Title
题目
Switch-UMamba: Dynamic scanning vision Mamba UNet for medical imagesegmentation
Switch-UMamba:用于医学图像分割的动态扫描视觉Mamba UNet模型
01
文献速递介绍
医学图像分割相关研究进展与Switch-UMamba模型设计 医学图像分割是医学图像分析中至关重要却又复杂的组成部分,是众多临床应用的基础。该过程能够精准勾勒出医学影像中的解剖结构、病变区域及其他感兴趣区域(Bai等人,2020;Mei等人,2020;Litjens等人,2017;Tajbakhsh等人,2020;Luo等人,2022;Gao等人,2023;Chen等人,2024a),对各类医疗操作而言不可或缺。传统上,图像分割需由专业放射科医生完成,这项工作耗时费力;且由于人类解读存在主观性,不同专家的判断存在差异,分割结果易出现不一致(Jungo等人,2018;Joskowicz等人,2019;Ma等人,2021a;Wang等人,2021;Ma等人,2021b)。因此,亟需自动化分割技术来提升医学图像分析的效率、准确性与一致性,从而实现精准快速的诊断(Tang等人,2019a;Khened等人,2019;Tang等人,2019b;Chen等人,2022)。 近年来,医学图像分割领域最先进的自动化分割方法以深度学习(DL)为基础。两种主流网络架构——卷积神经网络(CNNs)(LeCun等人,1995)与Transformer(Vaswani,2017)——在该领域取得了显著成功。知名的CNN模型包括U-Net(Ronneberger等人,2015)、nnU-Net(Isensee等人,2021)和SegResNet(Myronenko,2019),它们擅长提取层级特征,并能将低层级细节与高层级上下文信息有效融合,从而实现优异的分割效果。这类模型采用共享权重的架构,在捕捉平移不变性和识别局部特征方面表现突出,但也可能限制其处理图像中不同区域信息的能力。 与CNNs不同,基于视觉Transformer(ViT)的架构借助注意力机制,能够捕捉整个图像范围内的长程依赖关系(Alexey,2020;Zhou等人,2021;Mazurowski等人,2023;Zhang等人,2024)。例如,UNETR(Hatamizadeh等人,2022)将ViT与UNet结合用于3D分割,而Swin-UNet(Cao等人,2022)和DCSUnet(Wang等人,2023)则探索在受UNet启发的架构中应用Swin视觉Transformer块。尽管Transformer在建模长程依赖关系方面有所提升,但它的计算成本极高,对长序列建模时存在高二次复杂度问题(Gu和Dao,2023)。 近年来,状态空间模型(SSMs)(Gu和Dao,2023;Gu等人,2021;Mehta等人,2022;Huang等人,2025)因其出色的长序列建模能力,受到了广泛的研究关注。具体而言,Mamba(Gu和Dao,2023)通过循环机制实现长程依赖关系的捕捉,且计算复杂度与序列长度呈线性关系,保证了计算效率。 与一维序列不同,二维视觉数据本身具有方向性依赖(Yang和Farsiu,2023)。将Mamba的一维序列处理技术直接应用于二维数据,难以有效捕捉像素间的长程依赖关系,导致感受野受限。这一局限源于对二维数据固有空间属性的忽视,该问题被称为方向敏感性问题(Liu等人,2024c)。在医学影像领域,尤其是考虑到解剖结构的复杂性,该问题的影响更为显著。为解决这一问题,众多研究致力于探索图像序列化的扫描策略(Huang等人,2024;Ma等人,2024c;Tang等人,2024;Yang等人,2024;Zhao等人,2024;Zhu等人,2024b;Ma等人,2023b),以提升Mamba模型对图像的理解能力。部分研究尝试通过复杂的扫描策略(如多方向扫描或全向扫描)(Xing等人,2024;Zhao等人,2024)来保持相邻标记的邻近性,但现有方法均基于静态扫描策略,缺乏多样性,难以同时捕捉二维影像中的多方向依赖关系。这一局限制约了模型的感受野,可能降低其在分割、目标检测等密集预测任务中的准确性。简单的解决方案或许是融合多种不同的扫描策略,但这种方式会大幅增加计算成本。 为此,本研究提出了切换视觉状态空间(Switch VSS)块,该模块采用混合扫描(MoS)机制,旨在不增加计算成本的前提下捕捉二维图像中的多方向依赖关系。Switch VSS块包含多个扫描头,每个扫描头配备独特的扫描策略,能够针对特定扫描模式精准获取结构信息。如图1所示,MoS机制通过“路由器”为每个样本动态分配适配的扫描头。通过这种方式,我们可通过增加扫描头数量拓展扫描策略的范围;同时,利用MoS机制分配扫描头,能确保训练阶段扫描头的稀疏激活,从而显著降低计算开销。 本研究的主要贡献总结如下: 1. 提出Switch-UMamba——一种新颖的混合框架,在UNet架构中融合卷积神经网络(CNNs)与状态空间模型(SSMs),用于医学图像分割。该框架擅长捕捉图像中的局部细粒度特征与长程依赖关系。 2. 设计新颖的切换视觉状态空间(Switch VSS)块,该模块采用带有多个扫描头的混合扫描(MoS)机制,不仅能稳健且全面地提取空间信息,还能降低计算成本。 3. 在未使用任何预训练权重的情况下,Switch-UMamba的性能优于此前的分割模型(包括CNNs、ViTs及最新的基于Mamba的模型),充分证明了所提架构在医学图像分割任务中的有效性。
Aastract
摘要
Recently, State Space Models (SSMs), particularly the Mamba-based framework, have demonstrated exceptionalperformance in medical image segmentation. This is attributed to their capacity to capture long-rangedependencies efficiently with linear computational complexity. Nonetheless, current Mamba-based modelsencounter challenges in preserving the spatial context of 2D visual features, which is a consequence of theirreliance on static 1D selective scanning patterns. In this study, we present Switch-UMamba, an innovativehybrid UNet framework that integrates local feature extraction power of Convolutional Neural Networks(CNNs) with the abilities of SSMs for capturing the long-range dependency. Switch-UMamba capitalizeson the Switch Visual State Space (VSS) module to leverage the Mixture-of-Scans (MoS) approach, a newscanning mechanism that amalgamates diverse scanning policies by considering each scan head as an expertwithin the Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) framework. MoS employs a router to dynamically allocate appropriatescanning policies and corresponding scan heads for each sample. This sparse-activated dynamic scanningapproach not only ensures a rich and comprehensive acquisition of spatial information but also curtailscomputational expenses. Our comprehensive experimental evaluation on several medical image segmentationbenchmarks indicates that Switch-UMamba has achieved state-of-the-art performances without using anypretrained weights. It is also worth highlighting that our approach outperforms other Mamba-based modelswith fewer parameters
近年来,状态空间模型(SSMs),尤其是基于Mamba的框架,在医学图像分割领域展现出卓越性能。这得益于它们能够以线性计算复杂度高效捕捉长程依赖关系。然而,当前基于Mamba的模型在保留二维视觉特征的空间上下文方面面临挑战,这是由于它们依赖静态一维选择性扫描模式所致。 在本研究中,我们提出了Switch-UMamba——一种创新的混合UNet框架,该框架将卷积神经网络(CNNs)的局部特征提取能力与状态空间模型(SSMs)捕捉长程依赖关系的能力相结合。Switch-UMamba借助切换视觉状态空间(Switch VSS)模块,采用了混合扫描(MoS)方法。这是一种新的扫描机制,通过将每个扫描头视为混合专家(MoE)框架下的“专家”,融合多种扫描策略。混合扫描(MoS)通过“路由器”为每个样本动态分配合适的扫描策略及对应的扫描头。这种稀疏激活的动态扫描方法不仅能确保丰富且全面地获取空间信息,还能降低计算成本。 我们在多个医学图像分割基准数据集上进行了全面的实验评估,结果表明,Switch-UMamba在未使用任何预训练权重的情况下,仍实现了当前最先进(state-of-the-art)的性能。值得强调的是,我们的方法以更少的参数数量,性能优于其他基于Mamba的模型。
Method
方法
3.1. Preliminaries
Drawing inspiration from continuous linear time-invariant (LTI)systems, existing SSM-based frameworks utilize an implicit latent stateℎ(𝑡) ∈ 𝐑𝑁 to transform a 1D sequence input 𝑥(𝑡) ∈ 𝐑 into an output𝑦(𝑡) ∈ 𝐑. This transformation is mathematically formulated as anordinary differential equation (ODE):
ℎ ′ (𝑡) = 𝐀ℎ(𝑡) + 𝐁𝑥(𝑡),*(1)𝑦(𝑡) = 𝐂ℎ(𝑡).(2)
Where 𝐀 ∈ 𝐑*𝑁×𝑁* denotes the evolution matrix, while 𝐁 ∈ 𝐑𝑁×1and 𝐂 ∈ 𝐑1×𝑁* serve as the projection parameters. Addressing thecomplexity of solving these ODEs within the realm of deep learning, theS4 (Gu et al., 2021) and Mamba (Gu and Dao, 2023) models advocatefor the discretization of these equations by introducing a timescaleparameter ∆, which facilitates the conversion of continuous matrices𝐀 and 𝐁 into their discrete equivalents 𝐀̄ and 𝐁̄ :̄𝐀 = exp(∆𝐀), (3)
𝐁̄ = (∆𝐀) −1(exp(∆𝐀) − 𝐼) ⋅ ∆𝐁, (4)
ℎt = 𝐀̄ ℎ𝑡−1 + 𝐁̄ 𝑥𝑡 , (5)𝑦𝑡 = 𝐂ℎ𝑡 . (6)
Once discretized, the system’s output can be efficiently computed usingglobal convolution:
𝐊̄ = (𝐂𝐁̄ , 𝐂𝐀̄ 𝐁̄ , …, 𝐂𝐀̄ 𝐋−𝟏𝐁̄ ),𝑦= 𝑥 ∗ ̄𝐊(7)
where 𝐋 is the sequence length, and ̄
𝐊 ∈ 𝐑𝐋 represents the convolutionkernel. This approach leverages the power of convolution to integrate outputs across the sequence, thereby enhancing computationalefficiency and scalability.
3.1 预备知识 受连续线性时不变(LTI)系统的启发,现有基于状态空间模型(SSM)的框架借助隐状态(h(t) \in \mathbb{R}N),将一维序列输入(x(t) \in \mathbb{R})转换为输出(y(t) \in \mathbb{R})。该转换过程通过常微分方程(ODE)进行数学建模: [h’(t) = \mathbf{A}h(t) + \mathbf{B}x(t) \tag{1}] [y(t) = \mathbf{C}h(t) \tag{2}] 其中,(\mathbf{A} \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times N})表示演化矩阵,(\mathbf{B} \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times 1})和(\mathbf{C} \in \mathbb{R}^{1 \times N})为投影参数。为解决深度学习领域中求解这类常微分方程的复杂性问题,S4(Gu等人,2021)和Mamba(Gu与Dao,2023)模型提出引入时间尺度参数(\Delta)对上述方程进行离散化处理,从而将连续矩阵(\mathbf{A})和(\mathbf{B})转换为对应的离散形式(\bar{\mathbf{A}})和(\bar{\mathbf{B}}): [\bar{\mathbf{A}} = \exp(\Delta\mathbf{A}) \tag{3}] [\bar{\mathbf{B}} = (\Delta\mathbf{A})^{-1}(\exp(\Delta\mathbf{A}) - I) \cdot \Delta\mathbf{B} \tag{4}] [h_t = \bar{\mathbf{A}}h_{t-1} + \bar{\mathbf{B}}x_t \tag{5}] [y_t = \mathbf{C}h_t \tag{6}] 离散化后,系统输出可通过全局卷积高效计算: [\bar{\mathbf{K}} = (\mathbf{C}\bar{\mathbf{B}},\ \mathbf{C}\bar{\mathbf{A}}\bar{\mathbf{B}},\ \dots,\ \mathbf{C}\bar{\mathbf{A}}^{L-1}\bar{\mathbf{B}})] [y = x * \bar{\mathbf{K}} \tag{7}] 其中,(L)为序列长度,(\bar{\mathbf{K}} \in \mathbb{R}L)表示卷积核。该方法借助卷积的优势对序列中的输出进行整合,进而提升计算效率与可扩展性。
Conclusion
结论
In conclusion, this study presents Switch-UMamba, a novel hybridUNet framework that seamlessly integrates the superior local featureextraction capabilities of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) withthe sophisticated mechanisms of State Space Models (SSMs) for capturing long-range dependencies. The Switch Visual State Space (VSS)module, which is central to our innovation, employs a Mixture-of-Scans(MoS) mechanism to endow each SS2D module with a distinct scanningmechanism. Furthermore, it dynamically allocates a tailored scanningstrategy and the corresponding SS2D module to each individual sample,thereby effectively overcoming the limitations of previous Mambabased models that suffered from a lack of spatial context in their staticscanning modes. The comprehensive experimental assessments conducted across a spectrum of medical image segmentation benchmarksconfirm that Switch-UMamba has not only attained state-of-the-artresults but has also done so independently of pretrained weights.
本研究提出了Switch-UMamba——一种新颖的混合UNet框架,该框架将卷积神经网络(CNNs)出色的局部特征提取能力与状态空间模型(SSMs)先进的长程依赖捕捉机制无缝融合。 作为本研究核心创新点的切换视觉状态空间(Switch VSS)模块,采用混合扫描(MoS)机制,为每个SS2D模块赋予独特的扫描机制。此外,该模块能为每个样本动态分配定制化的扫描策略及对应的SS2D模块,从而有效克服了以往基于Mamba的模型因静态扫描模式而缺乏空间上下文的局限性。 在多个医学图像分割基准数据集上开展的全面实验评估表明,Switch-UMamba不仅取得了当前最先进(state-of-the-art)的结果,且该成果的取得未依赖任何预训练权重。 要不要我帮你整理一份该研究核心结论与创新点的精简对照表,方便快速梳理关键信息?
Figure
图
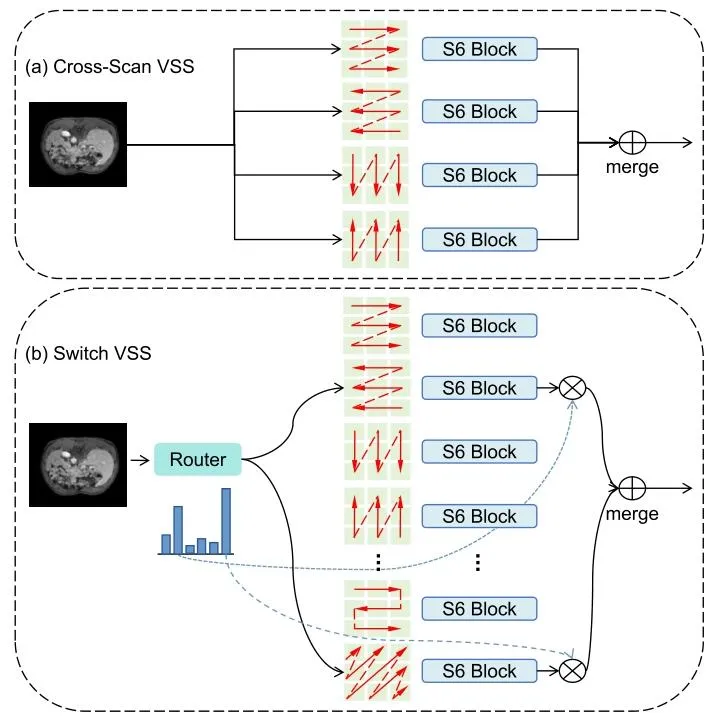
Fig. 1. (a) Cross-Scan VSS: Each sample undergoes processing via four predefined scanning strategies, followed by engagement with the respective S6Block. (b) Proposed Switch VSS: The Mixture-of-Scans (MoS) mechanismautomatically identifies the appropriate scan head for each sample, followedby output fusion through a weighted summation.
图1 (a)交叉扫描视觉状态空间(Cross-Scan VSS):每个样本通过四种预定义的扫描策略进行处理,随后进入对应的S6Block模块。 (b)所提切换视觉状态空间(Switch VSS):混合扫描(MoS)机制自动为每个样本确定适配的扫描头,之后通过加权求和对输出结果进行融合。
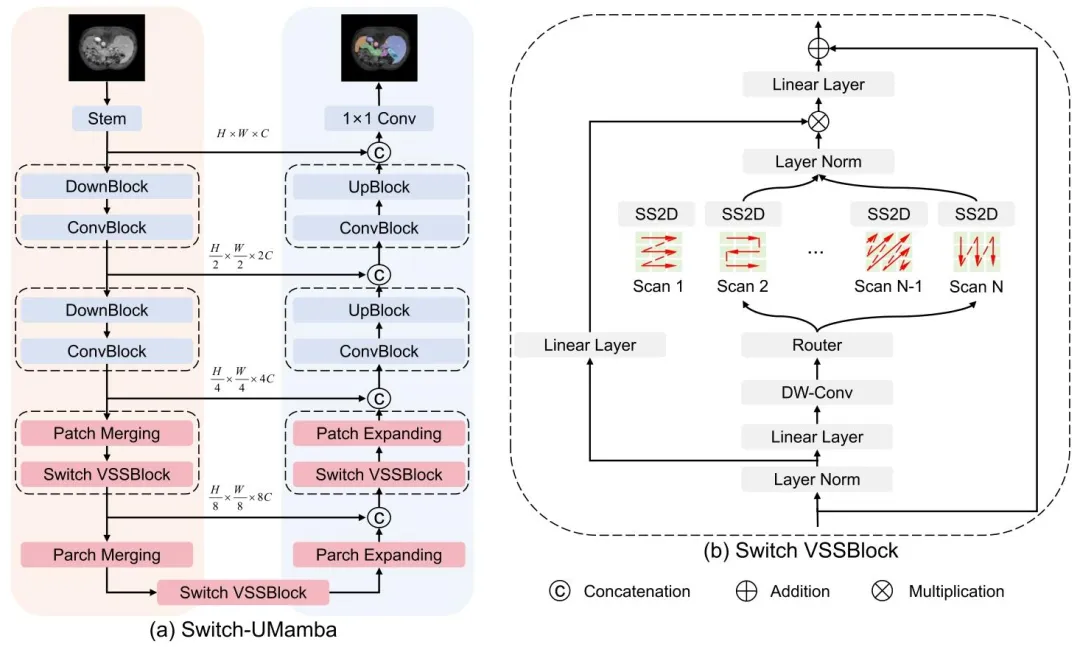
Fig. 2. The overall architecture of our proposed Switch-UMamba.
图2 所提Switch-UMamba模型的整体架构

Fig. 3. The scatter plot of the predicted brain ages and postmenstrual ages onthe two cohorts with each input sparse graph consisting of 5124 nodes. R: thecorrelation coefficient between the two axes for each cohort
图 3 输入为 5124 个节点的稀疏图时,两个队列中预测脑龄与月经后年龄(PMA)的散点图
Fig. 4. Visualization of the scan head load distribution within a single SwitchVSSBlock of our Switch-UMamba. This visualization corresponds to the resultsobtained from the Abdomen MRI dataset.
图4 Switch-UMamba模型单个Switch VSS块内扫描头负载分布可视化 该可视化结果对应于腹部MRI数据集上所得结果。

Fig. 5. Visualization of segmentation examples from the Abdominal MRI dataset. Switch-UMamba precisely discerns the morphology and classification of thesegmented anatomical structures
图5 腹部MRI数据集分割示例可视化 Switch-UMamba模型可精准识别被分割解剖结构的形态与类别。
Table
表

Table 1Results of organ segmentation on the Abdomen MRI dataset. For a faircomparison, the Swin-UMamba results are reported without the benefit ofImageNet-based pre-training
表1 腹部MRI数据集上的器官分割结果 为保证对比的公平性,所报告的Swin-UMamba模型结果未借助基于ImageNet的预训练(优势)。
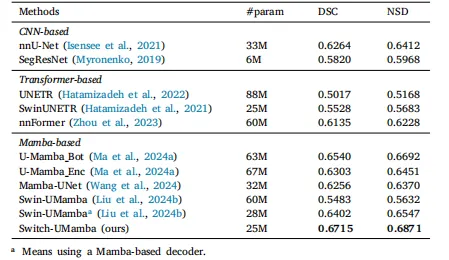
Table 2Results of instruments segmentation on the Endoscopy dataset. For a faircomparison, the Swin-UMamba results are reported without the benefit ofImageNet-based pre-training
表2 内窥镜数据集上的器械分割结果 为保证对比的公平性,所报告的Swin-UMamba模型结果未借助基于ImageNet的预训练(优势)。
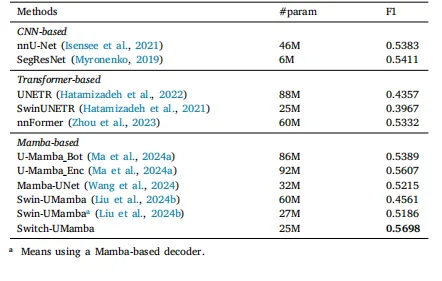
Table 3Results of cell segmentation on the Microscopy dataset. For a fair comparison,the Swin-UMamba results are reported without the benefit of ImageNet-basedpre-training.
表3 显微镜数据集上的细胞分割结果 为保证对比的公平性,所报告的Swin-UMamba模型结果未借助基于ImageNet的预训练(优势)。
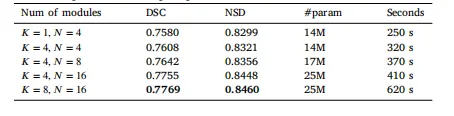
Table 4Ablation studies of Hyper-parameter. We present the performance across aspectrum of Hyper-parameters, alongside metrics of parameter count, as wellas the computational time per epoch.
表4 超参数消融实验 我们展示了不同超参数配置下的模型性能,同时提供了参数数量指标以及每个训练轮次(epoch)的计算时间。
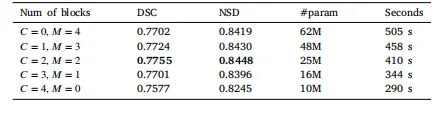
Table 5Ablation studies of model components. We present the performance of different combinations of CNN© and Mamba(M) blocks, alongside metrics ofparameter count, as well as the computational time per epoch.
表5 模型组件消融实验 我们展示了卷积神经网络(CNN,简称C)块与Mamba(简称M)块不同组合方式下的模型性能,同时提供了参数数量指标以及每个训练轮次(epoch)的计算时间。

Table 6Comparative experimental results on three datasets using different scantypes
表6 不同扫描类型在三个数据集上的对比实验结果

Table 7Ablation studies of fusion strategies. We evaluates the efficacy of variousfusion strategies on the Abdominal MRI dataset, along with the number ofparameters.
表7 融合策略消融实验 我们在腹部MRI数据集上评估了多种融合策略的有效性,并同时提供了参数数量(指标)。