 scans into 80 samples fortraining and 20 samples for evaluation.ISIC**5 (Codella et al., 2019; Tschandl et al., 2018) includes 2594 dermoscopy images and the corresponding skin lesion annotations. We divide the entire dataset in a 7:1:2 ratio, resulting in 1815 images fortraining, 260 images for validation, and 519 images for testing
4.2. Implementation details
Experimental environment: Hardware: NVIDIA A40 GPU with 48GGPU memory. Software: Python 3.8, PyTorch (Paszke et al., 2019)1.11.0, CUDA 11.3. We utilize AdamW (Kingma and Ba, 2014) as theoptimizer with a fixed learning rate of 1e-4. The training time is set to100 epochs for the ACDC and ISIC datasets and 1000 epochs for the LAdataset.
Framework: We employ U-Net (Ronneberger et al., 2015)/VNet (Milletari et al., 2016) as the supervised baseline architecture for2D/3D image segmentation, respectively. We utilize FixMatch (Sohnet al., 2020), MT (Tarvainen and Valpola, 2017), and CPS (Chen et al.,2021b) as the base frameworks for self-training, mean-teacher, and cotraining, respectively. These frameworks are built upon the conceptof strong-weak pseudo supervision (Sohn et al., 2020) to leverage unlabeled data. We set the confidence threshold *𝜏* = 0*.*95 following FixMatch (Sohn et al., 2020). For the hyperparameters of AdaMix, weset the mix-up patch size 𝑆 = 32 and the maximum number of mix-uppatches 𝐾 = 16. Detailed analysis for these hyperparameters is providedin Section 4.4.3. In the experiments, we adopt the Dice loss (Milletariet al., 2016) as the segmentation criterion.Data: In the 2D image segmentation tasks, all images are resized to256 × 256 for inference, while the outputs are recovered to their originalsizes for evaluation. For 3D segmentation, we randomly crop 80 × 112 ×112 (𝐷𝑒𝑝𝑡ℎ× 𝐻𝑒𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡× 𝑊 𝑖𝑑𝑡ℎ) patches for training and iteratively croppatches using a sliding window strategy to obtain the final segmentationmask for evaluation.Evaluation metrics.** Dice similarity coefficient (DSC), Jaccard, average surface distance (ASD), and 95 % Hausdorff distance (95HD) areemployed to estimate the segmentation performance in the experiments.
4.3. Comparison with the state of the art
We extensively compared the proposed AdaMix frameworks withstate-of-the-art semi-supervised learning methods, which can be dividedinto five groups based on their perturbation strategies: 1) Multi-task perturbation (using signed distance maps Li et al., 2020; Luo et al., 2021aor multi-scale features Luo et al., 2021b): SASSNet (Li et al., 2020),URPC (Luo et al., 2021b), and DTC (Luo et al., 2021a); 2) Noise perturbation: UA-MT (Yu et al., 2019), MC-Net (Wu et al., 2021), MCNet+ (Wu et al., 2022); 3) CutMix perturbation: FixMatch (Sohn et al.,2020), MT (Tarvainen and Valpola, 2017), CPS (Chen et al., 2021b); 4)UMix and I-UMix perturbations: UCMT (Shen et al., 2023) and ABD (Chiet al., 2024) (Note that we re-implemented ABD based on the FixMatchframework with a U-Net segmentation backbone for a fair comparison.);and 5) Feature perturbation (using feature statistics Yang et al., 2025 ordynamic graph Li et al., 2025): W2SPC (Yang et al., 2025) and DGC (Liet al., 2025) (Results of these two methods are adopted from their original papers.).
4.1 数据集 - ACDC(Bernard 等人, 2018):包含来自100名受试者的200张短轴cine-MRI图像,标注涵盖左心室、右心室和心肌。参考(Luo, 2020)的划分方式,将数据集分为训练集(70名患者数据)、验证集(10名患者数据)和测试集(20名患者数据)。 - LA(Xiong 等人, 2021):包含100组3D钆增强磁共振扫描图像及左心房分割真实标签。参考(Yu 等人, 2019)的划分方式,将100组扫描数据分为训练集(80个样本)和评估集(20个样本)。 - **ISIC**(Codella 等人, 2019; Tschandl 等人, 2018):包含2594张皮肤镜图像及对应的皮肤病变标注。按7:1:2的比例划分数据集,得到训练集(1815张图像)、验证集(260张图像)和测试集(519张图像)。 — ### 4.2 实现细节 #### 实验环境 - 硬件:配备48G显存的NVIDIA A40 GPU。 - 软件:Python 3.8、PyTorch(Paszke 等人, 2019)1.11.0、CUDA 11.3。 - 优化器:采用AdamW(Kingma 和 Ba, 2014),固定学习率为1e-4。 - 训练轮数:ACDC和ISIC数据集设为100轮,LA数据集设为1000轮。 框架设置 - 监督基线架构:2D图像分割采用U-Net(Ronneberger 等人, 2015),3D图像分割采用V-Net(Milletari 等人, 2016)。 - 半监督基础框架:自训练基于FixMatch(Sohn 等人, 2020),均值教师基于MT(Tarvainen 和 Valpola, 2017),协同训练基于CPS(Chen 等人, 2021b),均基于强弱伪监督(Sohn 等人, 2020)理念利用未标记数据。 - 置信度阈值:参考FixMatch(Sohn 等人, 2020)设为τ=0.95。 - AdaMix超参数:混合图像块大小S=32,最大混合图像块数量K=16,超参数详细分析见4.4.3节。 - 分割损失函数:采用Dice损失(Milletari 等人, 2016)。 #### 数据处理 - 2D图像分割:推理时所有图像调整为256×256大小,评估时将输出恢复至原始尺寸。 - 3D图像分割:训练时随机裁剪80×112×112(深度×高度×宽度)的图像块,评估时采用滑动窗口策略迭代裁剪以获取最终分割掩码。 评估指标 实验采用Dice相似系数(DSC)、Jaccard系数、平均表面距离(ASD)和95%豪斯多夫距离(95HD)评估分割性能。 4.3 与现有最优方法的对比 将所提AdaMix框架与现有最优半监督学习方法进行广泛对比,按扰动策略分为五类: 1. 多任务扰动(使用符号距离图(Li 等人, 2020; Luo 等人, 2021a)或多尺度特征(Luo 等人, 2021b)):SASSNet(Li 等人, 2020)、URPC(Luo 等人, 2021b)、DTC(Luo 等人, 2021a); 2. 噪声扰动:UA-MT(Yu 等人, 2019)、MC-Net(Wu 等人, 2021)、MC-Net+(Wu 等人, 2022); 3. CutMix扰动:FixMatch(Sohn 等人, 2020)、MT(Tarvainen 和 Valpola, 2017)、CPS(Chen 等人, 2021b); 4. UMix和I-UMix扰动:UCMT(Shen 等人, 2023)、ABD(Chi 等人, 2024)(注:为公平对比,基于FixMatch框架和U-Net分割骨干网络重新实现了ABD); 5. 特征扰动(使用特征统计(Yang 等人, 2025)或动态图(Li 等人, 2025)):W2SPC(Yang 等人, 2025)、DGC(Li 等人, 2025)(这两种方法的结果引自其原始论文)。 要不要我帮你整理一份**实验关键信息汇总表,包含数据集、实现参数、对比方法分类等核心内容,方便快速查阅实验配置?
Figure
图

Fig. 1. Comparison among CutMix, UMix (Shen et al., 2023), inverse UMix, and our AdaMix. (a) Original and auxiliary images; (b) CutMix randomly replacespatches of the original image with patches from the auxiliary image, with an uncontrollable perturbation degree; © UMix replaces low-confidence patches in theoriginal image with high-confidence ones from the auxiliary image, often generating perturbed examples with trivial perturbations; (d) I-UMix mixes high-confidencepatches in the original image with low-confidence ones from the auxiliary image, yielding overly strong-perturbed images; (e) Our AdaMix synthesizes images withmore high-confidence regions in the initial training stage and then gradually increases the perturbation degree to enhance the complexity of the perturbed imagesas training progresses; (f) The unsupervised learning loss curves; (g) The validation loss curves (and the Dice Similarity Coefficients on the ACDC test set).
图 1 CutMix、UMix(Shen 等人, 2023)、逆 UMix 与本文所提 AdaMix 的对比。(a) 原始图像和辅助图像;(b) CutMix 随机用辅助图像的图像块替换原始图像的图像块,扰动程度不可控;© UMix 用辅助图像的高置信度图像块替换原始图像的低置信度图像块,生成的扰动样本通常扰动微弱;(d) 逆 UMix 将原始图像的高置信度图像块与辅助图像的低置信度图像块混合,产生扰动过强的图像;(e) 本文所提 AdaMix 在训练初期合成包含更多高置信度区域的图像,随后随着训练推进逐步提高扰动程度,以增强扰动图像的复杂度;(f) 无监督学习损失曲线;(g) 验证损失曲线(以及 ACDC 测试集上的 Dice 相似系数)。

Fig. 2. Overview of the proposed Adaptive Mix framework for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. It includes our Adaptive Mix (AdaMix) algorithmfor generating perturbed images and a semi-supervised learning paradigm for providing pseudo labels and conducting consistency regularization. AdaMix can beseamlessly applied to the self-training, mean-teacher, and co-training paradigms, resulting in AdaMix-ST, AdaMix-MT, and AdaMix-CT frameworks, respectively
图 2 所提半监督医学图像分割自适应混合(Adaptive Mix)框架概览。该框架包含用于生成扰动图像的自适应混合(AdaMix)算法,以及用于提供伪标签和执行一致性正则化的半监督学习范式。AdaMix 可无缝应用于自训练、均值教师和协同训练范式,分别形成 AdaMix-ST、AdaMix-MT 和 AdaMix-CT 框架。

Fig. 3. Schematic diagram of the proposed Adaptive Mix algorithm (AdaMix). It performs image mix-up perturbation in a self-paced manner, synthesizing stronglyperturbed samples from easy to hard during training based on the model’s learning stat
图 3 所提自适应混合算法(AdaMix)示意图。该算法以自步学习方式执行图像混合扰动,根据模型的学习状态在训练过程中生成从易到难的强扰动样本。

Fig. 4. Qualitative examples on the ACDC, ISIC, and LA datasets. The yellow dash circles highlight some segmentation regions. Sup: the supervised baseline, MT:Mean-Teacher, CPS: Cross Pseudo Supervision, and GT: Ground Truth.
图 4 ACDC、ISIC 和 LA 数据集上的定性示例。黄色虚线圆圈突出显示部分分割区域。Sup:监督基线模型,MT:均值教师模型,CPS:交叉伪监督模型,GT:真实标签。

Fig. 5. Investigation of the effect of patch size 𝑆 and maximum No. patches 𝐾 for AdaMix on the ACDC val set with 10 % labeled data.
图 5 10%标注数据设置下,ACDC验证集上图像块大小𝑆和最大图像块数量𝐾对AdaMix的影响探究。

Fig. 6. Analysis of the effect of age parameter functions for AdaMix on the ACDC dataset with 10 % labeled data. Left: the age parameter function curves; middle:the training loss curves of models with different age parameter functions; right: the corresponding segmentation performance on the ACDC val set.
图 6 10%标注数据设置下,ACDC数据集上年龄参数函数对AdaMix的影响分析。左图:年龄参数函数曲线;中图:不同年龄参数函数对应的模型训练损失曲线;右图:ACDC验证集上的相应分割性能。

Fig. 7. Gradient variances of models trained with and without AdaMix on the ACDC, LA, and ISIC datasets. Each point on the curves represents the norm of thebatch-wise gradient variances for the entire training set.
图 7 ACDC、LA 和 ISIC 数据集上使用与不使用 AdaMix 训练的模型梯度方差对比。曲线上每个点代表整个训练集的批次梯度方差的范数
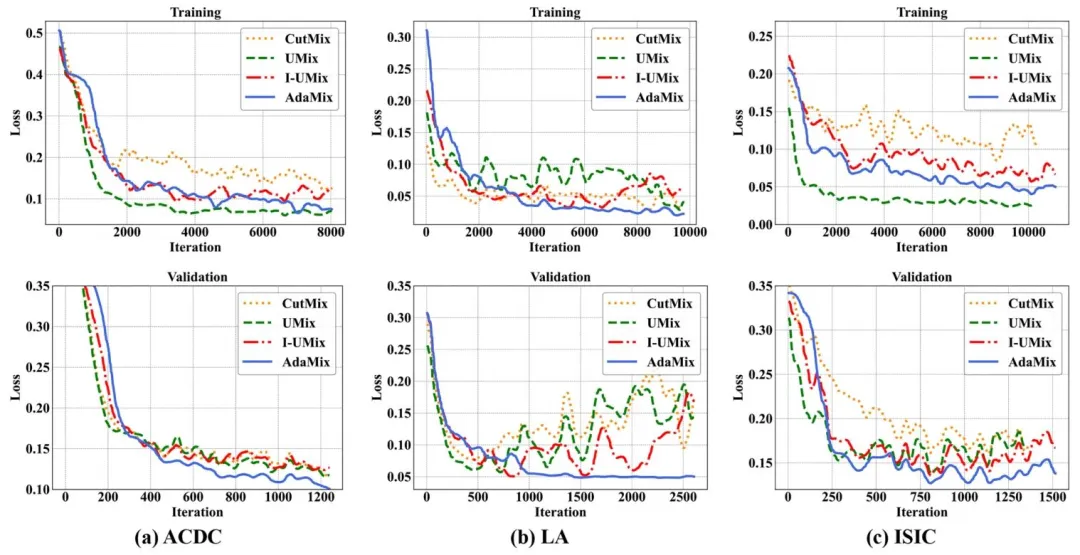
Fig. 8. Training and validation losses of CutMix, UMix, I-UMix, and the proposed AdaMix on the (a) ACDC, (b) LA, and © ISIC datasets, respectively
图 8 CutMix、UMix、逆UMix与所提AdaMix在各数据集上的训练损失和验证损失对比:(a) ACDC数据集、(b) LA数据集、© ISIC数据集。
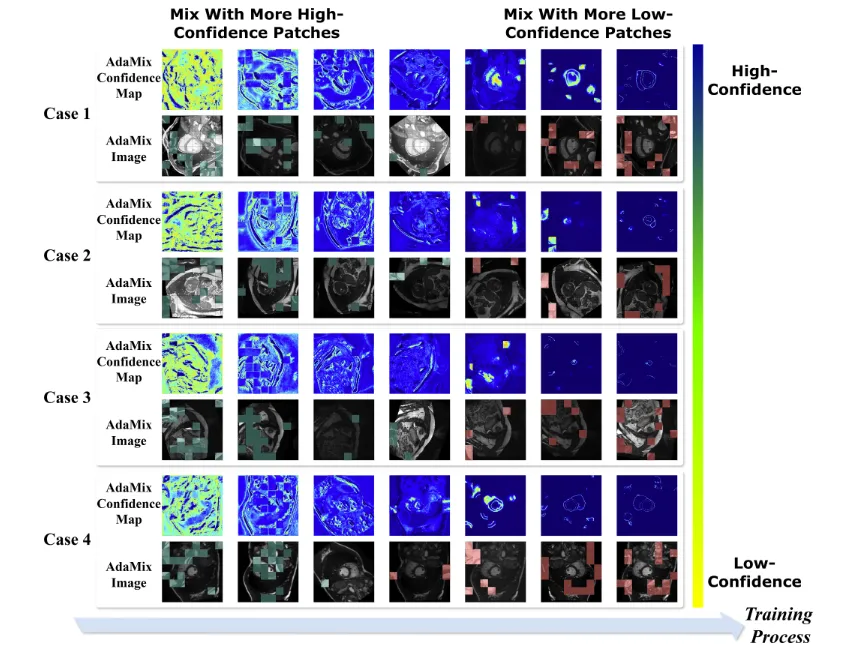
Fig. 9. Generation procedure of AdaMix images and AdaMix confidence maps during training. Initially, the AdaMix algorithm generates perturbed images (AdaMiximages) by mixing the original images with high-confidence patches (highlighted in **green**) from auxiliary images. As training progresses, it gradually incorporateslow-confidence regions (highlighted in red) from auxiliary images into the original images, resulting in perturbed images (AdaMix images) with progressivelyincreasing sample complexity
图 9训练过程中AdaMix图像及AdaMix置信度图的生成流程。训练初期,AdaMix算法通过将原始图像与辅助图像的高置信度区域(以**绿色**突出显示)混合生成扰动图像(AdaMix图像);随着训练推进,算法逐步将辅助图像的低置信度区域(以**红色**突出显示)融入原始图像,最终生成样本复杂度逐步提升的扰动图像(AdaMix图像)。
Table
表

Table 1Comparison with state-of-the-art methods under the 10 % || and 20 % || labeled data on the ACDC dataset. Note that all methods adopt U-Net as the backbone.The best and second-best results are highlighted in red and blue, respectively. ∗ indicates statistically significant improvements (𝑝-value < 0.05 based on a pairedt*-test) of our AdaMix frameworks over ABD, MT, and UCMT, respectively
表 1 ACDC数据集上10%标注数据和20%标注数据设置下与现有最优方法的对比。注:所有方法均采用U-Net作为骨干网络。最优结果和次优结果分别用红色和蓝色突出显示。∗ 分别表示所提AdaMix框架相较于ABD、MT和UCMT方法的统计显著改进(基于配对t检验,p值<0.05)。

Table 2Comparison with state-of-the-art methods on the LA dataset with 10 % || and 20 % || labeled data. Note that all methods adopt V-Net as the backbone. Thebest and second-best results are highlighted in red and blue, respectively. ∗ indicates statistically significant improvements (𝑝-value < 0.05 based on a pairedt*-test) of our AdaMix frameworks over ABD, MT, and UCMT, respectively
表 2 LA数据集上10%标注数据和20%标注数据设置下与现有最优方法的对比。注:所有方法均采用V-Net作为骨干网络。最优结果和次优结果分别用红色和蓝色突出显示。∗ 分别表示所提AdaMix框架相较于ABD、MT和UCMT方法的统计显著改进(基于配对t检验,p值<0.05)。

Table 3Comparison with state-of-the-art methods on the ISIC dataset with 5 % || and 10 % || labeled data. Note that all methods adopt U-Net as the backbone. The bestand second-best results are highlighted in red and blue, respectively. ∗ indicates statistically significant improvements (𝑝-value < 0.05 based on a paired t-test) ofour AdaMix frameworks over ABD, MT, and UCMT, respectively.
表 3 ISIC数据集上5%标注数据和10%标注数据设置下与现有最优方法的对比。注:所有方法均采用U-Net作为骨干网络。最优结果和次优结果分别用红色和蓝色突出显示。∗ 分别表示所提AdaMix框架相较于ABD、MT和UCMT方法的统计显著改进(基于配对t检验,p值<0.05)。
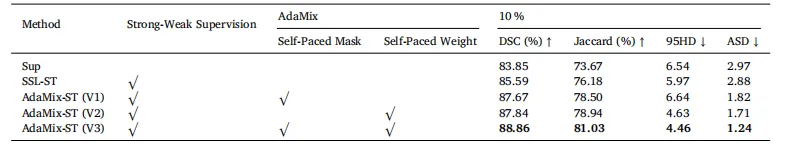
Table 4Ablation study of the AdaMix-ST framework on the ACDC val set under 10 % labeled data. Sup: the supervised baseline. Notethat without the self-paced mask, AdaMix is performed according to a fixed rule, i.e., replacing low-confidence patches with highconfidence ones. The best results are highlighted in bold.
表 4 10%标注数据设置下,ACDC验证集上AdaMix-ST框架的消融实验结果。Sup:监督基线模型。注:若不使用自步掩码,AdaMix将按固定规则执行(即用高置信度图像块替换低置信度图像块)。最优结果以粗体突出显示。