Title
题目
Transferring Adult-Like Phase Images for RobustMulti-View Isointense Infant Brain Segmentation
迁移类成人相位图像用于稳健的多视角等信号婴儿脑分割
01
文献速递介绍
婴儿脑部图像精确组织分割的研究背景与方法设计 将婴儿脑部图像精确分割为白质(WM)、灰质(GM)、脑脊液(CSF)等不同感兴趣区域,是实现大脑结构与生物标志物(如皮层厚度、脑沟深度、脑回指数)精细化量化分析的基础步骤。在出生后第一年,随着脑部快速髓鞘化与成熟过程,婴儿脑部磁共振(MR)图像呈现出三个显著阶段:a)婴儿期阶段(≤3月龄)、b)等信号阶段(6~9月龄)、c)类成人阶段(≥12月龄)。图1展示了等信号阶段(上图)与类成人阶段(下图)的典型婴儿脑部磁共振图像,及其分割图与各组织的信号强度分布。可见,在等信号阶段,T1加权和T2加权磁共振图像中白质与灰质的信号强度高度重叠;而类成人阶段的组织对比度显著更高,尤其是在T1加权磁共振图像中。因此,等信号阶段图像的组织分割难度极大,类成人阶段图像则相对易于分割。 在深度学习时代之前,已有诸多研究致力于等信号阶段图像的分割,例如通过将人工标注图谱配准到目标图像来实现分割。然而,由于等信号阶段图像的组织对比度较低,难以在图谱与目标图像间建立体素级对应关系,这一问题成为标签传播法实现高分割精度的瓶颈。近年来,基于学习的方法被提出以提升分割性能[7]-[11]。这些方法通过手工设计特征或深度卷积神经网络(CNN)自动学习特征,以判别式方式预测组织标签。但由于等信号阶段图像的组织边界模糊,且特征表示能力仍有限,这类方法得到的分割结果往往与真实脑组织拓扑结构存在较大偏差。 为解决上述问题,有研究考虑在分割过程中引入组织解剖结构作为全局先验,以校正分割结果的拓扑结构。但总体而言,这些方法所用的解剖先验知识仍基于手工设计特征,难以解释人类大脑中复杂的组织解剖结构。针对上述挑战,近年有研究提出直接利用易于分割的类成人阶段图像指导分割过程,并设计风格迁移网络,使类成人阶段图像中的解剖先验知识能有效用于等信号阶段图像分割。但这类方法的成功风格迁移需依赖大量带标注的等信号阶段与类成人阶段图像,而这类数据往往难以获取。 已有研究充分证实,正常出生后婴儿脑部的皮层脑回模式在早期发育过程中基本保持稳定。基于此,本文提出一种多视角分割流程,通过充分利用类成人阶段图像中的有用解剖先验知识,实现稳健的等信号阶段婴儿脑分割。具体而言,一方面,将类成人阶段图像迁移为与等信号阶段图像具有相似组织对比度的图像,利用迁移后的图像对“等信号视角分割网络”进行预训练;另一方面,将等信号阶段图像迁移至类成人视角,借助增强的组织对比度训练“类成人视角分割网络”。不同视角的分割网络构成多路径架构,通过多视角学习进一步提升分割性能。 由于双向保留解剖结构的风格迁移是类成人阶段图像发挥作用的关键,本文设计了一种解纠缠循环一致对抗网络(DCAN),并精心设计正则化项,以在等信号阶段与类成人阶段图像间精确迁移组织对比度。该过程无需组织标签即可在风格迁移中保持结构一致性。本文采用NDAR[18]与iSeg-2019两个数据集对所提方法进行评估,实验结果表明,该方法性能显著优于当前主流方法,且具有统计学意义。
Aastract
摘要
Accurate tissue segmentation of infant brainin magnetic resonance (MR) images is crucial for charting early brain development and identifying biomarkers.Due to ongoing myelination and maturation, in the isointense phase (6-9 months of age), the gray and whitematters of infant brain exhibit similar intensity levels in MRimages, posing significant challenges for tissue segmentation. Meanwhile, in the adult-like phase around 12 monthsof age, the MR images show high tissue contrast and canbe easily segmented. In this paper, we propose to effectivelyexploit adult-like phase images to achieve robust multi-viewisointense infant brain segmentation. Specifically, in oneway, we transfer adult-like phase images to the isointenseview, which have similar tissue contrast as the isointensephase images, and use the transferred images to train anisointense-view segmentation network. On the other way,we transfer isointense phase images to the adult-like view,which have enhanced tissue contrast, for training a segmentation network in the adult-like view. The segmentationnetworks of different views form a multi-path architecture that performs multi-view learning to further boostthe segmentation performance. Since anatomy-preservingstyle transfer is key to the downstream segmentation task,we develop a Disentangled Cycle-consistent AdversarialNetwork (DCAN) with strong regularization terms to accurately transfer realistic tissue contrast between isointenseand adult-like phase images while still maintaining theirstructural consistency. Experiments on both NDAR andiSeg-2019 datasets demonstrate a significant superior performance of our method over the state-of-the-art methods.Index Terms—Isointense infant brain segmentation,adult-like phase images, multi-view learning, disentangledcycle-consistent adversarial network.
婴儿脑部磁共振图像的精确组织分割 婴儿脑部磁共振(MR)图像的精确组织分割,对于绘制早期脑部发育图谱和识别生物标志物至关重要。由于婴儿脑部仍在进行髓鞘化和成熟过程,在等信号阶段(6-9月龄),其脑灰质与脑白质在磁共振图像中呈现出相近的信号强度,给组织分割带来了巨大挑战。与此同时,在12月龄左右的类成人阶段,磁共振图像具有高组织对比度,易于分割。 本文提出充分利用类成人阶段图像,实现稳健的多视角等信号婴儿脑分割。具体而言,一方面,我们将类成人阶段图像迁移至等信号视角(迁移后的图像与等信号阶段图像具有相似的组织对比度),并利用迁移后的图像训练等信号视角分割网络;另一方面,我们将等信号阶段图像迁移至类成人视角(迁移后的图像具有增强的组织对比度),用于训练类成人视角下的分割网络。不同视角的分割网络构成多路径架构,通过多视角学习进一步提升分割性能。 由于保留解剖结构的风格迁移是下游分割任务的关键,我们设计了一种带强正则化项的解纠缠循环一致对抗网络(DCAN),能够在等信号阶段与类成人阶段图像之间精确迁移真实的组织对比度,同时保持两者的结构一致性。在NDAR和iSeg-2019两个数据集上的实验表明,本文方法的性能显著优于当前主流方法。 关键词——等信号婴儿脑分割、类成人阶段图像、多视角学习、解纠缠循环一致对抗网络
Method
方法
The overview of the proposed segmentation method is presented in Fig. 2 (top), which is composed of an isointense-viewsegmentation network f i SEG, an adult-like-view segmentationnetwork fa SEG, and a style transfer network f SYN, i.e., thedisentangled cycle-consistent adversarial network (DCAN).The two segmentation networks form a multi-path architecture,where f i SEG generates segmentation results directly from theinput isointense phase image Ii , and fa SEG generates segmentation results from the synthetic adult-like phase image e Iaproduced by f SYN. e Ia is the input isointense phase image Iiin the adult-like contrast. The segmentation results generatedby f i SEG and fa SEG are aggregated to form final segmentation.Note that, in our method, given a set of labeled adult-likephase images as Xa = {Ia, Ya}, each segmentation networkcan exploit the relationship between image intensities Ia andlabels Ya to help isointense phase image segmentation. Specifically, as shown in Fig. 2 (bottom), each segmentation networkhas corresponding pretraining and fine-tuning stages. Thepretraining stage benefits from the anatomical prior knowledgefrom adult-like phase images, while, in the subsequent finetuning stage, each segmentation network can adapt to realisointense infant data as input. Besides, during fine-tuning,a consistency loss Lcon is applied to facilitate multi-viewlearning of the two segmentation networks.
所提分割方法概况 所提分割方法的整体框架如图2(上图)所示,由等信号视角分割网络(f{i}^{SEG})、类成人视角分割网络(f{a}^{SEG})以及风格迁移网络(f^{SYN})(即解纠缠循环一致对抗网络DCAN)构成。两个分割网络形成多路径架构:其中(f{i}^{SEG})直接从输入的等信号阶段图像(I{i})生成分割结果,(f{a}^{SEG})则从(f^{SYN})生成的合成类成人阶段图像(\tilde{I}{a})中生成分割结果。(\tilde{I}{a})是输入等信号阶段图像(I{i})转换为类成人对比度后的图像。(f{i}^{SEG})与(f{a}^{SEG})生成的分割结果经融合后,得到最终分割结果。 需说明的是,在本文方法中,给定带标签的类成人阶段图像集(X{a}={I{a},Y{a}}),每个分割网络均可利用图像强度(I{a})与标签(Y{a})之间的关联,辅助等信号阶段图像的分割。具体而言,如图2(下图)所示,每个分割网络均对应预训练与微调两个阶段:预训练阶段借助类成人阶段图像中的解剖先验知识提升网络初始化性能;在后续的微调阶段,每个分割网络可进一步适配真实的等信号阶段婴儿数据输入。此外,微调过程中还引入一致性损失(L{con}),以促进两个分割网络的多视角学习。
Conclusion
结论
In this paper, we propose to use adult-like phase images toachieve robust multi-view isointense infant brain segmentation.The adult-like phase images are transferred to isointensecontrast so that their anatomical prior knowledge can beeffective for isointense phase image segmentation. Besides,we also transfer isointense phase images to adult-like contrast,which can have a better visual details around tissue boundary.Two segmentation networks are applied on two views ofthe isointense phase images, performing multi-view learning to further boost the segmentation performance. Becauseanatomy-preserving style transfer is key to the downstreamsegmentation task, we propose a style transfer network DCANwith three regularization terms to accurately transfer tissue contrast between isointense and adult-like phase images.Both NDAR and iSeg-2019 datasets are adopted to evaluatethe proposed method. The evaluation results demonstrate asuperior performance of the proposed method over the stateof-the-art methods. Detailed ablation analysis is performedto demonstrate the effectiveness of each component of ourmethod. The robustness of our method is also evaluated.The major limitation of this work is the increased modelcomplexity. To alleviate this issue, for future studies, we wouldexplore lightweight models as well as knowledge transfer techniques that do not rely on style transfer networks. For example,a simple strategy of directly shifting intensity distribution ofeach tissue for style transfer could be explored [46]. Anotherlimitation is that the 12-month adult-like phase images maynot always be available. In this case, directly utilizing widelyavailable adult MR images could be an option. Besides,when isointense phase images are limited (e.g., iSeg-2019dataset), large segmentation error still occurs. In this case,some techniques such as surface and boundary constraintscould be explored to alleviate this issue.
本文方法总结与未来展望 本文提出利用类成人阶段图像实现稳健的多视角等信号婴儿脑分割。具体而言,将类成人阶段图像迁移为等信号对比度,使其包含的解剖先验知识能有效助力等信号阶段图像分割;同时,将等信号阶段图像迁移为类成人对比度,可增强组织边界周围的视觉细节。针对等信号阶段图像的两种视角,分别构建分割网络,通过多视角学习进一步提升分割性能。 由于保留解剖结构的风格迁移是下游分割任务的关键,本文设计了带有三个正则化项的风格迁移网络DCAN,以在等信号阶段与类成人阶段图像间精确迁移组织对比度。研究采用NDAR与iSeg-2019两个数据集对所提方法进行评估,结果表明该方法性能优于当前主流方法。此外,通过详细的消融分析验证了方法各组件的有效性,并对方法的稳健性进行了评估。 本研究存在的主要局限性在于模型复杂度较高。为缓解这一问题,未来将探索轻量级模型及不依赖风格迁移网络的知识迁移技术,例如可研究直接调整各组织信号强度分布以实现风格迁移的简易策略[46]。另一局限性是12月龄类成人阶段图像并非总能获取,这种情况下可考虑直接利用更易获取的成人脑部磁共振图像。此外,当等信号阶段图像数据有限时(如iSeg-2019数据集),分割仍会出现较大误差,后续可探索表面约束、边界约束等技术以缓解该问题。
Figure
图
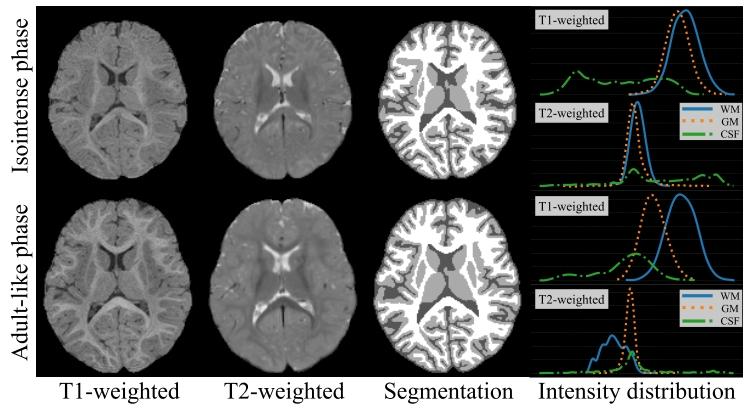
Fig. 1. Representative MR images, corresponding segmentation maps,and the intensity distribution of each tissue of the isointense phase (top)and the adult-like phase (bottom) infant brain.
图1 等信号阶段(上图)与类成人阶段(下图)婴儿脑部的典型磁共振(MR)图像、对应分割图及各组织的信号强度分布 (注:图中“分割图”通常以不同颜色区分白质、灰质、脑脊液等组织;“信号强度分布”一般以直方图形式呈现,可直观反映等信号阶段白质与灰质信号高度重叠、类成人阶段组织信号区分度高的特点,为两类阶段图像的分割难度差异提供可视化依据。)

Fig. 2. Overview of the proposed isointense infant brain segmentation method. Two segmentation networks (f SEG i and f SEG a ) segment inputisointense phase images under different views. The style transfer network f SYN (DCAN, with details in Section III-A) aims at transferring imagecontrast between isointense and adult-like phase images. Two segmentation networks form a multi-path architecture, and during training, multi-viewlearning is performed to further boost the segmentation performance.
图2 所提等信号婴儿脑分割方法概况 两个分割网络($f{\text{SEG}}i$ 和 $f{\text{SEG}}a$)在不同视角下对输入的等信号阶段图像进行分割。风格迁移网络 $f_{\text{SYN}}$(即解纠缠循环一致对抗网络DCAN,细节见第III-A节)旨在实现等信号阶段与类成人阶段图像间的对比度迁移。两个分割网络构成多路径架构,训练过程中通过多视角学习进一步提升分割性能。

Fig. 3. Overview of the proposed disentangled cycle-consistent adversarial network (DCAN), consisting of a style encoder Es, a contentencoder Ec, a decoder D, and two discriminators Di , Da. The input images are decomposed into style and content representation, based on whichthree regularization terms are applied to achieve successful style transfer betweenisointense and adult-like phase images.
图3 所提解纠缠循环一致对抗网络(DCAN)概况 该网络由风格编码器$E_s$、内容编码器$E_c$、解码器$D$以及两个判别器$D_i$、$D_a$构成。输入图像被分解为风格表征与内容表征,在此基础上施加三个正则化项,以实现等信号阶段与类成人阶段图像间的有效风格迁移。

Fig. 4. Representative segmentation results of all methods under comparison on NDAR and iSeg-2019 datasets. From top to bottom are thesegmentation results at normal and zoomed views, the error map, and the reconstructed inner cortical surface at zoomed views. The segmentationresults of our method are more consistent to the ground truth, especially at regions marked with red circles.
图4 NDAR与iSeg-2019数据集上所有对比方法的典型分割结果 从上到下依次为:正常视角与放大视角下的分割结果、误差图、放大视角下的重建皮层内表面。本文方法的分割结果与真实标签(ground truth)更为一致,尤其在红色圆圈标注的区域表现突出。
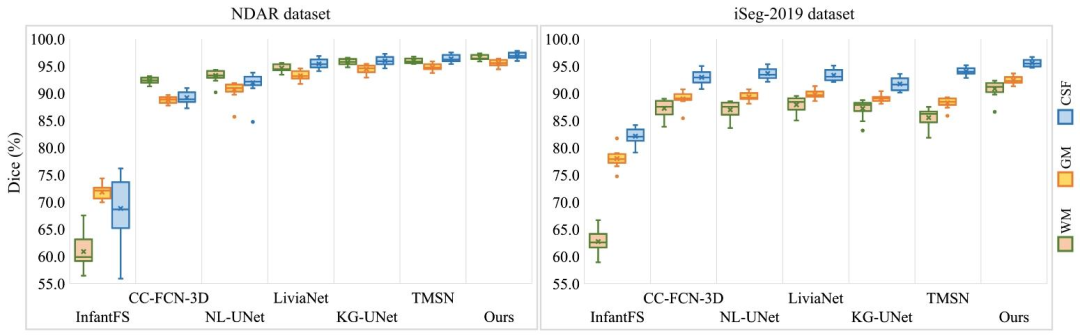
Fig. 5. Boxplots of Dice metric for all methods under comparison. The results of WM, GM, and CSF are plotted respectively. It is clear that thesegmentation performance of the proposed method is relatively stable across different testing samples.
图5 所有对比方法的Dice系数箱线图 分别绘制了白质(WM)、灰质(GM)和脑脊液(CSF)的结果。可见,所提方法的分割性能在不同测试样本间表现相对稳定。

Fig. 6. The segmentation performance of our method, the TMSN, and the Baseline under different proportions of training set. The performance ofTMSN and Baseline decrease by a large margin when training data are limited, meanwhile our method is less impacted
图6 本文方法、TMSN方法与基准方法(Baseline)在不同训练集比例下的分割性能 当训练数据有限时,TMSN方法与基准方法的性能大幅下降,而本文方法所受影响较小。
Table
表
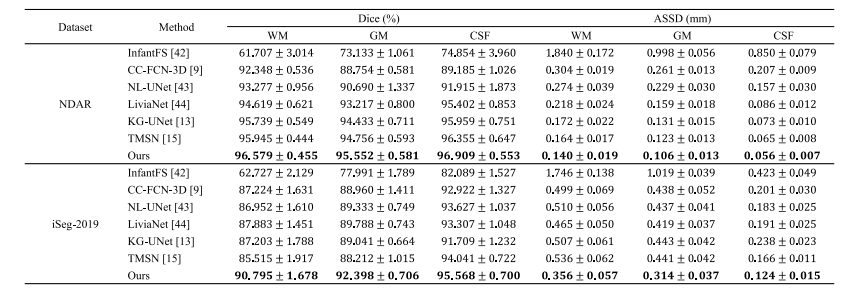
TABLE I EVALUATION RESULTS OF ALL METHODS UNDER COMPARISON
表1 所有对比方法的评估结果
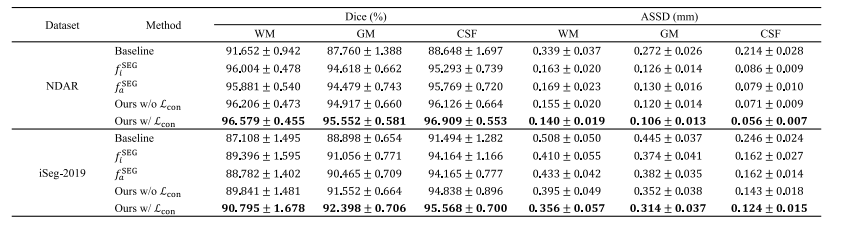
TABLE II ABLATION ANALYSIS OF THE PROPOSED SEGMENTATION METHOD
表2 所提分割方法的消融分析
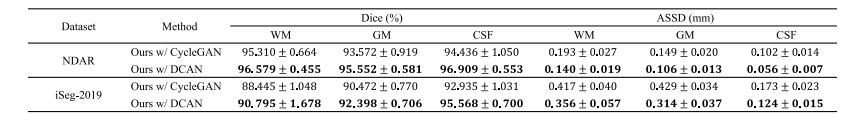
TABLE III EVALUATION RESULTS OF OUR METHOD BASED ON DIFFERENT STYLE TRANSFER NETWORK
表3 基于不同风格迁移网络的本文方法评估结果

TABLE IV EFFECT OF THE REGULARIZATION TERMS ON THE DOWNSTREAM SEGMENTATION PERFORMANCE
表4 正则化项对下游分割性能的影响